R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854: MINES AND MINING PLANTS, Occupational Health and Safety Act, R.S.O. 1990, c. O.1
Occupational Health and Safety Act
Loi sur la santé et la sécurité au travail
R.R.O. 1990, REGULATION 854
Amended to O. Reg. 630/05
MINES AND MINING PLANTS
Historical version for the period December 8, 2005 to September 29, 2006.
This Regulation is made in English only.
CONTENTS
|
|
|
Sections |
|
|
1 |
|
|
GENERAL |
2-24 |
|
|
FIRE PROTECTION |
25-45 |
|
|
ACCESS TO WORKPLACES |
46-54 |
|
|
PROTECTION OF WORKERS |
55-102 |
|
|
HAULAGE |
103-120 |
|
|
EXPLOSIVES |
121-154 |
|
|
ELECTRICAL |
155-180 |
|
|
MECHANICAL |
181-201 |
|
|
RAILROADS |
202 |
|
|
MINE HOISTING PLANT |
203-250 |
|
|
WORKING ENVIRONMENT |
251-293 |
|
|
CONFINED SPACES |
294-313 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
First aid equipment |
1-2 |
|
|
(subsection 182 (1)) diesel powered equipment notice |
|
1. In this Regulation,
Note: On September 30, 2006, section 1 is amended by adding the following definitions:
“adequate”, when used in relation to a procedure, plan, material, device, object or thing, means that it is,
(a) sufficient for both its intended and its actual use, and
(b) sufficient to protect a worker from occupational illness or occupational injury;
“adequately” has a meaning that corresponds to the meaning of “adequate”;
See: O. Reg. 630/05, ss. 1, 5.
“authorized” means authorized to do a specific task by a supervisor who is in charge of the workplace;
“automatic hoist” means a mine hoist that can be operated by controls situated at shaft stations or on the shaft conveyance;
“breaking strength” means the breaking strength of a shaft rope as determined by a cable testing laboratory approved by the Minister;
“bulkhead” means a structure for the impoundment of water, compressed air, hydraulic backfill or any material in an underground opening where the potential pressure against the structure will be in excess of 100 kilopascals;
“charge” means,
(a) an explosive and a detonator, or
(b) an explosive, a detonator and primer that is exploded as a single unit;
“CSA Standard” means a standard published by the Canadian Standards Association;
“dam” means a structure for the impoundment of more than twenty-five tonnes of water in an underground opening and constructed so as to permit an unobstructed overflow of the water;
“destructive test” means a test on a sample of shaft rope wherein the shaft rope is broken during the test by a tensile testing machine;
“detonator” means a device used in firing a charge of explosive and includes blasting cap and electric blasting cap;
“drum hoist” means a hoist where the rope is wound on a drum or drums;
“electromagnetic device” means a device using an electromagnetic system for examining a shaft rope;
“explosive” means a substance that is made, manufactured or used to produce an explosion or detonation and includes gunpowder, propellant powder, dynamite, detonating cord, shock tube, blasting agent, slurry, water gel and detonator;
“factor of safety” means the number of times the breaking strength of a shaft rope exceeds the weight it supports at a specified location on the rope;
“fire-extinguishing equipment” means a fire hose, an extinguisher or other similar equipment used to fight a fire;
“fire hazard area” means,
(a) an area where a fire hazard may be created by smoking, matches or other means of producing heat or fire and which has been designated as such by the supervisor in charge of the mine, or
(b) a storage area where oil, grease or flammable liquids are stored in excess of 500 litres;
“fire-resistance rating” means the rating in hours or fraction thereof that a material or assembly of materials will withstand the passage of flame and the transmission of heat when exposed to fire, as established for the material or assembly of materials under the Building Code Act;
“fire suppression system” means an installation for the specific purpose of controlling a fire in a particular place;
“friction hoist” means a hoist where the driving force between the drum and rope or ropes supporting the shaft conveyance is obtained through friction;
“hoist” means a drum or friction hoist used for transporting persons or materials in an underground mine;
“lifting device” means a permanently installed system for the purpose of raising, lowering or swinging materials, which includes its rails and supports but does not include a crane, elevator, mine hoist, utility hoist or tugger hoist;
“locomotive” means a unit propelled by any form of energy or a combination of such units operated from a single control running only on rails of a standard gauge railroad and used for moving standard gauge railroad cars but does not include a self-propelled track crane, motorized equipment used for the maintenance of a standard gauge railroad, a motor vehicle equipped with rail wheels in addition to rubber-tired wheels or other similar equipment;
“magazine” means a building, place or structure in which an explosive is kept or stored and includes a detonator storage building, or place, but does not include a storage container being used in an underground mine containing less than 160 kilograms of explosive;
“mine hoisting plant” means a hoist for an underground mine and includes the prime mover, transmission equipment, head-frame, sheaves, ropes, shaft, shaft conveyances, shaft sinking equipment, shaft furnishings, hoist controls, counterweight, signalling and communications equipment and any other equipment used in connection with a hoist;
“motor vehicle” means a vehicle propelled by other than muscular power, including an automobile, a caterpillar-tracked vehicle, a truck, a tractor and a motor vehicle running on rails but does not include a locomotive;
“non-combustible” means material or an assembly of materials that conforms to National Standard of Canada, CAN4-S114-80, “Standard Method of Test for Determination of Non-combustibility in Building Materials”;
“nondestructive test” means the examination of a part without subjecting it to physical distortion, damage or destruction;
“prime mover” means an engine or other device that provides an initial source of motive power;
“primer” means a small charge placed within the main charge to initiate an explosion;
“production crane” means an electrically operated device that travels on fixed overhead track or tracks, and,
(a) is used to handle hot or molten materials, or
(b) has a duty rating equal to or greater than Class C or D as determined under Part 3.4 of CSA Standard B167-1964, “General Purpose Electric Overhead Travelling Cranes”;
“professional engineer” means a person who is registered as a professional engineer or licensed as a professional engineer under the Professional Engineers Act;
“railroad” means a standard gauge railroad at a mine or mining plant;
“rockburst” means an instantaneous failure of rock causing an expulsion of material at the surface of an opening or a seismic disturbance to a surface or underground mine;
“SABS” means South African Bureau of Standards;
“service crane” means an electrically operated device that travels on fixed overhead track or tracks and has a duty rating equal to or less than Class A or B as determined under Part 3.4 of CSA Standard B167-1964, “General Purpose Electric Overhead Travelling Cranes”;
“shaft conveyance” means a conveyance raised or lowered by a mine hoist in a shaft and includes a bucket, a single or multi-deck cage, a skip or a combination of skip and cage;
“shaft rope” means a hoisting, tail, balance, guide or rubbing rope;
“shot” means the sound of a charge or charges being exploded;
“standard gauge” means that the space between the rails of a railroad is approximately 1,435 millimetres;
“surface mine” means a pit or quarry where metallic or non-metallic rock, mineral bearing substance, earth, clay, sand or gravel is being or has been removed by means of an excavation open to the surface to supply material for construction, industrial or manufacturing purposes and includes any work, undertaking or facility used in connection therewith but does not include a cutting for a right of way for a highway or a railroad;
“train”,
(a) except in Parts V and VI, means one or more locomotives without railroad cars or coupled with railroad cars, and
(b) in Parts V and VI, means one or more motor vehicles running on rails without cars or coupled with cars;
“transmission equipment” means any object or objects by which the motion of a prime mover is transmitted to a machine that is capable of utilizing such motion and includes a shaft, pulley, belt, chain, gear, clutch or other device;
“uncontrolled fall of ground” means a fall of ground, such as rock or fill falling from the walls or back of an underground or surface mine but does not include falls occurring as part of blasting or scaling operations;
“underground mine” means a mine that is not a surface mine and includes any work, undertaking or facility used in connection therewith;
“vehicle” includes a locomotive, railroad cars, motor vehicle, trailer or any vehicle propelled, drawn or driven by any kind of power. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 1; O. Reg. 584/91, s. 1; O. Reg. 571/92, s. 1; O. Reg. 272/97, s. 1; O. Reg. 174/01, s. 1; O. Reg. 31/04, s. 1.
2. (1) Subject to subsection (2), this Regulation applies to all mines and mining plants and to mining development. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 2 (1).
(2) Ontario Regulation 213/91 applies,
(a) during the construction of a mining plant on the surface; and
(b) to construction at the surface of a mine for the purpose of developing the mine. O. Reg. 571/92, s. 2.
3. An owner, constructor or employer may vary a procedure required by this Regulation or the composition, design, size or arrangement of a material, object, device or thing as required by this Regulation,
(a) if the procedure, composition, design, size or arrangement as varied affords protection for the health and safety of workers that is at least equal to the protection that would otherwise be given; and
(b) if the owner, constructor or employer gives written notice of the varied procedure, composition, design, size or arrangement to the joint health and safety committee or the health and safety representative, if any, for the workplace and to any trade union representing workers at the workplace. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 1.
4. Notices shall be posted in conspicuous places at each mine or mining plant, setting out the name, business address and business telephone number of,
(a) the inspector for the district in which the mine or mining plant is located;
(b) the person in charge of the mine or mining plant;
(c) the employer of workers at the mine or mining plant; and
(d) the owner of the mine or mining plant. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 4.
5. (1) Before proceeding with,
(a) the development or construction of a mine or a mining plant;
(b) the introduction of new process technology;
(c) the major alteration of mining technique or mining technology;
(d) the use of new methods of construction or of equipment installation;
(e) the making of a major addition or alteration;
(f) the design of a system and procedure for the transfer of fuel by gravity from the surface to an underground fuelling station;
(g) the construction of a bulkhead or dam;
(h) the construction of a tailings dam or any surface structure for the impoundment of tailings; or
(i) the design of a trolley line system, if the lines of the system are to have an operating voltage greater than 300 volts,
the owner of a mine or mining plant shall ensure that the drawings, plans and specifications are prepared or checked by a professional engineer under his or her seal and signature and are in compliance with the Act and this Regulation. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 5 (1); O. Reg. 60/94, s. 1; O. Reg. 272/97, s. 2 (1).
(2) The owner of a mine or mining plant shall ensure that the drawings, plans and specifications required under subsection (1) are kept readily available at the mine site. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 2 (2).
(2.1) A written statement of the proposed development, construction, introduction, alteration or use shall be given to the joint health and safety committee or health and safety representative, if any. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 2 (2).
(3) The employer shall notify an inspector,
(a) Revoked: O. Reg. 272/97, s. 2 (3).
(b) Revoked: O. Reg. 272/97, s. 2 (3).
(c) of the installation of portable crushing, screening or associated washing equipment in or about a surface mine; and
(d) before proceeding with the operation of a diamond drill on surface for the purpose of proving mineral bearing substance. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 5 (3); O. Reg. 272/97, s. 2 (3); O. Reg. 236/99, s. 1.
(4) Revoked: O. Reg. 272/97, s. 2 (4).
6. (1) The owner of a surface mine producing metallic ore or of an underground mine shall prepare and maintain a mine design assessing the ground stability of the active and proposed workings of the mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 6 (1).
(2) The mine design shall consist of drawings, plans, specifications or procedures to be used and shall be prepared under the direction of a competent person. O. Reg. 571/92, s. 3.
(2.1) The mine design shall be based upon sound geotechnical engineering practices and shall,
(a) describe the geology of the mine;
(b) outline the geometry of existing and proposed excavations;
(c) describe previous occurrences of ground instability;
(d) describe the mining method including stope sequencing and blasting methods;
(e) specify the ground support system; and
(f) describe measures planned and used to assess potential ground instability such as instrumentation and computer modelling. O. Reg. 571/92, s. 3; O. Reg. 60/94, s. 2.
(3) The mine design shall be assessed and updated at least annually and also before any alteration is made to the mine that may significantly affect the ground stability of the mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 6 (3).
(4) The mine design shall be kept readily available at the mine site for review by an inspector and by the joint health and safety committee or health and safety representative, if any. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 3.
(5) Revoked: O. Reg. 272/97, s. 3.
6.1 (1) In an underground mine, the geometry of an existing excavation that does not have ground support shall not be altered unless,
(a) the owner of the mine arranges for a professional engineer to prepare, in accordance with sound geotechnical engineering practices, a written report on the proposed alteration; and
(b) the report states that the safety of workers will not be endangered by the proposed alteration. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 2.
(2) In an underground mine, a new excavation that is planned to have no ground support shall not be made unless,
(a) the owner of the mine arranges for a professional engineer to prepare, in accordance with sound geotechnical engineering practices, a written report on the proposed excavation; and
(b) the report states that the safety of workers will not be endangered by the proposed excavation. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 2.
(3) The owner of the mine shall ensure that copies of reports prepared under subsections (1) and (2) are,
(a) kept readily available at the mine site; and
(b) given to the joint health and safety committee or health and safety representative, if any, and to any trade union representing workers at the workplace. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 2.
7. A tailings dam or any other surface structure for the impoundment of tailings shall be,
(a) designed in accordance with good engineering practice by a professional engineer;
(b) constructed in accordance with the design; and
(c) maintained so that the structure provides stability against any static and dynamic loading to which it may be subjected. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 7.
8. (1) Subject to subsection (2), the minimum age of,
(a) a worker; or
(b) a person who is permitted to be in or about a mine or mining plant,
shall be,
(c) sixteen years of age at a mining plant or a surface mine, excluding the working face; and
(d) eighteen years of age at an underground mine or at the working face of a surface mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 8 (1).
(2) Subsection (1) does not apply to prohibit tours of, or visits to, a mine or mining plant by persons under the prescribed ages who are accompanied by and under the direction of a guide. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 8 (2).
9. (1) No worker shall remain or be requested to remain in an underground mine for more than eight hours in any consecutive twenty-four hours, measured from the time the worker enters an underground mine until the time the worker leaves the underground mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 9 (1).
(2) Despite subsection (1), a worker may remain underground in a mine,
(a) when an emergency causes an extension of the time;
(b) for more than eight hours in any consecutive twenty-four hours on one day of a week but only for the purpose of changing shift or for the purpose of avoiding work on Sunday or on a holiday; or
(c) if the worker is a supervisor, pump operator, cagetender, or is a person engaged solely in surveying or measuring or in emergency repair work necessary to permit production. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 9 (2).
(3) A worker shall not be permitted to operate a mine hoist for more than eight hours in any consecutive twenty-four hours, except in a case provided for in clause (2) (a) or (b) or in subsection (4), but,
(a) where no competent substitute is available, the worker may work extra time not exceeding four hours in any consecutive twenty-four hours for a period not exceeding fourteen calendar days in any four week period; or
(b) where the work is not carried out continuously on three shifts per day, the worker may work such extra time as is necessary for lowering or hoisting the workers employed on the shift, at the beginning and end of their shift. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 9 (3).
(4) An employer at an underground mine may schedule hours of work in excess of eight hours in any 24-hour period with the consent of the trade unions representing the workers at the underground mine or, if there is no trade union, consent of the workers themselves. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 4.
10. A supervisor, deck attendant, shaft conveyance attendant or mine hoist operator shall be capable of communicating effectively in the English language. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 10.
11. (1) Employers in the following types of mines and mining plants shall establish and maintain the following training programs developed jointly by labour and management in the mining industry and the Ministry of Training, Colleges and Universities and approved by the Director:
1. Hard rock underground mines,
i. Common Core for Basic Underground Hard Rock Mining Skills (Program # P770010). (Basic Common Core Program),
ii. Speciality Modules Underground Hard Rock Mining (Program # P770010),
iii. Common Core for First Line Production Supervisors Underground Hard Rock Mining (Program # P770120).
2. Soft rock underground mines,
i. Common Core for Basic Underground Soft Rock Mining Skills (Program # P770130). (Basic Common Core Program),
ii. Speciality Modules Underground Soft Rock Mining (Program # P770130).
3. Mill Process Operations,
i. Common Core for Basic Mill Process Operations — Mineral Ore (Program # P810050),
ii. Speciality Modules Mill Process Operator — Mineral Ore (Program # P810050). R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 11 (1); O. Reg. 571/92, s. 4; O. Reg. 174/01, s. 2 (1).
(2) An employer shall train each full-time worker who commences employment after the 1st day of June, 1987 in the Basic Common Core Program described in subsection (1) appropriate for that worker and the training shall be given within the first year of employment. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 11 (2).
(3) Subsection (2) does not apply if the worker successfully completed the Basic Common Core Program appropriate for that worker prior to being employed by the employer or was accredited under the predecessor of this section and gives the employer proof thereof. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 11 (3).
(4) A certificate issued by the Ministry of Training, Colleges and Universities showing that a worker has successfully completed a training program referred to in subsection (1) is conclusive proof for the purposes of this section of the worker’s successful completion of the program. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 11 (4); O. Reg. 174/01, s. 2 (2).
11.1 (1) Employers engaged in the following types of mining operations shall establish and maintain the following training programs:
1. Underground diamond drilling operations,
i. Common Core for Underground Diamond Driller Skills — Helper Level (Program #P770150),
ii. Common Core for Underground Diamond Driller Skills — Runner Level (Program #P770150).
2. Surface diamond drilling operations,
i. Common Core for Surface Diamond Driller Skills — Helper Level (Program #P770200),
ii. Common Core for Surface Diamond Driller Skills — Runner Level (Program #P770200). O. Reg. 68/96, s. 1; O. Reg. 174/01, s. 3 (1).
(2) An employer shall train each full-time worker who commences employment after March 31, 1996 in the programs described in subsection (1) appropriate for that worker, and the training shall be completed before the worker has completed a total of 12 months of employment as a helper or runner in diamond drilling operations. O. Reg. 68/96, s. 1.
(3) Subsection (2) does not apply if the worker successfully completed a program described in subsection (1) before being employed by the employer. O. Reg. 68/96, s. 1.
(4) A certificate of achievement showing that a worker has successfully completed a training program referred to in subsection (1), issued by the Ministry of Training, Colleges and Universities, is conclusive proof for the purposes of this section of the worker’s successful completion of the program. O. Reg. 68/96, s. 1; O. Reg. 174/01, s. 3 (2).
11.2 (1) Employers engaged in surface mine operations shall establish and maintain the following training programs:
1. Modular Training Standards — Surface Miner (Program #770210) Common Core Modules U5030, U5031, U5032.
2. Modular Training Standards — Surface Miner (Program #770210) Specialty Modules. O. Reg. 251/01, s. 1.
(2) Employers shall train workers in the common core modules described in subsection (1),
(a) by September 30, 2002 if the worker commenced employment on or before September 30, 2001; or
(b) within 12 months after commencing employment, if the worker commences employment after September 30, 2001. O. Reg. 251/01, s. 1.
(3) Subsection (2) does not apply if the worker successfully completed a program described in subsection (1) before being employed by the employer. O. Reg. 251/01, s. 1.
(4) A worker shall be trained in the appropriate common core modules before beginning training in a specialty module. O. Reg. 251/01, s. 1.
(5) A certificate of achievement showing that a worker has successfully completed a training program referred to in subsection (1), issued by the Ministry of Training, Colleges and Universities, is conclusive proof for the purposes of this section of the worker’s successful completion of the program. O. Reg. 251/01, s. 1.
11.2.1 (1) Employers engaged in hard rock underground mine operations shall establish and maintain the training program described as Basic Underground Hard Rock Mine Service Types — Common Core (Program #P770225). O. Reg. 291/02, s. 1.
(2) Employers shall train workers in the common core module described in subsection (1),
(a) by December 31, 2003 if the worker commenced employment on or before December 31, 2002; or
(b) within 12 months after commencing employment, if the worker commences employment after December 31, 2002. O. Reg. 291/02, s. 1.
(3) Subsection (2) does not apply if the worker successfully completed the program described in subsection (1) before being employed by the employer. O. Reg. 291/02, s. 1.
(4) A certificate of achievement showing that a worker has successfully completed the training program referred to in subsection (1), issued by the Ministry of Training, Colleges and Universities, is conclusive proof for the purposes of this section of the worker’s successful completion of the program. O. Reg. 291/02, s. 1.
11.2.2 (1) Employers engaged in contiguous underground mine operations and smelter operations shall establish and maintain the following training programs:
1. Common Core for Basic Smelter Operations — Mineral Ore (Program #P810080).
2. Common Core for Non-Production Workers in a Smelter Operation — Mineral Ore (Program #P810090). O. Reg. 31/04, s. 3.
(2) Employers shall train workers in the common core modules described in subsection (1),
(a) by June 1, 2005 if the worker commenced employment on or before June 1, 2004; or
(b) within 12 months after commencing employment, if the worker commences employment after June 1, 2004. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 3.
(3) Subsection (2) does not apply if the worker successfully completed the program described in subsection (1) before being employed by the employer. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 3.
(4) A certificate of achievement showing that a worker has successfully completed the training program referred to in subsection (1), issued by the Ministry of Training, Colleges and Universities, is conclusive proof for the purposes of this section of the worker’s successful completion of the program. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 3.
11.3 In accordance with the Agreement on Internal Trade, 1995 and the Protocols of Amendment, a worker shall be deemed to hold a certificate referred to in subsection 11 (4), 11.1 (4), 11.2 (5) or 11.2.1 (4) if he or she has successfully completed equivalent training in another province or territory of Canada, as determined by the Director. O. Reg. 251/01, s. 1; O. Reg. 291/02, s. 2.
12. (1) Every worker who is exposed to the hazard of head injury shall wear a protective hat that consists of a shell and suspension system that will adequately protect a worker’s head against impact and from flying or falling small objects. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 12 (1).
(2) Every worker who is exposed to the hazard of foot injury shall wear protective footwear consisting of a boot or shoe which incorporates a protective box toe that will protect a worker’s toes against injury due to impact and which is capable of resisting at least 125 joules of impact energy. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 12 (2).
(3) An employer shall require a worker to wear or use such personal protective equipment, clothing and devices as are necessary to protect the worker from the particular hazard to which the worker may be exposed. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 12 (3).
(4) Every worker shall be properly fitted with personal protective clothing or equipment by a competent person or persons. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 12 (4).
(5) Loose clothing, adornments and hair shall be suitably confined to prevent entanglement with any machinery, device or thing in a workplace. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 12 (5).
13. (1) Where, in an emergency, the health or safety of a worker is likely to be endangered by lack of oxygen or the presence of a noxious gas, fume or dust,
(a) emergency breathing equipment and resuscitating equipment shall be provided for use in such emergency; and
(b) a worker trained in the use of the breathing equipment and the resuscitating equipment required by clause (a) shall be conveniently available on each shift. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 13 (1).
(2) The emergency breathing equipment and the resuscitating equipment required by clause (1) (a) shall each be stored in a dust-proof container. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 13 (2).
14. (1) Subject to subsection (5), where a worker is exposed to the hazard of falling more than three metres, a fall arrest system shall be used to protect the worker. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 14 (1).
(2) The fall arrest system required by subsection (1) shall consist of a suitable combination of a belt, a full body harness, a lanyard, an anchor and a rope-grabbing device or lifeline. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 14 (2).
(3) The belt, full body harness, lanyard and lifeline shall,
(a) be made of material with elastic properties capable of absorbing and minimizing the arrest force in case of a fall;
(b) be designed to distribute a fall arrest force in such a manner that the possibility of injury to the worker is minimized;
(c) be of sufficient strength to absorb twice the energy that may be transmitted to the fall arrest system; and
(d) not be knotted or allowed to become knotted, when used or worn. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 14 (3).
(4) When being used and worn against the hazard of falling, the lifeline of the fall arrest system shall be,
(a) anchored so that a worker will fall free of arrest not more than one metre; and
(b) connected to an object that is,
(i) capable of resisting the arrest force in case of a fall, and
(ii) free of sharp edges. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 14 (4).
(5) Subsection (1) does not apply to a worker employed in shaft sinking where measures and procedures are adopted and put into effect that will provide equal or greater protection to the worker. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 14 (5).
15. (1) No person under the influence of, or carrying, intoxicating liquor, shall enter or knowingly be permitted to enter a mine or mining plant. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 15 (1).
(2) Subject to subsection (3), no person under the influence of, or carrying, a drug or narcotic substance shall enter or knowingly be permitted to enter a mine or mining plant. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 15 (2).
(3) A person required to use a prescription drug and able to perform his or her work may enter a mine or mining plant upon establishing medical proof thereof. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 15 (3).
16. (1) This section applies with respect to a worker who is working alone in an underground mine. However, it does not apply with respect to a supervisor working alone in an underground mine. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 5.
(2) For the purposes of this section, a worker is not working alone if he or she,
(a) is assigned to work with at least one other worker and is in regular visual contact with the other worker;
(b) is in visual contact with another worker at least once every hour; or
(c) has ready access to a system of two-way communication such as radio, telephone or other electronic means. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 5.
(3) Only a competent worker shall work alone in an underground mine. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 5.
(4) Except as otherwise provided by this section, a supervisor or a competent worker designated by the supervisor shall visit a worker at least three times during the worker’s shift, if the worker is working alone in an underground mine. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 5.
(5) In the following circumstances, a supervisor or competent worker designated by the supervisor is required to visit a worker only once during the worker’s shift, if the worker is working alone in an underground mine:
1. The work conditions are standard.
2. A supervisor or competent worker designated by the supervisor visits or communicates with the worker at least once every two hours.
3. A record of the communications with the worker is kept. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 5.
(6) The communication required by paragraph 2 of subsection (5) must be either face-to-face communication or by a system of two-way communication such as radio, telephone or another electronic means. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 5.
17. (1) Mine rescue stations may be established, equipped, operated and maintained in such locations as the Minister considers advisable. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 17 (1).
(2) The cost of establishing, equipping, operating and maintaining the mine rescue stations shall be paid out of the Consolidated Revenue Fund in the first instance and shall be reimbursed quarterly by the Workplace Safety and Insurance Board from money assessed and levied by the Board upon employers in the mining industry to defray the cost certified by the Deputy Minister. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 17 (2); O. Reg. 236/99, s. 2.
(3) Money received from the sale or disposal of any equipment, buildings or machinery used in mine rescue or any handbooks or publications on mine rescue shall be credited against the cost of mine rescue stations. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 17 (3).
(4) A mine rescue station and the training of members of a mine rescue crew shall be under the direction of a mine rescue officer appointed by the Ministry. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 17 (4).
(5) A mine rescue crew member shall possess such physical qualifications, and establish competency in mine rescue skills as described in the Handbook of Training in Mine Rescue and Recovery Operations, current edition, issued by the Ministry. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 17 (5).
(6) The owner of a mine shall make available training facilities and workers to be taught and trained in mine rescue work at the expense of the owner. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 17 (6).
(7) A mine rescue operation at a mine shall be under the direction of the supervisor in charge of the mine and the costs of the rescue operation shall be at the expense of the owner of the mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 17 (7).
(8) Notice shall be given immediately to a mine rescue officer and to an inspector when the services of a mine rescue crew are required. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 6.
18. (1) Surface mines and openings on the surface to underground mines shall be protected to prevent inadvertent access where,
(a) the surface mine or opening is a hazard by reason of its depth;
(b) approaches and openings are not readily visible; or
(c) the hazard caused by the surface mine or opening is greater than the hazard caused by the natural topographical features of the area. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 18 (1).
(2) Prior to operations at a mine being terminated, a shaft or raise opening shall be,
(a) capped with a stopping of reinforced concrete; or
(b) filled and kept filled with material so that any subsidence of the material will not endanger any person. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 18 (2).
(3) The stopping prescribed in clause (2) (a) shall be,
(a) secured to solid rock or to a concrete collar secured to solid rock; and
(b) capable of supporting a uniformly distributed load of twelve kilopascals or a concentrated load of fifty-four kilonewtons, whichever is greater. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 18 (3).
(4) Where an underground mine is being developed after the 1st day of October, 1979, shafts or raise openings shall be provided with a collar of concrete secured to bedrock. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 18 (4).
19. (1) Subject to subsection (2), a pillar sixty metres thick shall be established on either side of a party boundary between adjoining underground mining properties. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 19 (1).
(2) Except for exploration headings and diamond drilling, before the pillar is mined, drawings, plans, specifications, mining methods and procedures for the mining of the pillar shall be prepared or checked by a professional engineer in accordance with good engineering practice, filed with the owners of adjoining mining properties and kept readily available at each mine site. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 7.
(3) The drawings, plans, specifications, mining methods and procedures to be filed shall be maintained and kept up to date in accordance with subsection 29 (2) of the Act. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 19 (3).
(4) The pillar dimensions and mining methods and procedures shall,
(a) provide ground support to control rockbursting, ground falls or pillar failures; and
(b) withstand inrush of water or waterbearing materials across the party boundary. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 19 (4).
(5) Subject to subsections (2), (3) and (4), the party boundary pillar may be mined if the owners of the adjoining mines agree. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 7.
20. (1) A laboratory may be approved by the Minister for the purpose of testing or examining shaft ropes or other hoisting appliances. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 20 (1).
(2) The fee for testing, at a laboratory, a rope of the type described in Column 1 of the Table to this subsection and the size set out in Column 2 is the corresponding amount,
(a) set out in Column 3, for a rope tested for a mine in Ontario; or
(b) set out in Column 4, for a rope tested for a mine outside Ontario or for the manufacturer of the rope.
TABLE
|
Column 1 |
Column 2 |
Column 3 |
Column 4 |
|
Type |
Diameter in Millimetres |
Fee |
Fee |
|
Round or flattened strand |
To and including 22.2 |
$160 |
$250 |
|
|
Over 22.2 to and including 34.9 |
250 |
400 |
|
|
Over 34.9 to and including 50.8 |
400 |
600 |
|
|
Over 50.8 to and including 57.2 |
630 |
860 |
|
|
Over 57.2 to and including 63.5 |
920 |
1,200 |
|
|
Over 63.5 to and including 76.2 |
1,440 |
1,670 |
|
|
Over 76.2 to and including 101.6 |
2,130 |
2,300 |
|
Lock coil |
To and including 22.2 |
180 |
300 |
|
|
Over 22.2 to and including 34.9 |
320 |
520 |
|
|
Over 34.9 to and including 44.4 |
480 |
750 |
|
|
Over 44.4 to and including 63.5 |
1,350 |
1,650 |
|
|
Over 63.5 to and including 76.2 |
1,840 |
2,070 |
|
|
Over 76.2 to and including 101.6 |
2,300 |
2,530 |
|
Plastic filled valley (PVC) |
To and including 22.2 |
320 |
410 |
|
|
Over 22.2 to and including 34.9 |
500 |
670 |
|
|
Over 34.9 to and including 50.8 |
800 |
1,040 |
|
|
Over 50.8 to and including 57.2 |
1,270 |
1,450 |
|
|
Over 57.2 to and including 63.5 |
1,840 |
2,120 |
|
|
Over 63.5 to and including 76.2 |
2,880 |
3,100 |
|
|
Over 76.2 to and including 101.6 |
4,260 |
4,430 |
|
Synthetic rope |
To and including 22.2 |
120 |
230 |
|
|
Over 22.2 |
230 |
350 |
|
|
Additional charge for testing resin socket material |
||
|
|
To and including 22.2 |
120 |
120 |
|
|
Over 22.2 |
230 |
230 |
O. Reg. 384/92, s. 1.
(3) For the purposes of the Table in subsection (2), the diameter in millimetres set out in Column 1 of the following Table shall be deemed to be equivalent to the diameter in inches set out opposite thereto in Column 2:
TABLE
|
Column 1 |
Column 2 |
|
Diameter in Millimetres |
Diameter in Inches |
|
22.2 |
7/8 |
|
34.9 |
1⅛ |
|
44.4 |
1¼ |
|
50.8 |
2 |
|
57.2 |
2¼ |
|
63.5 |
2½ |
|
76.2 |
3 |
|
101.6 |
4 |
R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 20 (3).
(4) A laboratory shall issue a Certificate of Test for each sample of shaft rope submitted to it for testing, setting out the breaking strength of the rope, and the breaking strength, as set out in the Certificate of Test, shall be the breaking strength of the rope from which the sample was taken. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 20 (4).
21. (1) The written report required by section 51 of the Act shall include,
(a) the name and address of the employer;
(b) the nature and the circumstances of the occurrence and the bodily injury sustained;
(c) a description of the machinery or equipment involved;
(d) the time and place of the occurrence;
(e) the name and address of the person who was killed or critically injured;
(f) the names and addresses of all witnesses to the occurrence and of all supervisors and workers who were involved; and
(g) the name and address of the physician or surgeon, if any, by whom the person was or is being attended for the injury. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 21 (1).
(2) For the purposes of section 52 of the Act, notice of,
(a) an accident, explosion or fire which disables a worker from performing his or her usual work; or
(b) an occupational illness,
shall include,
(c) the name, address and type of business of the employer;
(d) the nature and the circumstances of the occurrence and the bodily injury or illness sustained;
(e) a description of the machinery or equipment involved;
(f) the time and place of the occurrence;
(g) the name and address of the person suffering the injury or illness;
(h) the names and addresses of all witnesses to the occurrence;
(i) the name and address of the physician or surgeon, if any, by whom the person was or is being attended for the injury or illness; and
(j) the steps taken to prevent a recurrence. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 21 (2).
(3) A record of an accident, explosion or fire causing injury requiring medical attention but not disabling a worker from performing his or her usual work shall be kept in the permanent records of the employer and include particulars of,
(a) the nature and the circumstances of the occurrence and the injury sustained;
(b) the time and place of the occurrence; and
(c) the name and address of the injured person. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 21 (3).
(4) A record kept as prescribed by subsection (3) for the inspection of an inspector shall be notice to the Director. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 21 (4).
(5) In addition to the occurrences referred to in section 53 of the Act, a notice in writing shall be given where,
(a) a failure occurs in or to a hoist, sheave, hoisting rope, shaft conveyance, shaft timbering or shaft lining;
(b) flammable gas is present in a workplace in an underground mine;
(c) spontaneous heating with evolution of gas occurs in a workplace;
(d) a major failure or major damage occurs or is caused to electrical equipment, standard gauge railway equipment, a crane or a motor vehicle underground;
(e) a rockburst occurs causing damage to equipment or the displacement of more than five tonnes of material;
(f) an uncontrolled fall of ground occurs causing damage to equipment or the displacement of more than fifty tonnes of material;
(g) a fuse, a detonator or an explosive is found to be defective;
(h) a structural failure occurs in any matter or thing for which a design by a professional engineer is prescribed by this Regulation; or
(i) an unexpected and uncontrolled run of material, water or slimes in excess of one cubic metre occurs that could have endangered a worker. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 21 (5); O. Reg. 60/94, s. 3.
22. (1) For the purpose of subsection 29 (2) of the Act, drawings, plans and specifications to be kept and maintained shall be,
(a) a surface plan showing,
(i) the boundaries of a mining property,
(ii) the co-ordinates of the section of a mining property under which mining has been done,
(iii) all lakes, streams, roads, railways, electric power transmission lines, main pipe lines, buildings, adits, surface workings, diamond drill holes, out-croppings of rock, dumps, tailing-disposal sites and openings to an underground mine, and
(iv) stopping of openings on the surface to an underground mine;
(b) plans on a horizontal plane with separate drawings for each level showing all underground workings, including shafts, tunnels, diamond drill holes, dams and bulkheads;
(c) plans on a vertical plane of all mine sections at suitable intervals and azimuths, showing all shafts, tunnels, drifts, stopes and other mine workings in relation to the surface, including the location of the top of the bedrock, the surface of the overburden and the bottom and surface of any known watercourse or body of water; and
(d) a plan or diagram showing,
(i) the position of all fixed electrical apparatus and communication systems in the mine,
(ii) the routes of all fixed power feeders and fixed branch feeders properly noted and referenced, and
(iii) the rating of all electrical feeder control apparatus and equipment. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 22 (1).
(2) The surface plan prescribed by clause (1) (a) shall show,
(a) the boundaries of the mining property,
(i) related to the lot fabric where the property is in a subdivided township,
(ii) connected to the nearest mile post on a surveyed township boundary where the property is in an unsubdivided township, or
(iii) connected to the nearest,
(A) mile post on a surveyed township boundary,
(B) base line, or
(C) meridian line,
where the property is in unsurveyed territory, and
(iv) connected to a co-ordinate control survey monument if one exists within ten kilometres of the property; and
(b) the position and form of a permanent bench mark to which all elevations are related, and the permanent bench mark shall be related,
(i) where a Canadian Geodetic Datum bench mark exists within ten kilometres, to that bench mark, and
(ii) to the permanent bench mark of each adjoining property. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 22 (2).
(3) The measurements under clause (2) (a) shall be consistent with accuracy standards for third order horizontal control surveys based on Ontario Specifications for Horizontal Control Surveys, 1979. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 22 (3).
(4) Where operation at a mine is terminated or suspended, copies of the plans mentioned in subsection (1) shall be filed with the Ministry. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 22 (4).
(5) Copies of all plans shall be on a legible scale and suitable for microfilming. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 22 (5).
23. (1) If an underground mine has been permanently shut down or abandoned or if operations at the mine have been discontinued or suspended for more than three months, the owner shall, before dewatering, exploring or resuming work at the mine,
(a) notify an inspector of the owner’s intention to enter the mine; and
(b) furnish an inspector with such drawings, plans, specifications and descriptions of procedures as are necessary to determine whether it is safe to enter the mine. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 1; O. Reg. 272/97, s. 8 (1, 2).
(2) Subject to subsection (4), where a decision is made to discontinue or suspend operations at a mine or mining plant, notice shall be given forthwith to an inspector. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 23 (2).
(3) Where operations at a mine or mining plant are discontinued or suspended, the notice mentioned in subsection (2) shall advise whether,
(a) stopping and protection has been done as prescribed in section 18;
(b) explosives have been disposed of as prescribed in subsection 122 (5);
(c) removal and disposition of hoisting ropes has been done as prescribed in subsection 228 (17);
(d) disconnection from the electrical power source has been done and has been confirmed in writing by the appropriate electrical utilities inspection department; and
(e) plans required by section 22 have been filed with the Ministry. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 23 (3); O. Reg. 272/97, s. 8 (3).
(4) Subsections (2) and (3) do not apply to gravel pit operations that are discontinued during the winter months. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 23 (4).
24. A notice under subsection 57 (9) of the Act shall be in the following form:
Occupational Health and Safety Act
NOTICE
|
Take Notice that this |
|
|
.......................................................................................... |
|
|
(specify the “place”, “matter” or “thing”, as the case may be) |
|
|
|
|
|
is a danger or hazard to the safety of workers employed in or having access to these premises and the use thereof shall be discontinued immediately until the inspector’s order of ............................................................................ |
|
|
(date) |
|
|
|
|
|
to ...................................................................................... |
|
|
(name of employer or owner) |
|
|
|
|
|
........................................................................................... |
|
|
(address of employer or owner) |
|
|
|
|
|
has been complied with. |
|
|
|
|
|
No person, except an inspector appointed under the Occupational Health and Safety Act, shall remove this notice unless authorized by an inspector under that Act. |
|
|
|
|
|
Dated the ........................... |
day of ………….… , 20…. |
|
|
|
|
|
............................................ |
|
|
(signature of inspector) |
R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 24.
25. (1) Procedures in case of a fire in an underground mine, or in a structure or building on the surface at an underground mine, that may be a hazard to workers in the mine shall be prepared by the supervisor in charge of the mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 25 (1).
(2) An alarm system, that is effective to warn workers in an underground mine of a fire that is likely to endanger their safety, shall be provided. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 25 (2).
(3) The procedures required by subsection (1), or extracts therefrom, and a notice explaining the alarm system shall be set out in writing and shall be posted and kept posted in the shaft house and in a conspicuous place or places where they are most likely to come to the attention of a worker. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 25 (3).
(4) Every worker shall be advised by a supervisor of the procedures and the alarm system. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 25 (4).
(5) Once in at least every twelve months during each production shift a fire alarm test of the procedures shall be conducted. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 25 (5).
(6) The alarm system in an underground mine shall,
(a) consist of the introduction into all workplaces of sufficient quantities of ethyl mercaptan gas or similar gas to be readily detectable by all workers; and
(b) be kept ready for immediate use. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 25 (6).
(7) Despite clause (6) (a), an alternative means of alarm may be used if the alarm system is agreed upon by the employer and the joint health and safety committee or the health and safety representative, if any, for the workplace. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 2.
(8) A report of each fire alarm test of the procedures mentioned in subsection (5) shall be kept available at the mine for three years. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 9.
26. Where the procedure in case of a fire in an underground mine provides for the use of a refuge station for workers, the refuge station shall,
(a) be constructed with materials having at least a one hour fire-resistance rating;
(b) be of sufficient size to accommodate the workers to be assembled therein;
(c) be capable of being sealed to prevent the entry of gases;
(d) have a means of voice communication with the surface; and
(e) be equipped with a means for the supply of,
(i) compressed air, and
(ii) potable water. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 26.
27. (1) A fresh air base shall be provided underground where necessary to serve as a base for rescue and recovery work. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 27 (1).
(2) A fresh air base shall be,
(a) at least thirty square metres in area; and
(b) equipped with a means for the supply of potable water and compressed air. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 27 (2).
28. (1) Fire extinguishing equipment of suitable type and size for use on a fire shall be provided,
(a) at a fire hazard area;
(b) where an electrical installation or equipment may be a fire hazard;
(c) in or about a headframe;
(d) in a building or structure on surface where a fire might endanger the mine entrance; and
(e) at a shaft station in an underground mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 28 (1).
(2) A fire suppression system consisting of sprinklers, foam or other suitable means of suppressing fire shall be provided,
(a) in an underground mine,
(i) on equipment containing more than 100 litres of flammable hydraulic fluids,
(ii) in every storage area where more than 500 litres of oil, grease or flammable liquids are stored,
(iii) in every service garage, and
(iv) in every permanent fuelling station; and
(b) on the surface, in a building or structure, except a fan house, located above or adjacent to an opening to an underground mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 28 (2); O. Reg. 486/99, s. 1.
(3) At least once each month in an underground mine,
(a) fire extinguishing equipment;
(b) fire suppression systems;
(c) fire hydrants; and
(d) fire doors,
shall be inspected by a competent person who shall report in writing thereon to the supervisor in charge of the underground mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 28 (3).
29. (1) In an underground mine or in or about a headframe or shaft house, flammable refuse shall be,
(a) deposited in covered, fire-resistive containers; and
(b) removed at least once a week from the mine or headframe or shaft house. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 29 (1).
(2) Scrap timber shall safely be disposed of or removed from an underground mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 29 (2).
(3) A written report certifying that there is no accumulation of flammable refuse in the area under his or her supervision shall be made weekly by a supervisor to the supervisor in charge of the mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 29 (3).
30. (1) Oil, grease and other flammable material shall not be kept or stored in a shafthouse or in a portal house. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 30 (1).
(2) Oil, grease and flammable liquids with a flashpoint below 52º Celsius shall,
(a) when being used underground, be transported and stored only in metal containers or receptacles or in portable plastic containers for Petroleum Fuels as specified in CSA Standard No. B376-M1980, “Portable Containers for Gasoline and Other Petroleum Fuels”; and
(b) when stored underground, be restricted in quantity to the requirement for,
(i) the current day’s work in the case of volatile flammable liquids, and
(ii) seven days in the case of oil and grease. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 30 (2); O. Reg. 584/91, s. 2.
(3) No device for the generation of acetylene gas shall be used in an underground mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 30 (3).
(4) No internal combustion engine that uses gasoline, propane or other volatile substance as a fuel shall be used in an underground mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 30 (4).
(5) Except when used for burning or cutting, propane or other similar fuel that is heavier than air when in a gaseous state shall not be permitted to be or be kept underground. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 30 (5).
(6) When propane or other similar fuel that is heavier than air is being used underground for burning or cutting, the containers for the fuel shall be of a type certified under the Energy Act and shall not be larger than five kilograms in capacity. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 30 (6).
31. No worker shall build or set a fire in an underground mine unless the worker is specifically authorized to do so and has immediately available suitable fire extinguishing equipment. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 31.
32. Every workshop and lunchroom in an underground mine shall,
(a) be constructed of material with at least a one hour fire-resistance rating; and
(b) be located and maintained so as to reduce the fire hazard to a minimum. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 32.
33. A structure housing a fan used in connection with a ventilation system for an underground mine shall be constructed of non-combustible material. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 33.
34. (1) A fire hazard area shall be identified by suitable warning signs. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 34 (1).
(2) Except where special precautions are taken and written instructions issued, no use of matches, smoking or other means of producing heat or fire shall be permitted in a fire hazard area. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 34 (2).
35. (1) If a flow of flammable gas is encountered in a mine or in an enclosed building housing a diamond drill on the surface and the concentration of the flammable gas is unknown,
(a) all sources of ignition in the affected area shall be eliminated;
(b) all electrical equipment in the affected area shall be de-energized;
(c) the affected area shall be evacuated;
(d) precautions shall be taken to prevent persons from entering the affected area inadvertently;
(e) a supervisor shall be notified;
(f) the affected area shall be tested by a competent person; and
(g) the affected area shall be designated as a fire hazard area. O. Reg. 236/99, s. 3.
(2) Subject to subsections (3), (4) and (5), work may resume if the concentration of flammable gas is below 1.0 per cent. O. Reg. 236/99, s. 3.
(3) If the concentration is less than 0.25 per cent and the affected area is tested periodically to ensure that the level of concentration is known, no precautions are required. O. Reg. 236/99, s. 3.
(4) If the concentration is 0.25 per cent or greater but not more than 0.5 per cent, all of the following precautions shall be taken:
1. The supervisor shall provide written instructions of any special precautions.
2. The instructions, if any, shall be communicated to the workers.
3. The affected area shall be designated as a fire hazard area.
4. The affected area shall be tested at least once per shift before work begins and, again, on release of any further flow of gas.
5. A flammable gas detector shall remain in the affected area for the purpose of continued testing. O. Reg. 236/99, s. 3.
(5) If the concentration is 0.5 per cent or greater but not more than 1.0 per cent, all of the precautions set out in subsection (4) shall be taken and the electrical equipment, diesel engines, tools and other material used in the workplace shall be designed to function safely in a flammable gas atmosphere. O. Reg. 236/99, s. 3.
(6) If concentrations of flammable gas exceed 1.0 per cent in an area, all of the following precautions shall be taken:
1. All sources of ignition in the affected area shall be eliminated.
2. All electrical equipment in the affected area shall be de-energized.
3. All persons, other than competent persons necessary to measure the concentration of flammable gas and to make ventilation changes, shall be removed from the affected area. O. Reg. 236/99, s. 3.
(7) In mines where flammable gas is known to occur, workers who are underground or diamond drillers who are on the surface shall be advised of,
(a) the probability of encountering a flow of the gas; and
(b) the measures and procedures prescribed in this section. O. Reg. 236/99, s. 3.
(8) For the purposes of this section, the concentration of flammable gas means the percentage, by volume, of flammable gas in the general atmosphere. O. Reg. 236/99, s. 3.
36. (1) Where a blow torch or welding, cutting or other hot work equipment is used underground, or in a headframe, shaft house or other surface building in which a fire may endanger the mine entrance or the underground workings, a procedure for the safe use of hot work equipment shall be prepared in writing and signed by the supervisor in charge of the mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 36 (1).
(2) Only a worker who is a competent person or is under the direction of a competent person shall use hot work equipment. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 36 (2).
(3) In addition to the hot work procedure required by subsection (1), written instructions shall be issued to the worker by a supervisor before the hot work equipment is used respecting,
(a) the type of work;
(b) the location of the work;
(c) when the work is to be done; and
(d) any special measures and procedures to be taken before, during and after the work. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 36 (3).
(4) Where hot work equipment is used in a shaft, timbered area or fire hazard area,
(a) the area adjacent to the particular workplace shall be wet down,
(i) before the work is begun, and
(ii) when the work is stopped and the worker using the hot work equipment intends to leave;
(b) the area adjacent to the particular workplace shall be examined for potential fire hazards,
(i) before the work is begun, and
(ii) when the work is stopped and the worker intends to leave the area, and
(iii) on at least one other occasion approximately two hours after the work is stopped;
(c) fire-fighting equipment suitable for extinguishing any potential fire shall be available; and
(d) workers shall be protected from fumes, vapours or gases by,
(i) ventilation, or
(ii) the wearing of respirators. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 36 (4).
(5) Subsection (1) does not apply to hot work being performed in a repair station or garage protected by a fire suppression system. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 36 (5).
(6) Clause (4) (a) does not apply where the wetting down will create a hazard because of freezing or the presence of electrical equipment. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 36 (6).
37. (1) Except during the initial stages of exploration and development of mine, in addition to the opening through which workers are let into or out of the mine and the ore extracted, a separate escapement exit shall be provided. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 37 (1).
(2) The escapement exit required by subsection (1) shall be,
(a) located more than thirty metres from the main hoisting shaft or ramp;
(b) of sufficient size to afford an easy passageway;
(c) where necessary, provided with ladders from the deepest workings to the surface;
(d) marked on all levels by signs and arrows pointing the way of exit in a manner to expedite escape;
(e) made known to all underground workers who shall be instructed as to the route to the escapement exit; and
(f) inspected at least once a month by a competent person who shall give a written report of such inspection to the supervisor in charge of the mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 37 (2).
(3) A structure covering the escapement exit shall be constructed of material with at least a one hour fire-resistance rating. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 37 (3).
38. (1) Subject to subsection (2), unless there is a second means of exit from an underground mine, no building shall be erected within fifteen metres of any closed-in part of a headframe or portal house. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 38 (1).
(2) A building erected within fifteen metres of any closed-in part of a headframe or portal house shall be constructed of material with at least a one hour fire-resistance rating. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 38 (2).
(3) No steam boiler or diesel engine shall be installed in such a manner that any part thereof is within thirty metres of the centre of the collar of a shaft or other entrance to a mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 38 (3).
(4) No internal combustion engine shall be installed, serviced, garaged or stored in or within fifteen metres of the building housing the hoist nor within thirty metres of the centre of the collar of a shaft or other entrance to a mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 38 (4).
(5) Except for the fuel tanks of motor vehicles, no gasoline or liquid fuel shall be stored within thirty metres of the centre of the collar of a shaft or other entrance of a mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 38 (5).
(5.1) Subsections (3), (4) and (5) do not apply with respect to a diesel engine and an attached diesel fuel tank (other than an engine installed on a motor vehicle) if,
(a) the engine and tank are enclosed by a structure constructed of material that has a fire-resistance rating of at least one hour;
(b) the structure separates the enclosed area from the hoist or a shaft or other entrance to a mine; and
(c) the enclosed area has a fire suppression system and an automatic fire alarm. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 10.
(6) The natural drainage shall drain away from the shaft collar or other mine entrance. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 38 (6).
(7) Where a hoist is located above the mine shaft, the supporting and enclosing structures shall be constructed of material with at least a one hour fire-resistance rating. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 38 (7).
39. Fire doors in an underground mine shall,
(a) where practical, be installed to close off the shaft or main entrance to the mine and the mine openings directly associated with it from the other workings;
(b) be installed to close off,
(i) service garages, and
(ii) oil storage areas where a total of more than 500 litres of oil, grease or flammable liquid are stored;
(c) have at least a one hour fire-resistance rating; and
(d) be maintained in proper order and kept clear of all obstructions so as to be readily usable at all times. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 39.
40. (1) Where, in an underground or tower mounted hoistroom, the normal air supply may become contaminated in an emergency, uncontaminated air shall be available to the hoist operator and cagetender by means of,
(a) an enclosed booth with a positive supply of uncontaminated air; or
(b) one or more units of self-contained demand air or oxygen breathing apparatus, together with a fully charged cylinder of compressed air of at least 8.5 cubic metres capacity. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 40 (1).
(2) Every hoist operator and cagetender who may be required to use demand breathing apparatus shall be competent in its use. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 40 (2).
41. (1) Procedures in case of a fire at,
(a) the surface of an underground mine;
(b) a surface mine; or
(c) a mining plant,
shall be prepared by the supervisor in charge of the mine or mining plant. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 41 (1).
(2) The procedures required by subsection (1) or extracts therefrom shall be set out in writing and shall be posted and kept posted in a conspicuous place or places where they are most likely to come to the attention of a worker. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 41 (2).
(3) A suitable number of workers at each mine and mining plant shall be trained in the fire-fighting procedures and,
(a) the names of such workers shall be posted in a conspicuous place;
(b) such workers shall be tested for proficiency at least once a year; and
(c) a written report of the results of the tests shall be made and kept on file. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 41 (3).
(4) Fire-extinguishing equipment of a suitable type and size shall be provided at,
(a) the surface of every underground mine;
(b) every surface mine; and
(c) mining plant. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 41 (4).
(5) At least once each month, the,
(a) fire-extinguishing equipment;
(b) fire suppression systems;
(c) fire hydrants; and
(d) fire doors,
at the surface of an underground mine, a surface mine and a mining plant shall be inspected by a competent person who shall report thereon to the supervisor in charge of the mine or mining plant, as the case may be. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 41 (5).
42. (1) The fuel tank of an internal combustion engine installed in a building shall be arranged so that the transfer of fuel to the tank takes place at a point outside the building and the fuel is conducted to the tank in a tightly jointed pipe or conduit. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 42 (1).
(2) The air displaced from the fuel tank shall be conducted to a safe point outside the building before being discharged into the atmosphere. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 42 (2).
43. Any dangerous, flammable or explosive material or substance in a solid, liquid or gaseous state, or any combination thereof, other than explosive, that is kept, stored or handled, in a mining plant shall,
(a) be kept in a container that is suitable having regard to the nature and state of the material or substance;
(b) have labels on the container identifying the material or substance and warning of the hazards involved therewith;
(c) be kept apart or insulated from any source of ignition or from temperatures likely to cause combustion; and
(d) where the material or substance is not intended for immediate use, be kept, stored or handled,
(i) outside any building,
(ii) in a building not used for any other purpose, or
(iii) in a well ventilated compartment with at least a one hour fire-resistance rating which is located in conformity with clause (c). R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 43.
44. (1) In addition to the main exit, a building at a mining plant, except a magazine, shall be provided with a second means of exit, convenient to and having easy communication with all rooms regularly occupied by a worker, including,
(a) tower stairs equipped with doors and hardware with at least a one hour fire-resistance rating at each storey including the basement; or
(b) metal or other non-combustible fire escapes consisting of exterior stairways with railings and with landings at each storey connecting directly with the interior of the building through metal or other doors with at least a one hour fire-resistance rating. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 44 (1).
(2) No means of exit from a plant building shall be obstructed and no door to a fire escape, tower stair or other smokeproof enclosure shall be prevented from closing or remaining closed. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 44 (2).
45. A process that is likely to produce a gas, vapour, dust or fume to such an extent as to be capable of forming a flammable mixture with air shall be carried out in an area which,
(a) is isolated from other operations;
(b) has a system of ventilation which removes the gas, vapour, dust or fume;
(c) has no potential sources of ignition; and
(d) has vents, baffles, chokes, dampers or other means to reduce the effects of any explosion, as may be required. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 45.
46. (1) A safe means of access to a workplace shall be provided by a walkway, stairway or ladderway. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 46 (1).
(2) Where workers are required to work, operate, maintain or service equipment, a safe means of access shall be provided as prescribed in subsection (1). R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 46 (2).
(3) Every walkway and every working platform more than 1.5 metres above the ground shall be provided with,
(a) a handrail not less than 0.91 metre or more than 1.07 metres above the floor of the walkway or platform;
(b) a second rail placed at the mid-point between the top rail and the floor of the walkway or platform or have the space between the top rail and the floor closed by a screen; and
(c) toeboards which shall extend from the floor a height of not less than 100 millimetres. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 46 (3).
(4) The handrail required by clause (3) (a) shall be capable of withstanding a load applied in any direction to the top rail of at least 0.9 kilonewton. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 46 (4).
(5) Despite clauses (3) (b) and (c), toeboards and second rails are not required on a temporary walkway or working platform or on an underground drilling platform that is normally not more than three metres above the ground. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 46 (5).
(6) When a platform consists of wooden planks, the planks shall,
(a) be sound, unpainted and free of large knots;
(b) provide a minimum safety factor of three times the maximum load to which it is likely to be subjected; and
(c) be nailed or otherwise secured against movement. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 46 (6).
(7) Where a means of access to a workplace is inclined at more than twenty degrees and less than fifty degrees to the horizontal, a stairway or ladderway shall be provided. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 46 (7).
(8) Where a means of access to a workplace is inclined at more than fifty degrees to the horizontal, a ladder shall be provided. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 46 (8).
(9) A stairway shall,
(a) be at an angle not greater than fifty degrees to the horizontal;
(b) not have the rise or vertical distance between landings of a flight exceed 3.6 metres;
(c) have the treads and risers uniform in width and height respectively in any one flight; and
(d) be provided with handrails of adequate strength not less than 0.91 metre and not more than 1.07 metres in height above the treads of the stairs. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 46 (9).
47. (1) A ladder shall,
(a) be of strong construction;
(b) be free from broken or loose members or other faults;
(c) be installed and maintained so as to reduce to a minimum the hazard of a person falling therefrom;
(d) if made of wood,
(i) be of sound straight-grain lumber,
(ii) not be painted or otherwise treated in a manner to obscure the grain;
(e) have a distance between centres of the rungs not greater than 300 millimetres or less than 250 millimetres;
(f) have the spacing between rungs not vary more than fifteen millimetres in a ladderway;
(g) have not less than 100 millimetres clearance behind any rung from a wall or any timber or obstruction underneath the ladder; and
(h) project at least one metre above the landing or opening unless strong handholds are provided above the top of the ladder. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 47 (1).
(2) A fixed ladder shall be securely fastened in place. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 47 (2).
48. (1) Except in an underground mine, a ladderway at an angle steeper than seventy degrees to the horizontal shall be fixed in place and be provided with,
(a) platforms at intervals not greater than seven metres;
(b) a safety cage; or
(c) a protective device which when used will prevent a worker from falling. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 48 (1).
(2) Except in an underground mine, where platforms are used in conjunction with a ladderway,
(a) the ladders shall be offset;
(b) a platform shall be provided at each place where ladders are offset; and
(c) the platform shall be not less than 600 millimetres in width by 1.2 metres in length. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 48 (2).
49. A portable ladder shall,
(a) be equipped with non-slip feet or otherwise secured;
(b) where any activity in the vicinity may create a hazard to a person thereon, be protected at its base; and
(c) where the ladder has metal or metal-reinforced side rails, not be used near exposed and energized electrical circuits or equipment. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 49.
50. (1) Subject to subsection (2), a suitable ladderway shall be provided in every shaft. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 50 (1).
(2) An independently powered conveyance may be used in place of a ladderway. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 50 (2).
(3) Except for an auxiliary ladder used in shaft-sinking operations, a shaft ladder shall be inclined. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 11.
(4) During shaft-sinking operations, if a permanent ladder is not provided to the bottom, an auxiliary ladder that will reach from the permanent ladders to the bottom shall be provided in such convenient position that it may be promptly lowered to any point at which a worker is working. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 50 (4).
51. (1) Where a ladderway is installed in an underground mine or in a headframe used in conjunction with a shaft and the ladderway is inclined at more than seventy degrees from the horizontal,
(a) the ladderway shall be provided with substantial platforms at intervals not greater than seven metres;
(b) the ladders shall be offset at the platform;
(c) except for openings large enough to permit the passage of a worker, the platforms shall be fully closed; and
(d) if installed in a shaft manway, the ladders shall be placed over the openings of the platforms below. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 51 (1).
(2) Where the ladderway is inclined at less than seventy degrees to the horizontal, the ladders may be continuous and the provisions of clauses (1) (a) and (c) shall apply. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 51 (2).
(3) Where a ladderway is inclined at less than fifty degrees to the horizontal, no platform is required except at points of offset. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 51 (3).
(4) Where a ladderway is the only means of access for mine rescue purposes, the opening shall be large enough for such purpose. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 51 (4).
52. Wire ropes used for climbing purposes shall not be frayed or have projecting broken wires. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 52.
53. No person shall be, or be permitted to be, in a combined ladderway and hoistway compartment while a bucket or material is being,
(a) loaded or unloaded at the top; or
(b) hoisted or lowered. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 53.
54. (1) A walkway, stairway or ladderway shall be,
(a) maintained in a safe condition;
(b) free from obstructions;
(c) of sufficient size to ensure that crowding does not occur; and
(d) cleared of hazardous accumulation of material without undue delay. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 54 (1).
(2) Any opening in a floor or other surface which may be a hazard to a worker shall be,
(a) protected by a guardrail; or
(b) covered with securely fastened planks or other material capable of supporting any load to which it is likely to be subjected. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 54 (2).
55. No worker shall work in a location where another worker is working overhead unless measures are taken to protect the worker. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 55.
56. Where a gas, liquid or vapour is contained at a pressure other than atmospheric pressure, before any fastening of the container or system connected therewith,
(a) is loosened, any flow into or out of the container or system shall be effectively stopped; or
(b) is removed, the container or system shall be drained or bled so that the pressure in the container or system equals atmospheric pressure. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 56.
57. No liquids or solids shall be transferred from one location or container to another location or container by the application of air under pressure except where equipment specifically designed for the purpose is used. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 57.
58. Plastic pipe and fittings shall,
(a) meet CSA Standards B137.0-M 1981 and B137.3-M 1981 or, if installed after the 1st day of September, 1992, meet CSA Standards B137.0-M1986, “Definitions, General Requirements and Methods of Testing For Thermoplastic Pressure Piping” and B137.3-M1986, “Rigid Polyvinyl Chloride PVC Pipe For Pressure Applications”;
(b) be properly supported;
(c) not be used for the main supply or discharge of compressed air or water in mine shafts; and
(d) not be forced around bends that may unreasonably stress the pipe or its connections. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 58; O. Reg. 571/92, s. 5.
59. (1) All openings, sumps, vessels, bins, hoppers, elevated platforms or pits, other than grease pits, which constitute a hazard, shall be fenced or otherwise guarded. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 59 (1).
(2) Every power-operated door through which vehicles or pedestrians travel,
(a) shall be clearly distinguished from its surroundings; and
(b) shall be operated in accordance with the procedures adopted by the employer for its use. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 59 (2).
60. (1) Before a worker enters any silo, bin, hopper or other container or structure containing bulk material, all further supply of material thereto shall be stopped and any removal of material therefrom shall be prevented. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 60 (1).
(2) When working on top of bulk material in any silo, bin, hopper or other container or structure,
(a) a worker shall use a fall arrest system; and
(b) at least one other worker, who is a competent person, equipped with a suitable alarm shall be in constant attendance outside the silo, bin, hopper or other container or structure. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 60 (2).
61. (1) Stockpiles of unconsolidated material shall be,
(a) inspected for hazardous conditions regularly by a competent person; and
(b) made safe before a worker is allowed to work close to or on top of the stockpile. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 61 (1).
(2) Bulk or packaged material shall be piled or stacked in a manner to prevent accidental movement or collapse. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 61 (2).
(3) When a tunnel is used under a stockpile for the purpose of reclaiming material from the stockpile at least two exits shall be provided from the tunnel. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 61 (3).
62. A procedure shall be established and maintained at an underground mine to record every worker and other person who is underground in the mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 62.
62.1 (1) This section applies with respect to tasks at a workplace that are determined to be non-routine hazardous tasks jointly by the employer and the joint health and safety committee or the health and safety representative, if any, for the workplace. O. Reg. 60/94, s. 4.
(2) The employer and the joint health and safety committee or the health and safety representative shall jointly establish safe procedures for performing a non-routine hazardous task. O. Reg. 60/94, s. 4.
(3) The employer shall ensure that the safe procedures are set out in writing. O. Reg. 60/94, s. 4.
(4) The employer shall ensure that workers are informed that a task is a non-routine hazardous task and are informed about the procedures for performing it before beginning the task. O. Reg. 60/94, s. 4.
(5) A worker performing a non-routine hazardous task shall follow the established procedures. O. Reg. 60/94, s. 4.
63. (1) Every place where drilling and blasting is being carried on in an underground mine shall be examined by a supervisor during each work shift. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 63 (1).
(2) Every place other than where drilling and blasting is being carried on in an underground mine and where workers carry on work shall be examined by a supervisor at least once each work week. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 63 (2).
64. (1) Where in an underground mine a potential or actual danger to the health or safety of a worker has not been remedied or removed at the end of a work shift, a record in writing shall be made by the supervisor of the work shift and signed by the supervisor describing,
(a) the dangerous condition; and
(b) the state of corrective measures taken. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 64 (1).
(2) The record required by subsection (1) shall be read and countersigned by the supervisor of the next work shift before a worker on such shift does any work in the area of the dangerous condition and the workers on such shift who may be affected by the dangerous condition shall be advised of,
(a) the dangerous condition;
(b) the state of corrective measures undertaken; and
(c) the work required to be done to remove or remedy the dangerous condition. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 64 (2).
65. (1) An employer in an underground mine, in consultation with the joint health and safety committee, if any, for the mine, shall develop a written program to provide for the timely communication of information between workers and supervisors in the mine respecting ground stability, ground movement, falls of ground, ground monitoring equipment and emergencies. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 65 (1).
(2) The communications program shall set out,
(a) means and procedures for communicating information;
(b) the kind of information to be communicated; and
(c) the actions to be taken by supervisors and workers with respect to information that is communicated to them. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 65 (2).
66. (1) Before work is begun in a workplace in an underground mine, the ground conditions of the workplace shall be examined for dangers and hazards and, if required, made safe. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 66 (1).
(2) Revoked: O. Reg. 571/92, s. 6.
67. (1) An employer shall prepare written procedures to be used at an underground mine concerning,
(a) activities relating to the installation of ground support at the mine; and
(b) activities that require a worker to be exposed to unsupported ground before the ground support is installed. O. Reg. 571/92, s. 7.
(2) The procedures shall state the methods for undertaking the activities and for preventing workers’ exposure to unsafe ground conditions. O. Reg. 571/92, s. 7.
(3) The employer shall consult with the joint health and safety committee or, if no committee exists, with the health and safety representative in preparing the procedures. O. Reg. 571/92, s. 7.
67.1 During scaling procedures in a workplace in an underground mine, no other work shall be carried on that hinders the scaling procedures. O. Reg. 571/92, s. 7.
68. Where a workplace, travelway, manway or other area of an underground mine is under repair or where there is a danger or hazard to a worker,
(a) the workplace, travelway, manway or other area shall be closed by barricades, fencing or other suitable means; and
(b) warning signs shall be posted indicating that it is under repair or indicating the nature of the danger or hazard. O. Reg. 486/99, s. 2.
69. (1) Illumination shall be provided in an underground mine adequate for a worker to visually assess ground conditions at the worker’s workplace. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 69 (1).
(2) Where a cap lamp is used to provide the illumination as required by subsection (1), it shall be capable of providing a peak illuminance of at least 1500 lux at 1.2 metres from the light source. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 69 (2).
(3) An employer in an underground mine who supplies cap lamps to workers shall develop a procedure for assessing and maintaining cap lamps and a copy of the procedure shall be available at the mine site for review by the joint health and safety committee or health and safety representative, if any, for the mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 69 (3); O. Reg. 272/97, s. 12.
(4) A record of cap lamp maintenance test results shall be kept. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 69 (4).
(5) Despite subsection (2), if the ground to be assessed is at a distance that is greater than the effective range of a cap lamp, the employer shall supply, and the worker shall use, auxiliary lighting that will provide the illumination required by subsection (1). R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 69 (5).
70. Revoked: O. Reg. 272/97, s. 13.
71. (1) Devices to protect operators from falling objects shall be installed on every motorized trackless vehicle used,
(a) in a new underground mine that is developed after the 1st day of June, 1988; or
(b) in an area in an underground mine with respect to which the Director has given the owner a written opinion that local ground stability presents a hazard to the operators. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 71 (1); O. Reg. 272/97, s. 14.
(2) Devices required by subsection (1) shall consist of overhead protective devices built to withstand a minimum of 11.5 kilojoules of energy when tested in accordance with the Society of Automotive Engineers’ Standard SAE J231 “Minimum Performance Criteria for Falling Object Protective Structures (FOPS)” and the devices shall be maintained in good condition. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 71 (2).
(3) Clause (1) (a) does not apply to a motorized trackless vehicle while it is being used in an area in an underground mine that is made safe by scaling, timbering or rockbolting or by measures that provide safety equal to or better than scaling, timbering or rockbolting. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 71 (3).
72. A record of the occurrence of a rockburst or of an uncontrolled fall of ground at an underground mine shall be kept in writing setting out,
(a) the time, location and extent of the occurrence;
(b) injury, if any, caused to a worker thereby; and
(c) any other relevant information, including the records of any monitoring instruments or devices before the occurrence. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 72.
73. (1) An employer shall develop a quality control program for work in an underground mine to ensure that the ground support systems that are specified in the mine design are properly installed and remain effective while in use. O. Reg. 571/92, s. 8.
(2) The employer shall maintain a record of the tests that are required under the quality control program. O. Reg. 571/92, s. 8.
(3) If requested, the employer shall provide a copy of the quality control program and of the record of tests under the program to the joint health and safety committee or, if no committee exists, to the health and safety representative. O. Reg. 571/92, s. 8.
74. A shaft, raise or other opening in an underground mine shall be securely fenced, covered or otherwise guarded. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 74.
75. (1) A shaft shall be securely cased, lined or timbered. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 75 (1).
(2) During shaft-sinking operations, the casing, lining or timbering shall be maintained within a distance of the bottom not exceeding twenty metres. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 75 (2).
76. (1) Except during shaft-sinking operations, a shaft compartment used for the handling of material shall be enclosed at the collar and at all levels, except the side on which material is loaded on or off the shaft conveyance. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 76 (1).
(2) The enclosure referred to in subsection (1) shall,
(a) be made of substantial materials;
(b) extend above the collar and each level a distance of not less than the height of the shaft conveyance plus two metres but need not exceed seven metres;
(c) extend below the collar and each level a distance of not less than two metres; and
(d) conform to the size of the shaft conveyance, allowing for necessary operating clearance. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 76 (2).
77. (1) Subject to subsection (2), the manway in a shaft shall be separated from the hoisting or counterweight compartments by a partition which complies with subsection 76 (2). R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 77 (1).
(2) Between levels, the partition may consist of metal of suitable weight and mesh to prevent,
(a) a falling object from entering the manway; or
(b) the intrusion of an object from the manway into the hoisting compartment. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 77 (2).
(3) A safe passageway and standing room for a person outside the shaft shall be provided at all workings opening into a shaft and the manway shall be directly connected with such openings. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 77 (3).
78. (1) Except when the hoisting compartment at a shaft station is securely closed off, a substantial gate shall be installed. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 78 (1).
(2) The gate required by subsection (1) shall,
(a) be kept closed except when the shaft conveyance is being loaded or unloaded at the station;
(b) have a minimum of clearance beneath it; and
(c) be reinforced against impact of,
(i) a locomotive, train or car when rail tracks lead to the compartment, or
(ii) a motor vehicle when motor vehicles are used in the vicinity of the shaft. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 78 (2).
79. Where a counterweight is used in a shaft, the counterweight compartment shall be enclosed except when the counterweight travels on guides. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 79.
80. During shaft-sinking operations, no work shall be done in any place in a shaft while a worker is working in another part of the shaft below such place unless the worker in the lower position is protected from the danger of falling material by a securely constructed covering extending over a sufficient portion of the shaft to afford complete protection. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 80.
81. Hooks used in connection with the suspension of any equipment or material in a shaft or raise or over a worker shall be choked or equipped with a safety latch. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 81.
82. When work or an examination is taking place in the compartment of a shaft or in that part of the headframe used in conjunction therewith,
(a) hoisting operations in that compartment, except for those necessary to perform the work or examination, shall be suspended;
(b) protection from accidental contact with any moving shaft conveyance or counterweight, or falling objects shall be provided for a worker performing the work or examination; and
(c) the power supply to all conveyor belts, gates and other devices that are located above a worker and that could cause material to flow into the shaft shall be locked and tagged in the safe position and the gates shall be mechanically secured in the closed position. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 82; O. Reg. 571/92, s. 9.
82.1 Before the commencement of work or of an examination below a loading pocket in a shaft, a competent person who is authorized by the employer to proceed, and who proceeds, below the loading pocket shall inspect it to ensure that the work or examination can proceed safely. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 2.
83. (1) This section applies when a raise is being developed and there are workers in the raise. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 15.
(2) A raise that is inclined at an angle greater than 50 degrees and is longer than 10 metres from the collar to the face shall be divided into at least two compartments, one of which shall be a ladderway. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 15.
(3) Subsection (2) does not apply where a raise climber is used. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 15.
(4) The ladderway shall be maintained within five metres of the face of the raise. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 15.
84. (1) If a worker may be endangered by the withdrawal, collapse, shifting or movement of bulk material such as rock, ore or other material in a stope, pass or chute or in a storage area, the employer shall ensure that written procedures for the precautions to be taken before, during and after removal of the material are established and followed. O. Reg. 291/02, s. 3.
(2) The written procedures required by subsection (1) shall address the following matters:
1. The conditions under which workers are required to wear a fall arrest system.
2. The communication of hazards to all persons who may be at risk.
3. The identification of those locations that are not safe for workers to enter.
4. The need to post warning signs that indicate the nature of the danger or hazard and the need to erect barriers to prevent inadvertent access to the area.
5. Any additional protection to be provided to workers required to enter or work in the area. O. Reg. 291/02, s. 3.
(3) No worker shall be positioned so that when the worker is pulling a chute his or her access to an exit from the area may be blocked by an uncontrolled run of material, water or slime. O. Reg. 291/02, s. 3.
(4) A mechanical locking device shall be installed on overcut power operated chute gates, so that the gate may be locked in the open or closed position. O. Reg. 291/02, s. 3.
(5) A power-operated safety guard or gate shall be designed and installed to minimize hazards when the power fails. O. Reg. 291/02, s. 3.
85. Where the entrance or exit to a workplace in an underground mine cannot be used at all times, a second means of entrance or exit shall be provided. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 85.
86. A diamond drill hole in an underground mine shall at the time that drilling is discontinued or an intersection with the drill hole is made,
(a) be clearly marked at the collar and any points of intersection or breakthrough, with a single capital letter “H” that is,
(i) located within one metre of the collar or intersection, and
(ii) at least 300 millimetres by 300 millimetres in size;
(b) have the approach to the collar or to any intersection or breakthrough securely closed off or guarded,
(i) when mining is in progress towards the hole, and
(ii) when blasting is to be done within five metres of an intersection of the hole; and
(c) be shown on the plans of the mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 86; O. Reg. 68/96, s. 2.
87. (1) A workplace in an underground mine shall,
(a) be kept free from accumulations or flow of water which might endanger a worker in the area; and
(b) have a drainage system to conduct excess water to a pumping system capable of pumping the water to surface for disposal. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 87 (1).
(2) Where accumulations of water are likely to be present,
(a) a borehole shall be drilled at least six metres ahead of the working face to protect against a sudden breakthrough of the water; and
(b) precautions shall be taken to control the flow of water. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 87 (2).
(3) A positive displacement water pump shall be equipped with a relief valve or system. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 87 (3).
(4) Precautions shall be taken to guard against an accumulation of water in a chute or raise where the material in the chute or raise may block drainage. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 87 (4).
88. (1) Where earth, clay, sand or gravel is being removed from a surface mine by means of powered equipment,
(a) the working face shall be sloped at the angle of repose; or
(b) the vertical height of the working face shall not be more than 1.5 metres above the maximum reach of the equipment. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 88 (1).
(2) Where earth, clay, sand or gravel is being removed from a surface mine by means other than powered equipment,
(a) the working face shall be sloped at its angle of repose; or
(b) the vertical height of the working face shall not be more than three metres. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 88 (2).
(3) No undercutting of the working face shall be permitted or done. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 88 (3).
(4) Except when mining operations are being actively pursued, benches and walls shall be sloped to less than the angle of repose. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 88 (4).
89. Where metallic or non-metallic rock is being removed from a surface mine,
(a) the vertical height of the working face shall not be more than twenty-five metres; and
(b) except where a tunnelling method is used to remove the rock, no undercutting of the working face shall be permitted or done. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 89.
90. Every surface mine,
(a) that is dangerous because of its condition or depth shall be securely fenced or otherwise guarded against inadvertent access; and
(b) shall have a safe travelway leading from the working level to the surface. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 90.
91. (1) Trees and other vegetation and unconsolidated materials such as earth, clay, sand or gravel and rocks within two metres of the rim of a surface mine and likely to endanger any person shall be removed. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 91 (1).
(2) Overburden beyond two metres of the rim of a surface mine shall be sloped to an angle less than its natural angle of repose. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 91 (2).
92. (1) Subject to subsection (2),
(a) where earth, clay, sand or gravel is being removed from a surface mine no mining operations shall be carried on within a distance from the property boundary of half the total depth of the surface mine and earth, clay, sand or gravel that sloughs from within this distance shall not be removed; and
(b) where metallic or non-metallic rock is being removed from a surface mine, no mining operations shall be carried on within a distance of six metres from the property boundary. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 92 (1).
(2) Adjoining owners may, by agreement in writing, waive the provisions of subsection (1). R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 92 (2).
93. (1) In a surface mine where metallic or non-metallic rock is being removed, no work shall be carried on,
(a) near a working face following a blast; or
(b) near a face on which mining operations have been discontinued for a period of more than seven days,
until a supervisor examines the face for any potential or actual hazard to the health or safety of a worker. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 93 (1).
(2) When a surface mine is worked in benches, loose rock on berms or benches shall not be permitted to accumulate so that a worker on a lower bench is endangered. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 93 (2).
94. A worker barring loose rock, or scaling or cleaning on a face of a surface mine shall use and wear a fall-arrest system. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 94.
95. (1) An employer shall provide personal protective equipment, shield, appliance or other device where a worker is exposed to the hazard of being burned by molten materials. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 95 (1).
(2) An employer shall require a worker to use or wear personal protective equipment, shield, appliance or other device provided by the employer where the worker is exposed to the hazard of being burned by molten material. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 95 (2).
96. (1) Precautions shall be taken to prevent contact between molten material and damp surfaces, rusty surfaces, cold surfaces, moisture, water, or other substance where such contact may cause an explosion, and where such explosion may endanger a worker. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 96 (1).
(2) Precautions shall be taken to prevent spillage of molten material from a ladle, slag pot or similar vessel where such spillage may endanger a worker. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 96 (2).
(3) A ladle, slag pot or similar vessel shall be examined immediately before use and, if found to be defective or contaminated by a substance which may cause an explosion, shall not be used for molten material. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 96 (3).
97. (1) Where a worker is required to go above the casting floor level of an operating blast furnace, the worker shall notify a supervisor. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 97 (1).
(2) When a worker is above the casting floor level of an operating blast furnace, a second competent worker shall,
(a) be in attendance to render assistance to the worker; and
(b) remain in a safe place until such assistance is required. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 97 (2).
98. A suitable working platform shall be provided on the bustle pipe of a blast furnace. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 98.
99. A system of communication shall be provided and maintained between all dangerous workplaces of a blast furnace, including the blast furnace top structure and,
(a) the cast house;
(b) the skip operator’s room; and
(c) every other place where workers are continuously on duty. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 99.
100. A ladderway or stairway shall be provided from the foundation to the top of a blast furnace. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 100.
101. When a blast furnace is hanging, no worker or other person shall be, or be permitted to be, above the level of the casting floor. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 101.
102. Where a major repair is to be carried out at the top structure of a blast furnace that requires the blast furnace to be shut down,
(a) the blast furnace area shall be cleared of workers other than those carrying out the repair; and
(b) the major repair area shall be tested for gases likely to endanger the health and safety of a worker before the repair is commenced and during the carrying out of the repair. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 102.
103. (1) When in use, a motor vehicle running on rails, other than a standard gauge railroad, shall,
(a) be in safe working condition;
(b) have brakes that will stop and hold the vehicle or cars under full load condition;
(c) have headlights;
(d) have an audible warning system that shall be sounded,
(i) where a worker may be endangered by the movement of the vehicle and cars, if any, or
(ii) whenever the vehicle and cars, if any, are about to move underground or in an enclosed building;
(e) be provided, where possible, with a fixed seat for the operator;
(f) have a guard that will provide protection for the operator from collision or other impact;
(g) when manually operated, be operated only when the operator is in the proper position at the controls;
(h) when operated by remote control or by an automated system, be so arranged that in the event of failure of part of the control or system, the vehicle and cars, if any, will be brought to a stop immediately;
(i) when left unattended, have,
(i) the control placed in the parking position, and
(ii) the brake fully applied; and
(j) when electrically powered by storage battery or from a trolley wire, have control levers so arranged that they cannot be removed accidentally when the power is on. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 103 (1).
(2) Except for clauses (1) (a) and (g), this section does not apply to a motor vehicle propelled by compressed air. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 103 (2).
104. Except when used in areas where natural or artificial lighting provides good visibility, a train shall have a tail light on the last car. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 104.
105. (1) When in use, a motor vehicle, other than a motor vehicle running on rails, shall,
(a) be in safe working condition;
(b) have brakes which will stop and hold the vehicle under full load conditions on all operating grades;
(c) subject to subsection (2), have headlights and tail lights;
(d) where,
(i) equipped with power-assisted steering, and
(ii) operated on surface,
have a system such that in the event of a failure of the power-assistance element of the system, the vehicle can be held on course by the steering until the vehicle is stopped;
(e) except for purposes of training or testing, be operated only by a competent operator;
(f) be provided, where practical, with a fixed seat for the operator;
(g) when manually operated, be operated only when the operator is in a proper position at the controls;
(h) where operated by remote control or by an automated system, be so arranged that in the event of the failure of part of the control or system, the vehicle will be brought to a stop;
(i) when left unattended, have,
(i) the control placed in the parking position, and
(ii) the brake fully applied;
(j) except when used in an underground mine, have lights or reflectors that show the width of the vehicle to a person in the path of its direction of travel;
(k) where the motor vehicle is to be operated in reverse and the operator or another person may be endangered thereby, be operated only when another worker is stationed to direct and warn the operator of any hazard to himself or another person; and
(l) be equipped with a type BC fire extinguisher. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 105 (1); O. Reg. 31/04, s. 4 (1).
(2) In areas where natural or artificial lighting is adequate to enable the operator to have a clear view of the areas and persons, a motor vehicle may be operated without headlights or tail lights. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 105 (2).
(3) Where the view of the operator of a motor vehicle in the direction of its travel is limited,
(a) the vehicle shall be equipped with an audible or visible alarm that will warn a worker who may be endangered by the movement of the vehicle; and
(b) the alarm shall be activated before the vehicle is put in motion. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 4 (2).
(4) Except when the motor vehicle is used in an underground mine, a rear view mirror shall be installed in the motor vehicle where the view to the rear of the operator is limited. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 105 (4).
(5) The windshield and windows of the cab of a motor vehicle shall consist of safety glass and be maintained so as to provide unobstructed vision. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 105 (5).
(6) Where motor vehicles that restrict the view of the operator because of size or design are used, procedures to control and govern the movement of such vehicles, other vehicles and pedestrians shall be established. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 105 (6).
(7) A procedure for the testing, maintenance and inspection of each motor vehicle shall be adopted and the procedure shall,
(a) schedule the testing of brakes, steering, lighting and other safety components prior to initial use of the motor vehicle for the shift;
(b) schedule the motor vehicle for routine inspections and maintenance, taking into consideration the recommendations of the manufacturer and the conditions of use;
(c) itemize the tests to be carried out following maintenance work and before first use of the motor vehicle;
(d) provide a record of the testing, maintenance, inspection and testing that has been carried out; and
(e) provide for the testing, maintenance and inspections to be performed by competent persons. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 105 (7).
(8) Except for clauses (1) (a), (e) and (g), this section does not apply to a motor vehicle propelled by compressed air. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 105 (8).
106. (1) Where a motor vehicle is operated on a grade or ramp, traffic control procedures shall be established including provision for the control of emergency situations. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 106 (1).
(2) Where a motor vehicle is disabled or parked in the travelled portion of a roadway, a warning to approaching traffic shall be provided by,
(a) flashing lights;
(b) flares;
(c) reflectors;
(d) lamps; or
(e) a worker suitably equipped to be readily seen, who directs traffic approaching the area. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 106 (2).
(3) In the operation of a motor vehicle in an underground mine,
(a) the maximum load to be carried;
(b) the maximum speed; and
(c) the gear selection to be used,
on a grade or ramp shall be established and made known to the operator by the supervisor in charge of the mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 106 (3).
(4) Before ascending or descending a main access ramp in an underground mine, the operator of a motor vehicle shall,
(a) fully engage the forward-reverse lever;
(b) select the proper gear; and
(c) test the service and emergency brakes. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 106 (4).
107. (1) A motor vehicle in a mine shall be equipped with wheel chocks that comply with Society of Automotive Engineers Standard SAE J348 JUN90 “Wheel Chocks”. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 5.
(2) The wheel chocks shall be used to block movement whenever the vehicle,
(a) is left unattended on a slope; or
(b) is being maintained or repaired. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 5.
(3) Despite subsections (1) and (2), an alternative means of blocking the movement of a motor vehicle in the circumstances described in subsection (2) may be used if the alternative means is developed by the employer in consultation with the joint health and safety committee or the health and safety representative, if any, for the workplace. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 5.
(4) Whenever work is to be performed on an energized rubber tire with a multi-piece wheel, a device shall be used to prevent injury to a worker. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 5.
(5) The device mentioned in subsection (4) is not required when topping off the air pressure in a tire. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 5.
108. (1) When the controls are left unattended,
(a) the bucket of a front-end loader, backhoe or other excavating machine;
(b) the blade of a bulldozer; or
(c) the load of a fork-lift truck, mobile crane or other hoisting machine,
shall be in the lowered position or adequately supported. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 108 (1).
(2) Any part of a motor vehicle or other equipment, including the blade or bucket or dump box of a truck, the lowering of which may endanger a worker, shall be blocked so as to prevent its lowering accidentally. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 108 (2).
(3) A crane or other hoisting machine shall be operated in such a way that no part of its load will pass over a person, other than a worker receiving the load and a worker receiving a load shall, so far as is practicable, position himself or herself so that the load does not pass over him or her. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 108 (3).
(4) A shovel, backhoe or similar excavating machine shall be operated in such a way that no part of its load will pass over a person. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 108 (4).
(5) An operator who may be endangered during the loading of a vehicle shall vacate the vehicle. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 108 (5).
109. (1) A rail track switch in which a person’s foot may become trapped shall have guards at the frog and switch point to effectively protect against the hazard. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 109 (1).
(2) Rail tracks in use shall be in good working condition. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 109 (2).
110. (1) Vehicles being used for transporting workers shall,
(a) be provided with suitable seats or other facilities;
(b) be limited to a maximum number of passengers, which number shall be posted in or on the vehicle; and
(c) when enclosed, be equipped with an emergency exit. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 110 (1).
(2) Whenever the face of an inclined tunnel in a mine exceeds a vertical depth of 100 metres without intermediate access to the tunnel from a shaft with hoisting facilities for people, a vehicle shall be provided to transport workers down and up the tunnel. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 110 (2).
(3) Except for training purposes, only those workers authorized and required to handle the load shall ride on a vehicle that is transporting,
(a) explosives;
(b) steel or timber; or
(c) heavy equipment. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 110 (3).
(4) The load on a vehicle shall be adequately secured. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 110 (4).
(5) A worker may carry personal hand tools or equipment on a vehicle when,
(a) the vehicle is not crowded;
(b) the tools and equipment are properly protected by guards; or
(c) the tools or equipment are isolated in separate containers. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 110 (5).
(6) The maximum speed and the maximum load of a vehicle transporting workers or a service vehicle shall be posted on the vehicle in a conspicuous location. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 110 (6).
111. (1) Subject to subsections (2) and (3), a haulageway for a motor vehicle running on rails in an underground mine shall have,
(a) a walkway on one side so that there is at least 0.6 metres clearance between the sides of the haulageway and the motor vehicle running on rails or the train; or
(b) safety stations as prescribed in section 114 at intervals not exceeding thirty metres. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 111 (1).
(2) Despite subsection (1), a haulageway that is used by a motor vehicle running on rails that travels more than 12 kilometres per hour shall have a walkway on one side of at least 1.2 metres between the side of the haulageway and the motor vehicle and pedestrian traffic shall be restricted to designated periods during which no motor vehicle running on rails shall be used in the haulageway. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 111 (2).
(3) Where pedestrian traffic is permitted in a haulageway to which subsection (2) applies and the walkway is less than two metres in width, safety stations, as prescribed in section 114, shall be provided at intervals not exceeding thirty metres. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 111 (3).
(4) Subsection (1) does not apply to any haulageway that was driven prior to the 1st day of October, 1979 if the haulageway complies with section 245 of The Mining Act, being chapter 274 of the Revised Statutes of Ontario, 1970, as it read on the 30th day of September, 1979. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 111 (4).
112. A haulageway used by motor vehicles, other than motor vehicles running on rails, shall,
(a) except where pedestrian traffic is effectively prevented, be at least 1.5 metres wider than the maximum width of a motor vehicle using the haulageway; and
(b) where it is regularly used by pedestrians and it is less than two metres wider than the maximum width of a motor vehicle using the haulageway, have safety stations as prescribed in section 114 at intervals not exceeding thirty metres. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 112.
113. Except in an underground mine with a low clearance roof in which equipment designed to be operated herein is used, a haulageway used by a motor vehicle shall have sufficient clearance below the roof, support or overhead installations to enable the operator of a motor vehicle to sit erect at all times. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 113.
114. (1) A safety station shall consist of a recess in the wall of a haulageway that shall be,
(a) at least,
(i) 0.6 metre in depth, in addition to any existing clearance between the vehicle and the wall,
(ii) two metres in height, and
(iii) 1.5 metres in length;
(b) plainly marked; and
(c) clean and free of obstruction. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 114 (1).
(2) Clause (1) (a) does not apply to a safety station in a haulageway that was driven before the 1st day of October, 1979, if the safety station complies with section 245 of The Mining Act, being chapter 274 of the Revised Statutes of Ontario, 1970, as it read on the 30th day of September, 1979. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 114 (2).
115. (1) Subject to subsection (2), where the view of rail traffic at railway tracks on surface is obstructed in one or both directions, guardrails shall be placed at the approach to the tracks. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 115 (1).
(2) Subsection (1) does not apply where,
(a) restricted clearance makes guardrails impracticable; and
(b) a warning signal which automatically functions at the approach of a locomotive or train gives a warning signal that is both audible and visible; or
(c) a worker is guarding the approach. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 115 (2).
116. (1) Haulage roads on surface shall be designed, constructed and maintained to,
(a) minimize hazards from the slipping or skidding of vehicles;
(b) enable vehicles to pass each other safely; and
(c) avoid steep grades wherever practical. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 116 (1).
(2) The open side of a ramp haulage road in a surface mine shall be provided with a suitable protective barrier. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 116 (2).
(3) Every haulage road on surface shall be kept in good repair. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 116 (3); O. Reg. 693/92, s. 1.
117. (1) Where, on surface at a mine or mining plant, the clearance between the sides of a train or motor vehicle and the wall of a building or other structure is less than 500 millimetres, the location shall be plainly marked showing the danger. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 117 (1).
(2) Where the operator may be exposed to overhead hazards on surface at a mine or mining plant, a cab, screen or other adequate overhead protection shall be provided on,
(a) a power-driven crane, shovel or similar machine;
(b) a fork-lift truck; and
(c) a front-end loader or other excavating machine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 117 (2).
118. (1) When material is dumped from a vehicle that is occupied by a person, the dump point shall include features designed to prevent the vehicle from going over a bank, over a bench or into a raise or other open hole. O. Reg. 291/02, s. 4.
(2) In an underground mine, the features referred to in subsection (1) shall not include the use of a ridge of material. O. Reg. 291/02, s. 4.
119. (1) The brakes on motor vehicles operating on ramps shall consist of,
(a) a service braking system;
(b) an emergency stopping system; and
(c) a parking brake system. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 119 (1); O. Reg. 693/92, s. 2.
(2) Each such system shall be capable of being,
(a) tested independently; and
(b) readily applied by a worker seated in the driver’s seat. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 119 (2).
(3) A service braking system may consist of a hydraulic pump motor drive system. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 119 (3).
(4) The capacity of retarders shall not be considered in determining the capacity of the braking system prescribed in subsection (1). R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 119 (4).
(5) The service braking system and the emergency stopping system shall be capable of safely stopping a vehicle while free wheeling under its,
(a) maximum authorized load; and
(b) maximum authorized speed,
while proceeding on maximum grade in its area of operation. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 119 (5).
(6) The parking brake system shall be capable of holding the vehicle stationary under conditions of its maximum authorized load when on the maximum grade in its area of operation. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 119 (6).
(7) Revoked: O. Reg. 272/97, s. 17.
(8) Where components that apply the service brakes and the emergency brakes are common, the components shall be arranged so that a failure in a common component does not reduce the capability of one of the systems to stop the vehicle safely. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 119 (8).
(9) Before being put into service, tests shall be conducted on a newly acquired vehicle for the proper operation of the,
(a) service brakes;
(b) emergency brakes;
(c) parking brakes;
(d) steering;
(e) warning devices; and
(f) lighting. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 119 (9).
(10) A record of such tests shall be signed by a competent worker and kept for each such vehicle. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 119 (10).
(11) Braking systems on rubber-tired, self-propelled underground vehicles first used in an underground mine after the 1st day of September, 1992 shall meet the requirements of CAN/CSA-M424.3-M90, “Braking Performance — Rubber-Tired, Self-Propelled Underground Mining Machines”. O. Reg. 571/92, s. 11.
119.1 (1) This section applies with respect to motor vehicles first put into service by the employer on or after August 16, 1997 that are equipped with a stored energy braking system using a pneumatic system or a full hydraulic system to apply the service brakes. However, this section does not apply with respect to motor vehicles operating on rails. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 18.
(2) For the purposes of this section, a critical level of pressure is the level of pressure in a vehicle’s stored energy braking system, torque converter or transmission below which the vehicle manufacturer has determined that the vehicle is unsafe to operate. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 18.
(3) A motor vehicle operating on the surface must be equipped with a device that warns the operator that the vehicle’s stored energy braking system is approaching the critical level of pressure, so that the vehicle can be safely stopped. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 18.
(4) A motor vehicle operating underground must be equipped with a device that automatically applies the emergency stopping system and stops the vehicle before the vehicle’s stored energy braking system reaches the critical level of pressure. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 18.
(5) A motor vehicle operating underground that is equipped with a torque converter must be equipped with a device that automatically applies the emergency stopping system and stops the vehicle before the torque converter pressure or the transmission pressure reaches the critical level of pressure. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 18.
(6) A motor vehicle operating underground must be equipped with a device that warns the operator that the emergency stopping system is about to be applied. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 18.
120. (1) A service garage, service bay or fuelling station in an underground mine shall,
(a) be designed and protected to prevent inadvertent entry of an uncontrolled motor vehicle;
(b) be located so that in the event of a fire or explosion in the garage, bay or station there will be a minimum effect on working areas of the mine or on underground installations including shafts, magazines, refuge stations, transformer installations and other installations;
(c) have a concrete floor without service pits in the floor; and
(d) be equipped with a system to contain spills of oil and grease. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 6.
(2) A service garage or service bay shall be of sufficient size to,
(a) accommodate the longest and widest vehicle that will use the garage or bay; and
(b) provide clearance around the vehicles being serviced to permit the safe performance of all work in the garage or bay. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 6.
(2.1) A vehicle shall be serviced where practicable at a service garage or a service bay. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 6.
(2.2) Only one vehicle may be serviced at a service bay at any one time. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 6.
(3) A fuelling station shall be established before a heading has advanced 250 metres from the ramp or shaft unless vehicles can be fuelled at another fuelling station. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 120 (3).
(4) A fuelling station shall be separate from a service garage. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 120 (4).
(5) A vehicle shall be fuelled where practicable at a fuelling station. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 120 (5).
(6) Where a mobile fuelling supply tank is used the tank shall be clearly labelled with “No Smoking” signs. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 120 (6).
(7) Any spillage of oil or fuel shall be taken up at once, deposited in a fireproof receptacle and removed from the mine without undue delay. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 120 (7).
(8) All fuel handling, transfer, storage and dispensing systems in an underground mine shall be designed according to good engineering standards and subjected to a fire safety hazard review before first use. O. Reg. 291/02, s. 5.
(9) The employer, in consultation with the joint health and safety committee or the health and safety representative, if any, shall develop appropriate safeguards and procedures for the safe handling, transfer, storage and dispensing of fuel in an underground mine. O. Reg. 291/02, s. 5.
121. Where an explosive is used in an underground mine,
(a) it shall be of Fume Class 1 rating as established by the Explosives Branch of the Department of Energy, Mines and Resources, (Canada); or
(b) if other than of Fume Class 1 rating, a procedure shall be prepared and adopted by the supervisor in charge of the mine, to ensure that no worker is exposed to fumes that endanger his health or safety. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 121.
122. (1) Explosives stored or kept at a mine or mining plant shall be used only for authorized purposes and if not so used, returned to the supplier of the explosives. O. Reg. 236/99, s. 4.
(2) Smoking shall not be permitted and no fire or naked flame shall be taken,
(a) within a magazine; or
(b) within eight metres of any explosive. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 122 (2).
(3) Any careless act of placing or handling explosive shall be,
(a) reported forthwith to a supervisor in charge of the workplace;
(b) investigated by the supervisor; and
(c) reported forthwith by the supervisor to an inspector. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 122 (3).
(4) No explosive shall be used to blast or break up ore, salamander or other material where, by reason of its heated condition, there is any danger or risk of premature explosion of the charge. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 122 (4).
(5) When operations at a mine are discontinued or suspended for more than three months, all explosives shall be disposed of in a safe manner. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 19.
123. (1) Explosives kept or stored on the surface shall be kept or stored in compliance with the Explosives Act (Canada) and the regulations under that Act. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 20.
(2) If a magazine is required, it shall be,
(a) constructed in conformity with the Magazine Standards for Blasting Explosives and Detonators published by the Explosives Branch of the Department of Natural Resources (Canada);
(b) located in conformity with the User Manual, Quantity Distance Tables published by the Explosives Branch of the Department of Natural Resources (Canada); and
(c) protected by a fire break. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 20.
(3) A copy of the notification given to an inspector under subsection (4) shall be posted in the magazine. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 20.
(4) An operator of a surface magazine or a mine using explosives shall give written notice to an inspector and the joint health and safety committee or health and safety representative, if any,
(a) before a magazine is or explosives are first used; and
(b) annually after the magazine is or explosives are first used. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 20.
(5) The notice shall contain the following information:
1. The address of the operator.
2. Specific location of any surface magazine or a statement that the explosives are delivered directly to the underground workings.
3. The Ministry’s Premise Project Identification Number.
4. The nature and quantity of explosives to be stored or delivered.
5. A statement that any surface magazine conforms to this Regulation and to the Explosives Act (Canada) and the regulations under that Act. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 20.
124. Revoked: O. Reg. 272/97, s. 20.
125. (1) Explosives in an underground mine shall be kept or stored in a magazine but where less than 160 kilograms of explosives are kept or stored in the underground mine they may be kept or stored in suitable storage containers at locations removed from drilling and blasting operations. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 125 (1).
(2) If the necessary supply of explosives exceeds five working days, the explosives shall be kept or stored in a magazine. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 21.
(3) Suitable plans and specifications showing the design and location of magazines and detonator storage areas and the maximum quantities of explosives stored shall be kept readily available at the mine site. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 21.
(4) Revoked: O. Reg. 272/97, s. 21.
(5) Despite subsection (1), where long hole blasts or similar blasting operations are being carried on in an underground mine, such quantities of explosives as can be loaded in a twenty-four hour period together with an amount that may be necessary to maintain that supply may be kept in a suitable storage place that is not a magazine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 125 (5).
126. (1) A magazine, storage container or explosive storage area referred to in subsection 125 (5) that is in an underground mine shall be,
(a) located at least 60 metres from,
(i) the main access into or from a mine,
(ii) key mechanical and electrical installations that remain in service during a mine emergency,
(iii) areas of refuge or other areas where workers may congregate, and
(iv) storage areas for fuels or other potential sources of fire;
(b) located and designed to protect explosives from vehicle impact or vehicle fires; and
(c) conspicuously marked by a “DANGER EXPLOSIVES” sign. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 22.
(2) Subclause (1) (a) (i) does not apply during the initial stages of exploration and development of a mine. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 22.
127. (1) A magazine in an underground mine shall be under the control and direction of a competent person. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 23.
(2) A weekly inspection of a magazine in an underground mine shall be carried out by a competent person who shall report in writing to a supervisor,
(a) as to the condition of the magazine and the explosives; and
(b) as to the quantities of explosives stored therein. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 127 (2).
(3) Reports required by subsection (2) shall be kept for a period of at least six months. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 127 (3).
128. (1) Every magazine and every storage container shall be kept clean, dry and free from grit at all times. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 128 (1).
(2) The floors and shelves of a magazine where nitroglycerine explosives are kept shall be treated with a neutralizing agent to remove any traces of nitroglycerine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 128 (2).
(3) When explosive is issued or removed from a magazine, the explosive longest in the magazine, if not defective, shall be used first. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 128 (3).
(4) Explosive that is damaged shall be disposed of in accordance with the following rules:
1. The employer shall establish, in consultation with the joint health and safety committee or the health and safety representative, if any, a procedure for safely disposing of damaged explosive.
2. The procedure shall state,
i. what maximum accumulation of damaged explosive is permitted in a magazine or storage place before the damaged explosive must be disposed of,
ii. what means of disposal shall be used, and
iii. how frequently damaged explosive shall be disposed of, in addition to disposal under subparagraph i. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 7.
(5) Explosive that is unattended shall not be left in or about any working place but shall be returned to storage. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 7.
(6) Detonators and capped fuse shall be stored in a separate, suitable, closed storage container located at least eight metres from any other explosive. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 128 (6).
(7) Explosive shall not be heated above the ambient temperature of its storage place. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 128 (7).
129. Where, in a magazine or a storage place, electric fixtures or wiring are installed or used,
(a) wiring shall consist of,
(i) moisture-proof armoured cable, or
(ii) rigid conduit with water-tight joints;
(b) lighting fixtures shall have dust-tight enclosures;
(c) heaters shall,
(i) operate at a low surface temperature,
(ii) be of a type suitable for an explosive environment, and
(iii) be protected against operating in excess of 125 per cent of capacity;
(d) lighting circuits shall be protected against operating in excess of ten amperes;
(e) switches and protective devices shall be located outside the magazine or placed in a fire-resistant enclosure;
(f) metal parts shall be bonded and grounded; and
(g) the electric system shall be protected against a lightning strike or surge. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 129.
130. Revoked: O. Reg. 272/97, s. 24.
131. A motor vehicle when transporting explosives on the surface at a mine or plant shall,
(a) be kept in sound mechanical condition;
(b) be conspicuously marked by red signals or flags easily visible from front, rear and both sides;
(c) have all metal parts that could come in contact with containers of explosives covered with wood, tarpaulin or similar non-sparking material;
(d) not be used to transport other goods or materials at the same time as explosives are being transported;
(e) be equipped with a type BC fire extinguisher;
(f) not be loaded in excess of its rated carrying capacity;
(g) have explosives secured or fastened so as to prevent any part of the load from becoming dislodged;
(h) transport detonators with other explosives only if the detonators are,
(i) in a suitable container in a separated compartment, and
(ii) 5,000 or less in number;
(i) be attended at all times; and
(j) carry only those persons necessary for handling explosives. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 131.
132. (1) Except as provided for in subsection (2), explosives transported at a mine shall,
(a) be in suitable closed containers;
(b) have detonators, blasting caps and capped fuses kept separate from other explosives. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 132 (1).
(2) Capped fuses may be transported with other explosives without placing them in a container if they are kept separate from other explosives. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 132 (2).
(3) Primers shall be made up,
(a) as near to their point of use as is practicable; and
(b) only in sufficient numbers for the immediate work in hand. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 132 (3).
(4) Made-up primers shall be transported,
(a) in separate, suitable, closed containers conspicuously marked with the words “DANGER — EXPLOSIVES”; and
(b) in a separate vehicle or conveyance from other explosives. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 132 (4).
133. (1) When transporting explosives in a shaft conveyance the worker in charge of the operation shall give or cause to be given notice of the operation to the deck attendant and hoist operator. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 133 (1).
(2) No worker shall,
(a) place in;
(b) have while in; or
(c) take out of,
a shaft conveyance any explosive except under the immediate supervision of a worker authorized for the purpose by a supervisor. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 133 (2).
(3) No other material shall be transported with explosives in a shaft conveyance. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 133 (3).
134. (1) Explosives shall be removed without delay from,
(a) near the shaft collar;
(b) other entrances to the underground workings; and
(c) a shaft station. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 134 (1).
(2) Explosives underground shall be transported from a magazine to other magazines or place of use,
(a) without delay; and
(b) by the most direct and safe route. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 134 (2).
135. (1) Where explosives are transported underground by means of a motor vehicle or a train,
(a) the speed of the vehicle or train shall not exceed ten kilometres per hour;
(b) specific arrangements for the right of way of the vehicle or train shall be made before the vehicle or train is put in motion;
(c) the explosives shall be in suitable containers; and
(d) the requirements prescribed by section 131, except clauses (b) and (c), apply with necessary modifications. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 135 (1).
(2) Where explosives are transported underground by means of a train,
(a) the motor vehicle running on rails shall be maintained on the forward end of the train unless a worker walks in front of the train to effectively guard it;
(b) a car carrying explosives shall be separated from the motor vehicle by an empty car or spacer of equivalent length;
(c) no explosives shall be carried on the motor vehicle; and
(d) every car carrying explosives shall be protected from contact with a trolley wire. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 135 (2).
135.1 (1) This section applies when detonators are being transported otherwise than by means of a motor vehicle or train. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 8.
(2) Detonators shall be carried in containers that are,
(a) suitable for the purpose; and
(b) clearly marked as containing detonators. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 8.
(3) The employer shall make containers that comply with subsection (2) readily available to workers. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 8.
136. (1) Subject to subsection (2), before drilling or sampling is commenced in a working place in an underground mine, the exposed faces shall be,
(a) washed with water; and
(b) carefully examined for misfires, cut-off holes and remnants of blasted holes. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 136 (1).
(1.1) Despite subsection (1), if it is not practical to examine for misfires, cut-off holes or remnants of blasted holes, drilling or sampling may be done using methods and procedures described in subsection (7). O. Reg. 171/92, s. 1 (1).
(2) In gypsum mines and in mines containing soluble minerals and salts where water cannot be used,
(a) an alternate method shall be used for checking each face for misfires and cut-off holes; and
(b) a written procedure detailing the method shall be prepared and followed. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 136 (2).
(3) Where practical, after the face has been checked all remnants of blasted holes shall be conspicuously marked by,
(a) a ring of contrasting paint or crayon; and
(b) inserting sticks or plugs into the holes for lifter remnants in a heading. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 136 (3).
(4) In a mine, no drilling or sampling shall be done within 160 millimetres of the bottom remnant, or an intact portion, of a hole that has been charged and blasted unless the methods and procedures described in subsection (7) are followed. O. Reg. 171/92, s. 1 (2).
(5) In a mine, no drilling or sampling shall be done within one metre of any hole containing explosives unless the methods and procedures described in subsection (7) are followed. O. Reg. 171/92, s. 1 (3).
(6) No development heading shall be abandoned or work therein discontinued until,
(a) the material broken at the firing of the last round has been cleared from the face; and
(b) the whole face of the heading examined for explosives in misfires or remnants of holes. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 136 (6).
(7) For the purposes of subsections (1.1), (4), (5) and 139 (3), drilling or sampling may be done using methods and procedures developed by the employer and the workers involved in the task and agreed upon by the joint health and safety committee or the health and safety representative for the workplace,
(a) if the employer gives notice, at least ten days before implementing the methods and procedures, to each union representing workers at the workplace;
(b) if the employer ensures that workers are trained in the methods and procedures; and
(c) if the employer publicizes the methods and procedures and displays them in the workplace before implementing them. O. Reg. 171/92, s. 1 (4); O. Reg. 272/97, s. 25.
(8) Subject to subsection (9), if a frozen cut is encountered, drilling may be done only if it is done in accordance with methods and procedures developed by the employer and the workers involved in the task and agreed on by the joint health and safety committee or the health and safety representative for the workplace. O. Reg. 291/02, s. 6.
(9) No collaring may be done within 300 millimetres of a frozen cut or if there is a possibility of intersecting any portion of a frozen cut, unless the methods and procedures of subsection (7) are used. O. Reg. 291/02, s. 6.
(10) In subsections (8) and (9),
“frozen cut” means the first holes blasted in a development round that do not break the rock as intended, but rather shatter and cover over with no explosives visible. O. Reg. 291/02, s. 6.
137. (1) Subject to subsection (2), any explosive charge that has misfired or cut off,
(a) shall not be withdrawn; and
(b) shall be blasted without undue delay at a safe and suitable time. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 137 (1).
(2) Except for nitroglycerine sensitized explosives, water soluble explosives may be washed out of the hole by means of an approved device. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 137 (2).
(3) A worker who fires any charges shall, where possible, count the number of shots and if a misfire is suspected shall report it to his or her supervisor. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 137 (3).
(4) Where at the end of a shift a misfire is suspected, or if a misfire has been reblasted and it has not been checked, such fact, together with the location of the hole, shall be recorded in the shift log. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 137 (4).
(5) An employer shall establish and maintain a system for reporting to the employer and recording misfired explosives. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 3.
(6) An employer shall use reasonable efforts to determine the cause of a misfiring of an explosive and shall take such preventive action as is reasonable in the circumstances. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 3.
138. (1) Drill holes shall be of sufficient size to admit the free insertion to the bottom of the hole of a cartridge of explosive or a loading hose. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 138 (1).
(2) Before charging a hole with explosives, the hole shall be cleared of all obstructions. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 138 (2).
139. (1) Drilling or undercutting and charging operations at a mine shall not be carried on simultaneously,
(a) on the same face above or below each other; or
(b) within eight metres horizontal distance of each other. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 139 (1).
(2) In charging holes for blasting, no iron or steel tool or rod shall be used. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 139 (2).
(3) No iron or steel tool shall be used in a hole that contains an explosive unless the methods and procedures described in subsection 136 (7) are followed. O. Reg. 171/92, s. 2.
(4) Drill holes charged with explosives shall,
(a) have a properly prepared detonating agent placed in the charge;
(b) be fired in their proper sequence;
(c) when loaded in one loading operation, be blasted in one blasting operation, except where a procedure for doing otherwise has been prepared and adopted by the supervisor in charge of the mine; and
(d) when primed, not be left unfired, but shall be fired at the time for blasting required by the supervisor in charge of the mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 139 (4).
(5) Except when blasting electrically or when only one charge is to be fired, there shall be at least two workers present at a blasting operation. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 139 (5).
(6) Except when the blasting operation is conducted on surface in daylight or under artificial light, every worker engaged in a blasting operation shall carry a light. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 139 (6).
(7) Where detonating cord is used,
(a) loading shall be completed in all holes; and
(b) all equipment not required for the loading operation shall be removed from the blast site before,
(i) cords are interconnected between holes or attached to trunk line circuits, and
(ii) delay devices or initiating detonators are attached to trunk line circuits. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 139 (7).
140. Where holes are loaded pneumatically with explosives,
(a) only semi-conductive hoses manufactured for such purpose shall be used;
(b) pneumatic loading equipment shall not be grounded directly to pipes, rails or other similar continuous conductors; and
(c) where electrical blasting caps are used,
(i) no plastic or other non-conducting liners shall be used, and
(ii) the cap shall not be placed in the hole until the pneumatic loading of the hole has been completed, except where a procedure for doing otherwise has been prepared and adopted by the supervisor in charge of the mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 140.
141. (1) Before blasting,
(a) a worker shall be stationed at each entrance or approach and instructed to prevent inadvertent access to every place where,
(i) the blasting is to take place,
(ii) the safety of persons may be endangered by the blasting, or
(iii) a diamond drill hole intersection may connect with the blast;
(b) the worker doing the blasting shall,
(i) give or cause to be given due warning in every direction by shouting “FIRE”, or give warning of a primary blast by siren where the extent of the operation makes shouting ineffective,
(ii) satisfy himself or herself that all persons have left the workplace or the vicinity except those required to assist him or her in blasting and guarding, and
(iii) take necessary precautions to ensure that all areas of the mine to be affected by the blasting operation are vacated. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 141 (1).
(2) In surface mines,
(a) the warning of a primary blast by siren shall be given,
(i) at least five minutes prior to the blast, and
(ii) again at one minute prior to the blast;
(b) where it is necessary to stop traffic on a public road,
(i) signs shall be posted to warn traffic of the impending blast, and
(ii) guards equipped with suitable red flags shall be posted to stop traffic prior to the blast;
(c) an all-clear signal shall be sounded after all danger from the blast has passed; and
(d) where a worker is required near the blast area, blasting shelters shall be provided. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 141 (2).
(3) If there is a disagreement as to the time of setting off blasts in contiguous or adjacent claims or mines, the owners or employers shall jointly determine times at which blasting operations may be performed. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 26.
141.1 (1) In a blasting operation, the worker who makes the final connections necessary to allow the blast to be fired is the only person who is permitted to fire the blast. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 9.
(2) Despite subsection (1), if it is not possible for the same worker to perform both functions in a particular blasting operation,
(a) the employer, in consultation with the joint health and safety committee, or the health and safety representative, if any, shall establish safe procedures for performing the blasting operation;
(b) the employer shall ensure that the safe procedures are set out in writing and that the workers involved in the blasting operation are informed about the safe procedures before performing any tasks in connection with the blasting operation; and
(c) every worker involved in the blasting operation shall follow the safe procedures. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 9.
142. (1) A competent person shall be appointed to design each primary blast at a surface mine. O. Reg. 571/92, s. 13.
(2) The design of a primary blast shall include,
(a) the number of holes to be blasted;
(b) the burden, spacing and depth of each hole;
(c) the type and weight of explosives;
(d) the length of stemming and firing delay detonator used for each hole;
(e) the firing sequencing of the holes;
(f) the weight of explosives used per estimated tonne broken; and
(g) the guarding procedures necessary to protect the safety of workers. O. Reg. 571/92, s. 13; O. Reg. 60/94, s. 5.
(3) A competent person shall ensure that each blast is carried out according to the design. O. Reg. 571/92, s. 13.
(4) The person in charge of a blast shall keep a record of the design data for the blast and shall sign it. O. Reg. 571/92, s. 13.
143. (1) The person in charge of a primary blast at a surface mine shall keep a record setting out,
(a) the date, time and location of the blast;
(b) the wind direction and velocity at the time of the blast; and
(c) the atmospheric conditions at the time of the blast. O. Reg. 571/92, s. 13.
(2) The person shall sign the record. O. Reg. 571/92, s. 13.
144. A vehicle shall not be driven, parked or located over or under loaded holes except where a procedure for doing so has been prepared and adopted by the supervisor in charge of the mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 144.
145. Before a connection is made between two underground working places,
(a) an examination shall be made of the workings towards which the active working is advancing, where practicable, to determine that the work can proceed in a safe manner; and
(b) when the distance between the working places is less than,
(i) twice the length of the longest drill steel used, or
(ii) a minimum of five metres from the bottom of the longest hole,
all approaches to both working places shall be guarded before blasting. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 145.
146. Where safety fuse is used in any blasting operation,
(a) no fuse shorter than one metre shall be used;
(b) no fuse shall be lighted at a point closer than one metre from the capped end;
(c) capped fuses shall be supplied in standard lengths;
(d) the uncapped ends of fuses of the same length shall be identified;
(e) where more than one charge is to be fired, each fuse connected to a charge shall be lighted by a suitable and reliable timing device;
(f) where igniter cord is used, no connections shall be made to fuses until all holes are loaded; and
(g) where igniter cord is used, a worker shall, immediately after the ignition of the igniter cord, leave the workplace which will be affected by the blasting operation. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 146.
147. (1) A worker performing blasting operations shall not permit any person to return to a workplace affected by the operation until the applicable minimum period of time described in this section has elapsed. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 3.
(2) If safety fuses are used, the minimum period is,
(a) 10 minutes after the worker performing the blasting operations hears the last shot, if a single fuse is used; or
(b) 30 minutes after the worker performing the blasting operations hears the last shot, if more than one fuse is used. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 3.
(3) In the case of a misfire when at least one safety fuse is used, the minimum period is 30 minutes after a reblast. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 3.
(4) If detonators that are not safety fuses are used, the minimum period is,
(a) the time for the blasting contaminants to clear, if one detonator is used; or
(b) 10 minutes after the worker performing the blasting operations hears the last shot, if more than one detonator is used. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 3.
(5) If the worker performing the blasting operations does not hear a shot when using detonators that are not safety fuses, the minimum period is 10 minutes after,
(a) the worker has disconnected the lead wires from the power source and short-circuited them and locked the blasting switch, if any, in the open position; or
(b) the worker has disconnected the initiation device from the blasting system. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 3.
147.1 (1) No worker shall use safety fuses in an underground mine to blast hang-ups in chutes, passes, millholes or drawpoints. O. Reg. 68/96, s. 3.
(2) No worker shall insert a safety fuse into a drilled hole in an underground mine. O. Reg. 60/94, s. 6.
148. (1) Blasting in a shaft, shaft station or other workings being driven from a shaft shall be done by means of electricity,
(a) after the first three metres of advance has been made in the shaft; and
(b) until such time as the permanent timbers and ladders have reached the level upon which blasting is being done. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 148 (1).
(2) Blasting in a raise, where free escape is not readily available, shall be done by means of electricity from a safe location outside the raise. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 148 (2).
149. When blasting by means of electricity,
(a) where balanced circuits are required, each circuit shall be tested before firing with a suitable galvanometer or other similar suitable instrument;
(b) where electric blasting caps are used,
(i) the protective shunt shall not be removed from the leg wire until connections are made,
(ii) the leg wire shall not be shortened to less than one metre,
(iii) the firing cables leading to the face or faces shall be short-circuited while the leads from the blasting caps are being connected to each other and to the firing cables,
(iv) the short-circuit prescribed in subclause (iii) shall not be removed until all workers have left the workplaces to be affected by the blasting operation, and
(v) the short-circuit prescribed in subclause (iii) shall be located so that a premature explosion will be harmless to the worker opening the short-circuit; and
(c) before any person returns to the workplace affected by the blasting operation,
(i) the firing cables shall be removed from the battery, blasting machine or other source of electricity and shall be short-circuited, and
(ii) the blasting switch shall be locked in the open position. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 149.
150. (1) Where the source of current is a portable direct current battery or blasting machine the firing cables or wires shall,
(a) not be connected to the source of current until,
(i) the workplace to be affected by the blasting operation has been cleared of persons, and
(ii) immediately prior to blasting; and
(b) be disconnected and short-circuited immediately after the blast has been fired. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 150 (1).
(2) A blasting machine shall,
(a) be of a type and design specifically manufactured for the purpose;
(b) be kept in good mechanical and electrical condition;
(c) be tested regularly using methods specified by the manufacturer;
(d) be tested before any blasts that may require the maximum output of the machine;
(e) be clearly marked with the capacity of the machine; and
(f) not be used in excess of its rated capacity. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 150 (2).
151. Blasting cables and blasting wires shall,
(a) be distinguished from other cables and wires;
(b) be used for blasting purposes only; and
(c) not come into contact with,
(i) detonating cords,
(ii) power, lighting or communication cables, or
(iii) pipes, rails or other continuous metal grounded circuits. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 151.
152. (1) When a common electrical source is used to fire blasts in more than one workplace provision shall be made for,
(a) the continued shorting of the blasting cables;
(b) a three-way switch for each individual blasting circuit which can be locked in either the shorted or closed position to provide for,
(i) shorting of the circuit,
(ii) energizing the circuit, and
(iii) testing of the circuit;
(c) identification of blasting cables and switches; and
(d) a written blasting procedure setting forth,
(i) the method of connecting the blasting wires to the electrical supply,
(ii) the evacuation of all workers from the area of the blast, and
(iii) the method of testing the system to ensure that the proper connections have been made. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 152 (1).
(2) The written blasting procedure shall be followed. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 152 (2).
153. (1) Circuits from a source other than from a portable hand-operated device used for blasting shall be,
(a) from an isolated, ungrounded power source; and
(b) used for blasting only. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 153 (1).
(2) A blasting device shall,
(a) be designed for the purpose;
(b) be kept in good mechanical and electrical condition;
(c) be constructed so that it automatically opens the circuit by gravity to short-circuit the blasting conductor;
(d) have the live side enclosed within a fixed box with a door,
(i) that can be locked and unlocked only by the worker doing the blasting, and
(ii) so arranged that the door cannot be closed unless the contacts of the firing circuit are in the opened and shorted position; and
(e) where the power source exceeds 300 volts be electromagnetically operated. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 153 (2).
154. (1) No electrical blasting circuit connections shall be made on or near to surface or in or near to a shaft during an electrical storm in the vicinity. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 154 (1).
(2) If electrical blasting operations are undertaken, an employer shall ensure that the operations are conducted so as to ensure that there is no interference from any system, device or controller capable of producing radio frequencies or radiating electromagnetic energy. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 27.
(3) An employer shall ensure that a system, device or controller that is capable of producing radio frequencies or radiating electromagnetic energy does not set off detonators. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 27.
(4) Subsections (1), (2) and (3) do not apply with respect to blasting operations that use,
(a) a combination blast initiation device and high-frequency radio signal that have been designed for that purpose; or
(b) a high-frequency impulse-initiated detonator. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 27.
155. (1) If electrical equipment is installed or modified, the work shall be done in accordance with good electrical practices. O. Reg. 486/99, s. 3.
(2) The electrical equipment shall be operated in accordance with good electrical practices. O. Reg. 486/99, s. 3.
(3) The quantity and trade name of any liquid insulant or coolant when in excess of one litre shall be shown on the name plate of the electrical equipment in which it is contained. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 155 (3).
(4) A person who is competent in the electrical trade shall be appointed to be in charge of electrical equipment. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 155 (4).
156. If the employer intends to make a major electrical installation or a major alteration to existing electrical installations, the employer shall give the joint health and safety committee or the health and safety representative, if any, written notice of that fact. O. Reg. 486/99, s. 4.
157. Revoked: O. Reg. 486/99, s. 5.
158. Revoked: O. Reg. 486/99, s. 5.
159. (1) Electrical work shall not be performed on live equipment except where,
(a) live line techniques are used;
(b) approved live line equipment is used;
(c) no hazard from explosive or flammable materials exists; and
(d) all necessary precautions to work safely are taken. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 159 (1).
(2) Except as provided for in subsection (1), no object shall be brought closer than the distance specified in Column 2 of the following Table to an exposed, energized overhead electric supply line of the voltage specified in Column 1:
TABLE
|
Column 1 |
Column 2 |
|
Voltage of Powerline |
Minimum Distance |
|
300 to 150,000 volts |
3 Metres |
|
150,000 to 250,000 volts |
4.5 Metres |
|
Over 250,000 volts |
6 Metres |
R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 159 (2).
(3) Precautions to guard workers against injury by moving or energized parts shall be taken before maintenance, repair or adjustment work is performed on a machine that is energized. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 159 (3).
(4) When located less than 1.5 metres measured in a horizontal plane or 2.5 metres measured in a vertical plane from a walkway or landing, any bare part of electrical equipment energized in excess of 150 volts DC or 50 volts AC shall be guarded. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 159 (4).
(5) Machines that have movable or extendable booms must not be operated in close proximity to energized electrical supply lines unless,
(a) they are operated in accordance with subsection (1); or
(b) the operator of the machine has been authorized to perform such work and,
(i) there is a clearance between any part of the machine and the energized line that is more than the greater of,
(A) one-half the maximum horizontal reach of the boom, or
(B) the distance determined under subsection (2),
(ii) the lines are disconnected and grounded,
(iii) the machine is a railroad crane operating on railroad tracks and the supply line is energized to less than 750 volts direct current, or
(iv) the supply lines are guarded against contact by any part of the machine or its load. O. Reg. 60/94, s. 7.
(6) Subsections (2) to (5) apply only with respect to electrical lines installed on the surface and electrical equipment used on the surface. O. Reg. 486/99, s. 6.
160. (1) All switches controlling electrical equipment or lines shall be locked and tagged in the open position while work is being done on the equipment or lines but the locking device may be omitted where,
(a) the locking device in itself creates a hazard due to a switch design; or
(b) circuit breakers or fuses for voltages of less than 150 volts to ground are not equipped with a means of locking. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 160 (1).
(2) Despite subsection (1), locking and tagging is not required where live work is permitted by subsection 159 (1). R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 160 (2).
(3) A tag required by subsection (1) shall,
(a) be secured to prevent its inadvertent removal;
(b) state the reason the switch is opened;
(c) show the name of the person responsible for opening the switch; and
(d) show the date on which the switch was opened. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 160 (3).
(4) Tags on electrical equipment shall be of nonconducting materials. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 160 (4).
161. A portable ladder which has metal or metal reinforced side rails shall not be,
(a) stored in or about electrical equipment having energized and exposed parts; or
(b) used about electrical equipment having energized exposed parts. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 161.
162. Revoked: O. Reg. 486/99, s. 7.
163. (1) The supports for electrical equipment and the compartments in which it is installed shall be of such material and arranged in such a manner as to reduce the potential for a fire to a minimum. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 163 (1).
(2) No flammable material shall be stored or placed in the same compartment as electrical equipment. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 163 (2).
(3) Lamps or heating units shall be installed and protected so as to prevent the heat generated from causing a fire. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 163 (3).
(4) A fire extinguishing device shall be provided in each area where electrical equipment creates a fire hazard. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 163 (4).
(5) The fire extinguishing device prescribed in subsection (4) shall be,
(a) of a type approved for use on electrical fires;
(b) of a size recommended for the size and type of equipment;
(c) located convenient to an exit from the area; and
(d) maintained in condition for immediate use. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 163 (5).
164. (1) Electrical mobile equipment operating at more than 300 volts to ground shall be supplied by a system wherein,
(a) the neutral is grounded through a current limiting device in such a manner as to limit the possible rise of ground fault potential to a maximum of 100 volts to ground; and
(b) ground fault protection is provided. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 164 (1).
(2) Electrical mobile equipment operating at more than 300 volts to ground must have a fail safe circuit that prevents the supply of electricity to the equipment when the conductivity of the ground return circuit is not continuous. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 29 (1).
(3) In this section,
“electrical mobile equipment” means equipment which, during its operating cycle, is required to move along the ground while energized and which receives its current through a trailing cable and includes drills which connect to an electrical power supply. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 29 (2).
165. Revoked: O. Reg. 486/99, s. 7.
166. Revoked: O. Reg. 486/99, s. 7.
167. Clause 36-204 of CSA Standard C22.1-1982 is modified to the extent that a single pole disconnecting fuse of adequate interrupting capacity may be used to protect a transformer whose capacity is 100 kilovoltamperes per phase or less when operating at a voltage less than 7,500 volts. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 167.
168. Revoked: O. Reg. 486/99, s. 7.
169. Revoked: O. Reg. 486/99, s. 7.
170. (1) The power supply to a motor shall not be run through the enclosure of the controller for another motor. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 170 (1).
(2) A motor branch circuit shall be arranged so that when its disconnecting means is opened, all parts on the load side within the controller enclosure are de-energized. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 170 (2).
171. Revoked: O. Reg. 486/99, s. 7.
172. (1) Revoked: O. Reg. 486/99, s. 8.
(2) Revoked: O. Reg. 486/99, s. 8.
(3) Switchboards shall be made of materials that are non-combustible. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 172 (3).
173. Revoked: O. Reg. 486/99, s. 9.
174. (1) This section applies with respect to equipment that can be operated or moved by remote control using a system, device or controller that produces radio frequencies or radiates electromagnetic energy. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 31.
(2) An employer shall ensure that the system, device or controller is not capable of operating or moving equipment unless it is intended to do so. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 31.
(3) An employer shall ensure that only one system, device or controller can be used at a time to operate or move the equipment. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 31.
(4) The system, device or controller must be equipped with a device that enables the operator to stop the equipment in an emergency. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 31.
(5) The employer shall establish procedures to ensure that the operator and other workers are in a safe location when the equipment is being operated or moved. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 31.
175. (1) Cables supplying electrical power from surface to underground shall be fed through a circuit breaker located on surface. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 175 (1).
(2) Revoked: O. Reg. 486/99, s. 10.
(3) Revoked: O. Reg. 486/99, s. 10.
(4) Revoked: O. Reg. 486/99, s. 10.
(5) Revoked: O. Reg. 486/99, s. 10.
(6) Revoked: O. Reg. 486/99, s. 10.
176. Revoked: O. Reg. 486/99, s. 11.
177. Revoked: O. Reg. 486/99, s. 11.
178. Revoked: O. Reg. 486/99, s. 11.
179. The voltage of any underground lighting circuit shall not exceed 150 volts to ground except in circuits using direct current where the voltage shall not exceed 300 volts to ground. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 179.
180. (1) In an underground mine with trolley lines installed underground, the owner shall ensure that the requirements of this section are met. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 5.
(2) The lines must be designed to have a nominal voltage less than 1,200 volts and operated with a nominal voltage less than 1,200 volts. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 5.
(3) The lines must have ground fault protection if they use alternating current. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 5.
(4) If the operating voltage of the lines is greater than 300 volts, there must be,
(a) lighting or reflectors sufficient to indicate the location of the lines; and
(b) warning signs installed at points of access to the lines. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 5.
(5) Trolley lines of the bare conductor type must be protected by guards made of insulating materials. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 5.
(6) The guards must extend at least 75 millimetres below the lowest point of the trolley line and must be placed not more than 150 millimetres from the nearest line. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 5.
(7) Despite subsection (5), guards are not required on trolley lines of the bare conductor type that use alternating current if the trolley lines have ground fault protection that prevents a worker from being exposed to an electrical current sufficient to cause ventricular fibrillation. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 5.
(8) Trolley lines of the bare conductor type that are installed underground after December 31, 1994 must be located,
(a) at least 2.4 metres above grade, if the operating voltage is 300 volts or less;
(b) at least 2.7 metres above grade, if the operating voltage is more than 300 volts but less than 750 volts;
(c) at least 4.0 metres above grade, if the operating voltage is 750 volts or more. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 5.
(9) Trolley lines of the busway conductor type that are installed underground after December 31, 1994 must be located at least 2.4 metres above grade. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 5.
(10) Subsections (8) and (9) do not apply with respect to trolley lines that are an extension of a trolley line system,
(a) if the system is installed before January 1, 1995;
(b) if the system has an operating voltage of 300 volts or less; and
(c) if the extension is located at least 1.8 metres above grade. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 5.
(11) The employer shall establish written procedures to require all necessary precautions to work safely around trolley lines. O. Reg. 486/99, s. 12.
181. (1) An explosive actuated fastening tool shall,
(a) when in storage be,
(i) accessible only to an authorized worker, and
(ii) kept in a locked container; and
(b) be of a type and design that conforms to CAN3-Z166-M85 Series “Power Actuated Fastening Tools”. O. Reg. 174/01, s. 4 (1).
(1.1) An explosive actuated tool or explosive actuated system shall be,
(a) maintained in proper condition; and
(b) serviced in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations. O. Reg. 174/01, s. 4 (1).
(2) The shells for use with an explosive actuated tool or explosive actuated system shall,
(a) be identified as to size and strength;
(b) be kept in containers which contain only one size and strength;
(c) not be left unattended except when in storage; and
(d) when in storage be,
(i) accessible only to an authorized worker, and
(ii) kept in a locked container. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 181 (2); O. Reg. 174/01, s. 4 (2).
(3) The operator of an explosive actuated tool or explosive actuated system shall,
(a) be a competent person;
(b) operate the tool or system in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions; and
(c) ensure before use that the barrel is clean and free from any obstruction. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 181 (3); O. Reg. 174/01, s. 4 (3, 4).
182. (1) Before diesel powered equipment is first used in an underground mine, the employer shall complete Form 1. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 32.
(1.1) Once the information is completed on Form 1, the employer shall ensure that the form is kept readily available at the mine site. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 32.
(2) Non-rail-bound diesel-powered equipment that is first used in an underground mine after June 1, 1995 must meet the requirements set out in CAN/CSA-M424.2-M90 “Non-Rail-Bound Diesel-Powered Machines for use in Non-Gassy Underground Mines” excluding the requirements in sections 4.5, 5.3 and 5.4 of that document. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 6.
(3) Gasoline or another volatile fuel shall not be used in the starting mechanism of diesel-powered equipment. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 6.
(4) The fuel used in a diesel engine shall conform to CAN/CGSB-3 16-99 “Mining Diesel Fuel”, Special-LS or CAN/CGSB-3.517 “Automotive Low Sulphur Diesel Fuel” Type AL-S. O. Reg. 174/01, s. 5.
(5) An employer shall ensure that the undiluted exhaust gases from diesel-powered equipment is less than 1,500 parts per million by volume of carbon monoxide. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 6.
(6) For each piece of diesel-powered equipment, the employer shall ensure that a record containing the following information is maintained:
1. The company identification number.
2. The make and model of the piece of equipment.
3. The prescribed ventilation rate in cubic metres per second.
4. The maximum rated load in kilowatts.
5. The maximum speed at the maximum rated load in revolutions per minute.
6. The maximum fuel injection rate at the maximum rated load and speed in kilograms per hour.
7. The results of any test made under paragraph 2 of subsection 183.2 (1). O. Reg. 779/94, s. 6.
183. (1) An employer shall maintain a chart of procedures for the use and operation of diesel-powered equipment that sets out,
(a) the actual volume of air flowing in the underground haulageways and workings where the equipment is operating; and
(b) the total ventilation requirements for the equipment when it is operating normally in a single continuous course of air. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 7.
(2) The employer shall post the chart in a location where it is clearly visible and readily accessible to the operator of the diesel-powered equipment. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 7.
183.1 (1) The employer shall ensure that a flow of air that meets the requirements of this section is provided to the workplace where diesel-powered equipment is operating. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 7.
(2) The flow of air must be provided by a mechanical ventilation system. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 7.
(3) The flow of air must be at least 0.06 cubic metres per second for each kilowatt of power of the diesel-powered equipment operating in the workplace. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 7.
(4) The flow of air must reduce the concentration of toxic substances in diesel exhaust emissions to prevent exposure of a worker to a level of no more than,
(a) the concentration limits prescribed under section 4 of Regulation 833 of the Revised Regulations of Ontario, 1990 (“Control of Exposure to Biological or Chemical Agents”) made under the Act; or
(b) if no limits are prescribed under that section, the threshold limit values adopted as criteria or guides under section 283. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 7.
(5) The flow of air must reduce the time-weighted average exposure of a worker to airborne respirable combustible dust to not more than 1.5 milligrams per cubic metre of air. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 7.
183.2 (1) The employer shall ensure that tests are conducted to determine the following matters at the times indicated:
1. The volume of air flowing in underground haulageways and workings where diesel-powered equipment is operating. This must be tested at least weekly.
2. The carbon monoxide content of the undiluted exhaust discharging from diesel-powered equipment to the atmosphere. This must be tested,
i. immediately after repairs are made to the engine or the exhaust system or both, and
ii. at routine intervals for maintenance as the manufacturer recommends or, if there is no such recommendation, at least once a month.
3. The volume of air flow and the carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, formaldehyde or respirable combustible dust contents of the atmosphere. These must be tested at the request of a worker. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 7.
(2) The employer shall provide the results of every test conducted under subsection (1) to the joint health and safety committee or the health and safety representative, if any, for the workplace. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 7.
(3) The employer shall record the results of every test conducted under paragraph 3 of subsection (1) and shall maintain the record. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 7.
(4) If a test indicates that a worker has been exposed to diesel exhaust emissions containing a toxic substance in excess of the level set out in subsections 183.1 (4) and (5) and if this test result could not have been predicted in the circumstances, the employer shall,
(a) investigate the cause and take remedial action, if possible, to prevent a recurrence of the situation;
(b) notify the worker and the joint health and safety committee or the health and safety representative, if any, for the workplace; and
(c) conduct tests of the emissions until the results show that the concentration of the toxic substance does not exceed the level set out in subsections 183.1 (4) and (5). O. Reg. 779/94, s. 7.
184. The exhaust of an internal combustion engine which is temporarily or permanently installed within a building on surface shall be,
(a) conducted to a point outside the building; and
(b) prevented from,
(i) re-entering the building,
(ii) entering the intake of any compressor,
(iii) contaminating the atmosphere of another building, and
(iv) contaminating mine workings. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 184.
184.1 A temporary attachment used to connect a lifting device to its load or to anchor it,
(a) shall be appropriate for the use;
(b) shall be designed and installed in accordance with safety factors recognized by good engineering practice; and
(c) shall be used in a manner that minimizes shock loading. O. Reg. 571/92, s. 14.
185. (1) In this section,
“machine” includes a prime mover, transmission equipment and thing. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 10.
(2) A machine that has an exposed moving part that may endanger the safety of any person shall be fenced or guarded unless its position, construction or attachment provides equivalent protection. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 10.
(3) A machine shall be provided with a device that automatically prevents a worker operating it from coming in contact with any moving part. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 10.
(4) The travelway of a counterweight shall be guarded or located to prevent,
(a) inadvertent entry thereto by a worker; and
(b) injury to a worker should the counterweight become detached from its fastenings. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 10.
(5) Clearance sufficient for the safety of a worker shall be provided from the path of travel of,
(a) a load carried by a machine;
(b) a moving part of a machine; and
(c) another machine. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 10.
(6) A revolving set screw, bolt, key or other similar device shall be recessed, encased or guarded to prevent inadvertent contact by a worker. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 10.
(7) If any work is being done on a machine,
(a) the moving parts shall be stopped;
(b) any hydraulic, pneumatic or gravity stored energy shall be dissipated or contained;
(c) energy isolating devices shall be installed if the machine is not already equipped with them; and
(d) all energy isolating devices shall be properly engaged, locked and tagged. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 10.
(8) Before doing any work to which subsection (7) applies, a worker shall verify, by testing, that the requirements of that subsection have been complied with. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 10.
(9) A tag required by clause (7) (d) shall,
(a) be secured to prevent its accidental removal;
(b) state the reason the energy isolating devices are locked and tagged;
(c) show the name of the person responsible for locking and tagging the energy isolating devices; and
(d) show the date on which the energy isolating devices were locked and tagged. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 10.
(10) If it is not practical to comply with subsection (7) or with subsection 160 (1), work to which those subsections apply may be done if, while it is being done, barriers, shields or other effective precautions are used or taken for the safety of a worker. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 10.
186. (1) Subject to subsection (10), no elevator shall be put into service without a professional engineer giving written statement to the owner setting out,
(a) the location of the elevator;
(b) the maximum loading of number of persons and material that may be carried by the elevator when it is installed, maintained and operated in compliance with this Regulation;
(c) that the elevator is designed and manufactured in accordance with appropriate engineering standards and installed where it is to be put into service in compliance with good engineering practice. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 33 (1).
(2) Subsection (1) does not apply to an elevator that is operated for testing purposes. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 33 (1).
(3) The owner shall ensure that a copy of the statement is posted at the mine site in a location readily visible to workers and that a copy is given to the joint health and safety committee or the health and safety representative, if any. O. Reg. 236/99, s. 5 (1).
(4) The maximum loading set out in the statement required under subsection (1) or a permit referred to in subsection (10) shall not be exceeded. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 33 (1).
(5) An elevator installation shall meet the following standard:
1. If it was installed before October 15, 1991, CSA Standard B44-1975, “Safety Code for Elevators, Dumbwaiters, Escalators and Moving Walks”.
2. If it was installed on or after October 15, 1991 and before the day on which O. Reg. 236/99 came into force, National Standard CAN/CSA-B44-M90, “Safety Code for Elevators”.
3. Otherwise, National Standard CAN/CSA-B44-94, “Safety Code for Elevators”. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 8; O. Reg. 236/99, s. 5 (2).
(6) Each component that may affect the safe operation of an elevator shall be examined and tested by a competent person before an elevator is initially used and thereafter at intervals not exceeding one month. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 186 (6).
(7) A log book shall be kept in which the date, findings and name of the competent persons performing the examinations and tests prescribed in subsection (6) shall be recorded. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 186 (7).
(8) In addition to the standards required to be met under subsection (5), an elevator shall,
(a) have a safe means of access to the machinery room which access shall be located outside the hoistway;
(b) not have hoisting or balance ropes that are spliced;
(c) have the entry to the machinery room restricted to authorized persons;
(d) have a means by which a person stranded in an elevator can alarm persons outside the elevator when the elevator is operated on automatic control; and
(e) have its controls and machine parts protected against physical damage, moisture, dust or extreme temperatures. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 186 (8).
(9) The machinery room of the elevator shall be kept clean and contain only those materials required for the elevator. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 186 (9).
(10) Subsections (1) and (3) do not apply to an elevator being operated under a permit issued by the Ministry of Labour before August 16, 1997. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 33 (2).
187. A dumbwaiter, escalator or moving walk shall meet the following standard:
1. If it was installed before April 1, 1994, CSA Standard No. B44-1975, “Safety Code for Elevators, Dumbwaiters, Escalators and Moving Walks”.
2. If it was installed on or after April 1, 1994 and before the day on which O. Reg. 236/99 came into force, National Standard CAN/CSA-B44-M90, “Safety Code for Elevators”.
3. Otherwise, National Standard CAN/CSA-B44-94, “Safety Code for Elevators”. O. Reg. 236/99, s. 6.
188. (1) Devices commonly known as “manlifts” shall meet the standards set out in the Code for Manlifts dated the 25th day of September, 1979 and issued by the Ministry. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 188 (1).
(2) A manlift shall not be used before drawings showing its arrangements are completed and readily available. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 34.
(2.1) After the manlift’s initial use, the drawings shall be kept readily available at the mine site. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 34.
(3) Each component which may affect the safe operation of a manlift shall be examined and tested by a competent person,
(a) before initial use; and
(b) at intervals not exceeding one month. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 188 (3).
189. (1) No worker shall be raised or lowered or be permitted to be raised or lowered by any hoist, derrick, crane or similar device unless,
(a) such device is examined and tested by a competent person before being used to raise or lower the worker;
(b) a safe procedure for raising or lowering the worker is established in accordance with subsection (2) and is used; and
(c) there is a device by which the hoist operator and the worker being raised or lowered can exchange movement signals except where the worker being transported is visible at all times to the hoist operator. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 189; O. Reg. 571/92, s. 15; O. Reg. 60/94, s. 9 (1).
(2) The procedure must be jointly developed by the employer and the joint health and safety committee or health and safety representative, if any, for the workplace. O. Reg. 60/94, s. 9 (2).
190. A worker using a bosun’s chair, suspended scaffold or mobile staging shall be protected by a fall arrest system as prescribed by section 14 if the worker may fall more than three metres from the chair, scaffold or staging. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 190.
191. No elevator, dumbwaiter, escalator, moving walk or manlift shall be used when a component, which may affect its safe operation, is defective. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 191.
192. (1) A lifting device shall be,
(a) designed to factors of safety recognized by good engineering practice;
(b) installed in accordance with such design criteria;
(c) provided with overwind protection if power operated; and
(d) provided with an identification plate. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 192 (1).
(2) The maximum load that a lifting device may carry, based on its design criteria, shall be established by its designer. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 192 (2).
(3) A notice showing the maximum load established under subsection (2) shall be posted in a location visible to the operator of the device. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 192 (3).
(4) Except during testing, the maximum load established under subsection (2) shall not be exceeded. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 192 (4).
(5) Each component that may affect the safe operation of a lifting device shall be examined and tested by a competent person before initial use and thereafter at intervals not exceeding one year. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 192 (5).
(6) The dates, findings and names of the competent persons performing the examinations and tests prescribed in subsection (5) shall be recorded and the records shall be kept available for inspection. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 192 (6).
(7) Where a combination of lifting devices is used simultaneously, the work shall be supervised by a competent person. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 192 (7).
193. (1) A grinder shall be assembled and adjusted in accordance with the manufacturer’s specifications. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 193 (1).
(2) The maximum speed at which a grinding wheel may be operated shall be indicated on the grinding wheel or in a manner by which the speed may be readily ascertained. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 193 (2).
(3) A grinding wheel shall be,
(a) enclosed by a protective hood except for the area at the workrest;
(b) stored where it will not be damaged by impact, extreme heat and cold;
(c) stopped when the grinder or workrest is being adjusted; and
(d) not operated in excess of the manufacturer’s recommended maximum speed. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 193 (3).
(4) The operator of a grinder shall wear eye protection. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 193 (4).
(5) The workrest of a grinder shall be mounted above the centre line of the grinding wheel not more than three millimetres from the wheel. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 193 (5).
(6) An air operated grinder shall have a governor to prevent its operation in excess of the rated speed of the grinding wheel. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 193 (6).
(7) The governor required by subsection (6) shall be inspected regularly and maintained in proper operation. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 193 (7).
194. (1) A person directing workers who perform welding, burning or cutting operations shall be a competent person. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 194 (1).
(2) Every worker who as part of his or her work performs welding, burning or cutting operations shall be a competent person. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 194 (2).
(3) Protection for workers to protect them against injury from fumes, radiation and electric arcs produced during welding, burning or cutting operations shall be provided and used. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 194 (3).
(4) A device to extinguish a fire that may be caused by heat or cuttings produced during welding, burning or cutting shall be provided with each oxygen-acetylene unit. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 194 (4).
(5) The device required by subsection (4) shall,
(a) have a capacity for extinguishing a fire that is equal to or greater than a minimum Underwriters’ Laboratories of Canada classification of 1A 10B; and
(b) be suitable for class A and B fires. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 194 (5).
(6) Equipment for welding, burning or cutting shall be protected against physical damage and from damage by heat, fire and sparks. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 194 (6).
(7) No gas welding, burning or cutting equipment shall be used unless it is free from defects, leaks, oil and grease. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 194 (7).
(8) Acetylene cylinders shall be placed in an upright position for at least thirty minutes before use. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 194 (8).
(9) The valve protection cover or cap of an oxygen or acetylene cylinder shall be secured in place when the cylinder is not in use and, in the case of a threaded cover or cap, the cover or cap shall be secured at least hand-tight. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 194 (9).
(10) The valves of oxygen and acetylene cylinders shall be closed when,
(a) a job is completed;
(b) the oxygen and acetylene cylinders are on portable units and unattended underground; and
(c) the oxygen and acetylene cylinders are transported. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 194 (10).
(11) The regulators and manifolds of oxygen and acetylene cylinders shall be disconnected when the cylinders are being transported underground. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 194 (11).
(12) Unless procedures for safe use have been established by a supervisor in charge of the workplace, a charged gas system installed for welding, burning or cutting shall not be used for any other purpose. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 194 (12).
(13) An insulated conductor of adequate size shall be used to carry the welding current back to an electric welder unless another safe return path has been provided. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 194 (13).
(14) No welding, cutting, burning or soldering shall be done on a container in which an explosive or flammable substance has been stored unless the substance,
(a) has been completely removed; or
(b) has been made non-flammable or non-explosive. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 194 (14).
(15) No explosive or flammable substance shall be put in a container on which welding, burning, cutting or brazing has been done until the container has cooled sufficiently to prevent ignition of the substance. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 194 (15).
(16) A second worker who is a competent person shall attend oxygen and acetylene control devices when oxygen and acetylene cylinders are set up in,
(a) a position not readily available to the worker performing cutting, welding or burning operations; and
(b) a shaft conveyance while a worker is welding, burning or cutting on or from the conveyance. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 194 (16).
195. (1) A multi-girder top-running electric overhead travelling crane for general use shall meet the standards set out in CSA Standard B167-1964, “General Purpose Electric Overhead Travelling Cranes”. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 195 (1).
(2) An electric overhead travelling crane for steel mill service shall meet the standards set out in the Association of Iron and Steel Engineers Standard No. 6, “Specifications for Electric Overhead Travelling Cranes for Steel Mill Service”. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 195 (2).
(3) Every production crane shall be provided with,
(a) a safe means of access and egress for the operator from the cab mounted on the crane when,
(i) it is parked in the normal parking position, and
(ii) it cannot be brought to the normal parking position; and
(b) an alarm by which the operator can warn persons that may be endangered by the moving crane. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 195 (3).
(4) Every service crane shall be provided with an alarm that is visible to persons in the vicinity of the crane when the crane is operating on,
(a) pendant control, where the worker controlling the crane does not have a clear view of the area in which the crane is operating; or
(b) radio frequency control. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 195 (4).
(5) Every production crane and every service crane shall be provided with,
(a) protection against inadvertent operation by radio frequencies when equipped with radio frequency controls;
(b) an operating procedure to guard against colliding with other cranes on the same track;
(c) a load rating plate, stating the maximum load that can be carried by the crane, posted on the crane;
(d) a means by which the power conductors for the crane can be safely disconnected from the source of electrical supply; and
(e) a switch or circuit breaker by which the maximum power to the crane can be safely interrupted from the cab on the crane, unless the crane collectors can be safely removed. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 195 (5).
(6) Before a crane is first used, a person trained in and using the test requirements contained in CSA Standard B167-1964 “General Purpose Electric Overhead Travelling Cranes” shall test devices that may affect the safe operation of the crane. O. Reg. 571/92, s. 16 (1).
(6.1) While a crane is in use a trained person shall examine and service devices that may affect the safe operation of the crane at a frequency at least equal to that recommended by its manufacturer or, if there is no manufacturer’s recommendation, at a frequency at least equal to that specified by a competent person. O. Reg. 571/92, s. 16 (1).
(7) In addition to the requirements of subsection (6), devices that may affect the safe operation of,
(a) a production crane shall be tested daily when in use; and
(b) a service crane shall be tested daily when in use and the test shall be made before the first use of the crane on that day. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 195 (7).
(8) A trained person shall examine, using non-destructive testing techniques, the shafting of each hoist drive train of a production crane to determine if it is in sound condition before the crane is first used. O. Reg. 571/92, s. 16 (2).
(8.1) After a production crane has been first used, a trained person shall examine, using non-destructive techniques, the shafting of each hoist drive train of the crane at a frequency at least equal to that recommended by its manufacturer or, if there is no manufacturer’s recommendation, at a frequency at least equal to that specified by a competent person in order to determine if it is in sound condition. O. Reg. 571/92, s. 16 (2).
(9) A log book shall be kept for each crane and the log book shall contain,
(a) a record of the dates on which testing, servicing and inspections were performed;
(b) a record of the findings of any tests and examinations;
(c) a record of repairs and modifications performed and the signature of the person performing such work; and
(d) the signature of the supervisor authorizing the repairs or modifications referred to in clause (c). R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 195 (9).
(10) No crane shall be operated,
(a) when in the hoisting rope,
(i) the number of broken wires in one lay length exceeds 5 per cent of the total in the rope, or
(ii) defects that seriously affect its strength are known to exist;
(b) when a person is in the vicinity of the wheel tracks unless precautions have been taken to ensure his or her safety;
(c) by an unauthorized person;
(d) by a person who is not a competent person, except for the purpose of training;
(e) when any device that may affect safe operation is found to be faulty; and
(f) when the load exceeds the load rating of the crane, except for the purpose of a test. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 195 (10).
(11) No person shall ride or be permitted to ride,
(a) on the load being carried by a crane;
(b) on a crane except,
(i) the crane operator and any trainee,
(ii) personnel performing maintenance, inspection, or testing of the crane,
(iii) supervisors, and
(iv) for the purpose of maintenance repairs from the crane when precautions for the safety of workers doing the repair have been implemented. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 195 (11).
(12) A production crane shall be operated by a competent person who is in possession of a subsisting crane operator’s medical certificate. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 195 (12).
(13) A person operating a production crane shall,
(a) be physically and mentally fit to discharge the duties of a crane operator;
(b) undergo a medical examination by a physician before commencing work as a crane operator and every twelve months thereafter;
(c) obtain a crane operator’s medical certificate from the physician certifying that the person is physically fit to operate a crane and is not subject to any infirmity of body or mind that may interfere with the duties of a crane operator. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 195 (13).
(14) The crane operator’s medical certificate shall,
(a) expire one year from its date; and
(b) be kept on file and recorded on a posted list of active crane operators. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 195 (14).
(15) The crane operator’s medical certificate shall be in the following form:
Occupational Health and Safety Act
CRANE OPERATOR’S MEDICAL CERTIFICATE
|
I have this day examined |
||
|
|
||
|
name: ……………………………………..…………….. and certify he (she) is physically fit to operate a crane and is not subject to any infirmity of body or mind that may interfere with the duties of a crane operator. |
||
|
|
||
|
|
…………………………………………..…………………… |
|
|
|
(signature of qualified medical practitioner) |
|
|
|
||
|
……………………………….……..… |
|
|
|
(date) |
|
|
R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 195 (15).
196. (1) No person shall ride on a conveyor belt. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 196 (1).
(2) A conveyor shall have,
(a) a pull cord at accessible locations along the conveyor by means of which the conveyor can be stopped;
(b) a means whereby belt dressing may be applied safely while the conveyor is in motion;
(c) when the conveyor is started automatically, by remote control or where a portion or portions of the conveyor are not visible from the operator’s position, a start-up warning device; and
(d) head, tail, drive, deflection and tension pulleys guarded at any pinch point that is or may become accessible. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 196 (2); O. Reg. 68/96, s. 4 (1).
(3) A pull cord required by clause (2) (a) shall,
(a) be within easy reach of accessible locations along the conveyor; and
(b) operate a manual reset type switch that stops the conveyor. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 196 (3).
(3.1) A guard for a pulley referred to in clause (2) (d) must extend at least 0.9 metres from the pinch point. O. Reg. 68/96, s. 4 (2).
(4) Guards shall be provided beneath a conveyor,
(a) that passes over a worker; or
(b) from which falling materials or parts may endanger a worker. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 196 (4).
(5) A conveyor in an underground mine shall have,
(a) devices that guard against excessive slip between the belt and the driving pulley; and
(b) a fire suppression system at the driven end unless fire retardant belting is used or the conveyor is continually attended by a worker. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 196 (5).
(6) A conveyor shall be stopped and the prime mover de-energized, locked and tagged out when the conveyor is undergoing repairs, adjustments or maintenance unless,
(a) it is necessary to run the conveyor during such work; and
(b) special precautions are taken to prevent injury to a worker from moving parts. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 196 (6).
197. (1) A power driven raise climber shall,
(a) have at least two independent means of braking,
(i) one of which shall be as close as practical to the final drive of the motor,
(ii) each capable of stopping and holding the climber with its maximum rated load, and
(iii) each arranged to permit independent testing;
(b) have the maximum load that it may carry as certified by its manufacturer, displayed on the climber or at the raise service position;
(c) be operated within the maximum load limit;
(d) except when the track on which it operates is being extended, have a stop block to prevent the climber being taken beyond the track;
(e) have an effective means for communication between the climber and the raise service position; and
(f) have an overspeed safety device approved by the manufacturer of the climber that will stop and hold the climber if it travels faster than its design speed. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 197 (1); O. Reg. 60/94, s. 10.
(2) A raise climber that is electrically powered shall,
(a) not be operated in excess of 750 volts;
(b) be protected by a ground fault system;
(c) have a visible break switch at the raise service area by which its power can be isolated;
(d) have a switch at the raise service area by which its power can be safely interrupted; and
(e) have a control switch on the climber by which power to its motor can be removed. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 197 (2).
(3) The electrical supply to a raise climber shall be disconnected while explosives and electric caps are being loaded into a position for blasting. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 197 (3).
(4) A means by which workers can be reached and removed from a raise climber shall be available for use. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 197 (4).
(5) Devices that may affect the safe operation of a raise climber shall be examined by a competent person,
(a) before the raise climber is first used at the raise and daily thereafter when in use; and
(b) during every major overhaul of the raise climber. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 197 (5).
(6) A major overhaul shall be performed on a raise climber at the frequency recommended by the manufacturer of the climber or a competent person, whichever is the more frequent. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 197 (6).
(7) A raise climber being used at a raise shall be cleaned thoroughly weekly. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 197 (7).
(8) The brakes and controls of the raise climber shall be tested prior to first being used during a workshift. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 197 (8).
(9) The main shafting of the drive train of a raise climber shall be subjected to a nondestructive test by a competent person to determine if it is in sound condition,
(a) before the raise climber is first put into service; and
(b) during every major overhaul of the raise climber and not less frequently than once for every 4,000 hours of use. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 197 (9); O. Reg. 174/01, s. 6.
(10) A log book shall be kept for each raise climber and the log book shall contain,
(a) a record of the dates the examinations prescribed in subsections (5) and (9) are performed;
(b) a record of the findings during the examinations referred to in clause (a);
(c) a record of any repairs and modifications, and the signature of the person performing such examinations, repairs and modifications; and
(d) the signature of the supervisor authorizing the repairs and modifications referred to in clause (c). R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 197 (10).
(11) The owner shall give written notice to the joint health and safety committee or a health and safety representative, if any, of a proposed raise climber installation. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 35.
(12) A raise climber shall be,
(a) designed, maintained and operated in accordance with good engineering practice; and
(b) built and installed in accordance with the design. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 35; O. Reg. 236/99, s. 7 (1).
(13) The employer of workers operating the raise climber shall ensure that a notice showing the maximum number of persons or load weight is posted on or near the raise climber and that the number or weight is not exceeded. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 35; O. Reg. 236/99, s. 7 (2).
(14) Revoked: O. Reg. 236/99, s. 7 (3).
198. (1) Procedures for the safe operation of a steam or compressor plant shall be prepared in writing and made available to the workers operating and maintaining the plant. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 198 (1).
(2) A steam boiler or compressor to which Ontario Regulation 220/01 (Boilers and Pressure Vessels) made under the Technical Standards and Safety Act, 2000 does not apply shall be regularly cleaned and examined for proper and safe condition. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 11.
199. (1) An air compressor driven by a prime mover exceeding twenty-five kilowatts when installed in an underground mine shall be,
(a) designed and installed so as to minimize the hazard of fire or explosion due to the accumulation of carbonaceous materials in the air system;
(b) provided with protective devices that prevent its operation if,
(i) the temperature of the air at the discharge line is in excess of normal,
(ii) the temperature of the compressor cooling water and cooling air is in excess of normal, or
(iii) the flow and pressure of compressor lubricating oil is below normal;
(c) provided with an alarm that,
(i) is audible and visible to the worker in charge of the compressor,
(ii) operates when a device as prescribed in clause (b) is activated,
(iii) operates as long as the conditions exist that cause a device as prescribed in clause (1) (b) to operate. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 199 (1).
(2) No protective device prescribed in clause (b) shall be,
(a) capable of automatically restarting the compressor; and
(b) used unless tested and found to function properly. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 199 (2).
200. (1) A reciprocating type air compressor driven by a prime mover exceeding thirty kilowatts, that is lubricated by oil and discharges to a closed system over 100 kilopascals, shall have,
(a) a temperature-indicating device installed at the high-pressure discharge pipe; and
(b) the normal operating temperature marked on the device. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 200 (1).
(2) The discharge air temperature shall be,
(a) read at least once every operating shift; and
(b) recorded in a compressor log book. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 200 (2).
201. (1) An operator of mobile cranes, shovels and boom trucks, or similar equipment, whereby rope is wound onto a drum driven by an engine for the purpose of raising, lowering or swinging materials, shall,
(a) have a subsisting certificate of qualification as a hoisting engineer under the Trades Qualification and Apprenticeship Act; or
(b) be qualified in accordance with a program approved by the Director, when the person is an employee of the mine or mining plant. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 201 (1); O. Reg. 60/94, s. 11.
(2) An approved program referred to in clause (1) (b) shall consist of,
(a) instruction time;
(b) field time;
(c) familiarization with the equipment to be used; and
(d) a method of examination. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 201 (2).
(3) Mobile cranes, shovels, boom trucks and similar equipment shall be inspected for safe and proper condition by a competent person,
(a) before being used at the start of each workshift; and
(b) at regular intervals as recommended by the manufacturer. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 201 (3).
202. (1) Standard practices to govern the safe operation of a standard gauge railroad, a self-propelled track crane, motorized equipment used for the maintenance of a standard gauge railroad, a motor vehicle equipped with rail wheels in addition to rubber-tired wheels or other similar equipment shall be prepared in writing. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 202 (1).
(2) A copy of the standard practices prepared in accordance with subsection (1) shall be provided to each railroad worker and each railroad worker,
(a) shall be trained and instructed in and be knowledgeable of the standard practices for his or her work; and
(b) shall have a copy of the standard practices readily available while on duty. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 202 (2).
(3) Where a railroad of a mine or mining plant interconnects with a railroad of a railway company a standard procedure shall be established and followed for carrying on operations on the first mentioned railroad. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 202 (3).
(4) A railroad shall be built to safely withstand speeds and loads to which it will normally be subjected by a train. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 202 (4).
(5) A low bridge warning sign shall be installed at an approach of a railroad to an overhead structure, where the clearance between the underside of the structure and the top of any railway car is less than two metres. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 202 (5).
(6) Guard rails shall be placed at the approach to railroad tracks where the view is obstructed in one or both directions. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 202 (6).
(7) A locomotive shall,
(a) have an audible warning system in proper working condition;
(b) have a suitable headlight for each travel direction when operating in areas without adequate lighting;
(c) be equipped with brakes in proper working condition; and
(d) have the control lever so mounted as to prevent its inadvertent removal. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 202 (7).
(8) The locomotive operator shall be in position at the controls when operating the locomotive on manual control. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 202 (8).
(9) Before leaving a locomotive unattended, the operator shall,
(a) set the controls in position for parking;
(b) set the brakes; and
(c) on a grade, use hand brakes or wheel chocks to prevent movement of the locomotive. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 202 (9).
(10) The owner shall give notice to the joint health and safety committee or the health and safety representatives, if any, before installing remote or automatic controls for the operation of a locomotive. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 36.
(11) A standard practice shall be prepared for the use of radio communications systems on a railroad. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 202 (11).
(12) Only authorized persons shall ride on a train. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 202 (12).
(13) One or more workers shall be stationed to direct the operator of a locomotive when backing a train in a location where persons may be endangered. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 202 (13).
(14) A car shall not be permitted to run free unless,
(a) adequate control thereof is maintained; and
(b) there is no hazard to a worker. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 202 (14).
203. (1) Subject to subsection (5), no mine hoisting plant shall be operated without a professional engineer giving written statement to the owner setting out,
(a) the location of the plant;
(b) the maximum loading of number of persons and material that may be carried by the plant when it is installed, maintained and operated in compliance with this Regulation;
(c) that the plant is designed and manufactured in accordance with appropriate engineering standards and installed where it is being operated in compliance with good engineering practice. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 37.
(2) Subsection (1) does not apply to a plant that is operated for testing purposes. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 37.
(3) The owner shall ensure that a copy of the statement for each plant is available at the mine site and readily reviewable by the workers and that a copy is given to the joint health and safety committee or health and safety representative, if any. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 37.
(4) The mine owner shall ensure that the mine hoisting plant is installed, maintained and operated in compliance with this Regulation. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 37.
(5) Subsections (1) and (3) do not apply to a plant being operated under a permit issued by the Ministry of Labour before August 16, 1997. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 37.
204. (1) Subject to subsection (5), no shaft conveyance shall be operated without a professional engineer giving written statement to the owner setting out,
(a) the location of the conveyance;
(b) the maximum loading of number of persons and material that may be carried by the conveyance when it is installed, maintained and operated in compliance with this Regulation;
(c) that the conveyance is designed and manufactured in accordance with appropriate engineering standards and installed where it is being operated in compliance with good engineering practice. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 37.
(2) Subsection (1) does not apply to a conveyance that is operated for testing purposes. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 37.
(3) The owner shall ensure that a copy of the statement is posted at the shaft collar and that a copy is given to the joint health and safety committee or health and safety representative, if any. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 37.
(4) The owner shall ensure that the conveyance is installed, maintained and operated in compliance with this Regulation. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 37.
(5) Subsections (1) and (3) do not apply to a conveyance being operated under a permit issued by the Ministry of Labour before August 16, 1997. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 37.
205. Tests for compliance with this Regulation shall be conducted on a mine hoisting plant before being put into initial service in a particular location. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 205.
206. (1) In determining the maximum weight to be included in the written statement required under subsection 204 (1), the professional engineer shall take into consideration the maximum load that a mine hoisting plant is capable of safely carrying. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 38.
(2) Subject to subsection (3), the maximum number of persons that can be carried on a shaft conveyance shall be determined as follows:
1. Where the clear floor area of a deck of a shaft conveyance is 1.86 square metres or less, there shall be at least 0.19 square metre for each person.
2. Where the clear floor area of a deck of a shaft conveyance is more than 1.86 square metres and less than 4.64 square metres, there shall be at least 0.16 square metre for each person.
3. Where the clear floor area of a deck of a shaft conveyance is 4.64 square metres or more, there shall be at least 0.14 square metre for each person. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 206 (2).
(3) The maximum number of persons that may be carried by a shaft conveyance shall not exceed 85 per cent of the maximum weight of materials divided by ninety kilograms. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 206 (3).
207. The following log books shall be obtained from the Ministry and used for each mine hoisting plant:
1. Electrical Hoisting Equipment Record Book.
2. Hoisting Machinery Record Book.
3. Hoist operator’s Log Book.
4. Rope Record Book.
5. Shaft Inspection Record Book. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 207.
208. A headframe on surface or underground in an underground mine shall,
(a) be designed in accordance with good engineering practice;
(b) have the plans of the design certified by a professional engineer;
(c) be constructed in accordance with the design;
(d) be of sufficient strength to safely withstand all loads to which it is likely to be subjected; and
(e) be of sufficient height to provide a distance for an overwind that exceeds the greater of,
(i) twice the stopping distance of the hoist at the maximum speed permitted by the hoist controls, or
(ii) three metres. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 208.
209. (1) A mine shaft shall,
(a) be designed in accordance with good engineering practice;
(b) have a means to guide each shaft conveyance to prevent contact with another shaft conveyance or shaft furnishings;
(c) have underwind clearances that exceed the stopping distance of the shaft conveyance when travelling at the maximum speed permitted by the hoist-controls, except,
(i) during shaft sinking, or
(ii) when chairs are used to land a skip during loading; and
(d) where a friction hoist is installed, have tapered guides or other such devices above and below the limits of regular travel of the shaft conveyance and counterweight, arranged to act as a direct physical brake to decelerate and stop the counterweight and shaft conveyance in the event of an over-travel. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 209 (1).
(2) A barrier or obstruction to prevent a shaft conveyance from being lowered into water in the shaft bottom must be installed in the shaft except,
(a) when the shaft is being sunk; or
(b) where a friction hoist is installed. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 9.
(3) A probe indicating the high water level shall be installed below the lowest working level in a shaft in which natural drainage is not provided and in which flooding may occur due to equipment failure. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 9.
(4) The probe shall be installed so that it can be read by the person in control of the hoist. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 9.
(5) The probe shall be installed so that,
(a) it enables the person in control of the hoist to prevent a shaft conveyance from being lowered into water; or
(b) it prevents a shaft conveyance from being lowered into water. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 9.
(6) If a probe is installed, a procedure must be established to prevent a conveyance with occupants from being lowered into water. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 9.
(7) The employer shall establish the procedure in consultation with the joint health and safety committee. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 9.
(8) The procedure shall be implemented when the probe indicates that there is water at the high water level. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 9.
210. (1) Subject to subsection (5), protective devices and procedures shall be used to prevent a shaft conveyance or counterweight from coming into contact with an intermediate shaft obstruction. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 210 (1).
(2) A device which may become an intermediate shaft obstruction shall be positively locked out of the shaft compartment to prevent inadvertent entry into the compartment. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 210 (2).
(3) The location of the intermediate shaft obstruction shall be marked on the depth indicator of a hoist. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 210 (3).
(4) The protective procedure for operating the intermediate shaft obstruction shall be prepared in writing and posted for use by the hoist operator. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 210 (4).
(5) Doors for covering the shaft at the collar to facilitate the maintenance of a shaft conveyance are not an intermediate shaft obstruction if,
(a) they are positively latched out of the shaft compartments when not in use; and
(b) dual lights are installed to indicate to the hoist operator whether such doors are in or out of the shaft compartment. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 210 (5).
(6) Equipment used to directly discharge material into a skip shall operate in such a way that actuating power is required before any gate will open. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 5.
211. (1) This section applies if a shaft conveyance is being used to transport persons. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 12.
(2) The hoist shall be equipped with control devices that prevent the shaft conveyance from being taken,
(a) to the dump position, unless a procedure is established and followed that ensures persons on the shaft conveyance remain securely in place if the conveyance is taken to the dump position; or
(b) below a loading pocket, unless the controls for loading the shaft conveyance from that pocket have been made inoperative or the persons are being transported in a separate compartment of the shaft. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 12.
(3) If a shaft conveyance that is being used to transport persons is not a cage or a combination skip and cage designed to normally transport persons, the hoist shall not be permitted to travel at a speed that is more than the lesser of,
(a) one-half the normal speed of the hoist; or
(b) five metres per second. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 12.
(4) The control devices of the hoist shall be designed and installed to be fail safe. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 12.
(5) An audible or visible signal that the control devices for the hoist are set in operation shall be given to persons entering the shaft conveyance. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 12.
212. (1) Chairs used for landing a cage shall be,
(a) arranged to fall clear and remain clear of the shaft compartment when the cage is lifted off the chairs;
(b) operable only from outside the cage; and
(c) so arranged as not to distort the cage. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 212 (1).
(2) Chairs fastened to shaft station posts shall be of a chain type. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 212 (2).
213. A certificate for each hoist shall be obtained from the manufacturer of the hoist or a professional engineer competent in the design of mine hoisting plants certifying,
(a) the maximum rope pull;
(b) the maximum suspended load; and
(c) the maximum unbalanced load in the case of a friction hoist,
and no hoist shall be loaded above the maximums as certified. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 213.
214. (1) No hoist shall be used for the transporting of persons unless it has a braking system consisting of at least two sets of mechanical brakes to stop and hold the drum for the shaft conveyance transporting the persons. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 214 (1).
(2) Each set of mechanical brakes shall,
(a) stop and hold the drum when the shaft conveyance or counterweight is operating at its maximum load;
(b) be so arranged to be capable of being tested independently; and
(c) be arranged to apply normal braking effort before a linkage or brake piston reaches a limit of travel. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 214 (2).
(3) At least one of the mechanical brakes shall be designed and arranged so that the brake,
(a) applies directly to the drum; and
(b) applies automatically when,
(i) the safety circuit of the hoist is interrupted, or
(ii) the pressure in the hydraulic or pneumatic system for applying brakes has dropped below normal. O. Reg. 486/99, s. 13.
(4) The braking system shall be arranged so that,
(a) the brakes are applied by control levers that are pulled unless brake and power control levers are common;
(b) any brake weights installed to provide auxiliary braking force can be readily tested for freedom of movement; and
(c) the hoist brakes are applied automatically upon the loss of electrical, hydraulic or pneumatic power. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 214 (4).
(5) Subject to subsection (6), the brakes of a drum hoist shall be arranged to decelerate the hoist at a rate greater than 1.5 metres per second per second and less than 3.7 metres per second per second where braking is initiated by an interrupted safety circuit and the hoist is,
(a) normally used for the transporting of persons; and
(b) operating in the normal full speed zone. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 214 (5).
(6) Subsection (5) does not apply to a drum hoist installed at a particular location prior to the 1st day of October, 1979. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 214 (6).
(7) The brakes of a drum hoist installed in a particular location before the 1st day of October, 1979 and that is normally used for transporting persons shall be tested to determine its deceleration rates. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 214 (7).
(8) Where the tests prescribed in subsection (7) establish that the deceleration rates are in excess of 5.5 metres per second per second and where it is practical to do so, the hoist shall be modified before the 1st day of October, 1981 so as to reduce the deceleration rate to 5.5 metres per second per second or less. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 214 (8).
(9) The braking system of a hoist not normally used to transport persons shall be designed and arranged to safely stop and hold the hoist under all conditions of normal load, speed and direction of travel. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 214 (9).
(10) Clause (4) (a) does not apply to a hoist that was installed before the 1st day of October, 1979. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 214 (10).
215. (1) A clutch of a drum hoist shall be interlocked with the brake so that,
(a) the clutch can be disengaged only when the brake of the drum is fully applied;
(b) the clutch is fully engaged before the brake of the drum can be released; and
(c) the brake will apply if the clutch begins to disengage inadvertently. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 215 (1); O. Reg. 60/94, s. 12 (1).
(2) The controls for engaging and disengaging a clutch shall be guarded to prevent their inadvertent operation. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 215 (2).
(3) No band type friction clutch shall be used. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 215 (3).
(4) A device must be installed that indicates to the hoist operator whether or not the clutch is fully engaged. O. Reg. 60/94, s. 12 (2).
(5) The following apply if a hoist is installed on or after October 25, 2002 or if a brake control system or clutch control system on a hoist is modified after that date:
1. The hoist shall be designed and equipped with at least two independent clutch brake interlocking systems to prevent any single component from causing a failure.
2. The hoist shall be designed so that the clutch brake interlocking systems may be safely examined.
3. The clutch control shall be designed so that the selection of clutch disengagement automatically applies the clutch drum brake. O. Reg. 291/02, s. 7.
216. (1) Except as prescribed in subsections (2), (3) and (4), the drum diameter to rope diameter ratio for a drum hoist shall be equal to or greater than,
(a) 60 to 1, where the nominal rope diameter is 25.4 millimetres or less; or
(b) 80 to 1, where the nominal rope diameter is greater than 25.4 millimetres. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 216 (1).
(2) The drum diameter to rope diameter ratio for a drum hoist in use for shaft sinking or for preliminary development work during shaft sinking shall be equal to or greater than,
(a) 48 to 1, where the nominal rope diameter is 25.4 millimetres or less; and
(b) 60 to 1, where the nominal rope diameter is greater than 25.4 millimetres. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 216 (2).
(3) The drum diameter to rope diameter ratio of a friction hoist shall be equal to or greater than,
(a) 80 to 1, for stranded ropes; and
(b) 100 to 1, for locked coil ropes. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 216 (3).
(4) Subsection (1) does not apply to a drum hoist where the drum diameter to rope diameter is,
(a) 54 to 1, where the nominal rope diameter is 25.4 millimetres or less; or
(b) 72 to 1, where the nominal rope diameter is greater than 25.4 millimetres,
so long as the drum hoist was manufactured prior to 1954 and the original load rating given by its manufacturer is not exceeded. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 216 (4).
217. (1) No drum hoist shall have,
(a) more than three layers of rope where the drum has helical or spiral grooving or does not have grooving;
(b) more than four layers of rope if the drum has parallel and half pitch grooving; and
(c) less than three dead turns of the rope on the drum. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 217.
(2) Despite clause (1) (b), a drum hoist may have a maximum of five layers of rope if,
(a) the mine hoisting plant meets the standards set out in SABS Code of Practice 0294, Ed. 1, “The performance, operation, testing and maintenance of drum winders relating to rope safety”, as approved according to procedures of SABS on August 4, 2000; and
(b) the rope is used, maintained and examined according to the requirements set out in SABS Code of Practice 0293:1996, “Condition assessment of steel wire ropes on mine winders”, as approved by the President of SABS on September 16, 1996. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 13.
218. (1) Subject to subsection (2), the drum of a drum hoist shall be provided with,
(a) grooves that properly fit the rope, unless the hoist is being used for shaft sinking or preliminary development work during shaft sinking in which case the drum may be smooth; and
(b) flanges of sufficient height to contain all the rope and which are strong enough to withstand any loading by the rope. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 218 (1).
(2) A conical drum hoist shall be provided with grooves that prevent the rope from slipping off. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 218 (2).
219. A drum hoist and a sheave shall be arranged so that the rope,
(a) coils properly across the face of the drum;
(b) winds smoothly from one layer to another; and
(c) winds without cutting into the rope layer beneath. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 219.
220. Bolts and other fittings of a mine hoisting plant shall be properly secured. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 220.
221. A hoist shall be provided with depth indicators that continuously, accurately and clearly show to the hoist operator the position,
(a) of a shaft conveyance and counterweight, if any;
(b) in an inclined shaft, of a change in gradient that requires a reduction in hoist speed;
(c) at which the overwind, underwind and track limit devices are set to operate;
(d) of any intermediate shaft obstruction;
(e) of the limits of normal travel for the shaft conveyance and counterweight, if any; and
(f) of any collar doors, dump doors and crosshead landing chairs. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 221.
222. (1) A steam or air powered hoist shall be provided with devices that,
(a) protect against an overwind;
(b) protect against an underwind, except during shaft sinking;
(c) indicate the air or steam pressure for the hoist operator; and
(d) permit the air or steam supply to the hoist engine to be readily shut off by the hoist operator. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 222 (1).
(2) Where the hoisting plant consists of a single shaft conveyance without a counterweight, the compression of the engine of an air or steam powered hoist may be used as an automatic brake if,
(a) the engine is non-reversing;
(b) the exhaust restraining valve is fail safe;
(c) the piping system is strong enough to withstand the air or steam pressures;
(d) the compression has sufficient braking capacity to stop the hoist carrying its maximum load;
(e) the normal speed of the hoist is less than 2.5 metres per second; and
(f) specifications and arrangements of the hoist have been prepared or checked by a professional engineer and comply with this section. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 222 (2); O. Reg. 272/97, s. 39.
223. A hoist being used as a tugger or a utility hoist shall be maintained and used so as not to endanger the safety of a worker. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 223.
224. A hoist that is relocated shall comply with the requirements of this Regulation. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 224.
225. (1) Before a sheave is used, a certificate for the sheave shall be obtained from the manufacturer of the sheave or a professional engineer competent in sheave design certifying as to,
(a) the maximum rated load;
(b) the diameter of rope for which it was designed;
(c) the breaking strength of the rope for which it was designed; and
(d) the maximum amount of groove wear that shall be permitted. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 225 (1).
(2) No sheave shall be,
(a) loaded above the maximum rated load; or
(b) used other than in compliance with the certificate. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 225 (2).
(3) The ratio of the diameter of the sheave to the diameter of the rope shall be as prescribed in section 216. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 225 (3).
(4) A sheave shall,
(a) be made of materials which will safely withstand the ambient temperatures;
(b) be fitted with a groove to fit the rope being used; and
(c) bear a serial number and the date of its manufacture. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 225 (4).
(5) The shaft of a sheave shall be examined for flaws by a non-destructive test by a person competent in such testing,
(a) before being put into service in a particular location;
(b) after installation; and
(c) at a regular frequency as recommended by a person competent in such testing. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 225 (5).
226. (1) No hoist that is electrically powered shall be used unless it has a safety circuit that,
(a) is fail safe;
(b) when interrupted, operates to,
(i) set the brakes,
(ii) remove power from the hoist motor or motors, and
(iii) stop the mine hoist when in motion. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 226 (1).
(2) The safety circuit of a hoist shall be interrupted when,
(a) there is a failure of a power supply to the hoist electrical system which may affect safe operation;
(b) there is an overload on the hoist motors of a magnitude and duration exceeding normal;
(c) there is a short circuit in the hoist electrical system; and
(d) a prescribed safety device has operated. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 226 (2).
(3) A switch to interrupt the safety circuit of a hoist shall be installed and the switch shall be,
(a) manually operable;
(b) located within easy reach of the hoist operator when at the controls;
(c) readily recognizable; and
(d) readily operable. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 226 (3).
(4) A track limit device shall be installed in each shaft compartment that will be operated directly by the shaft conveyance or counterweight to interrupt the safety circuit of a hoist in the case of an overwound shaft conveyance or counterweight. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 226 (4).
(5) Devices shall be installed to protect a shaft conveyance or counterweight against,
(a) an overwind;
(b) an underwind, except during shaft sinking;
(c) approaching the limits of travel at an excessive speed; and
(d) operating or being operated at an overspeed in excess of that for which the hoisting plant was designed and intended. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 226 (5).
(6) The devices required by subsection (5) shall,
(a) operate to interrupt the safety circuit when activated;
(b) be driven directly by the drum;
(c) be protected for loss of motion;
(d) prevent the paying out of excess rope during shaft sinking; and
(e) be set to stop the hoist before a shaft conveyance, counterweight and their attachments make contact with a fixed part of a mine shaft or headframe. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 226 (6).
(7) Devices shall be installed for a friction hoist that are set to interrupt the safety circuit where,
(a) there is abnormal slip between the hoist drum and the hoist ropes;
(b) there is abnormal wear of the rope treads or the tread wear limit has been reached;
(c) a shaft conveyance and counterweight approaches the collar of a mine shaft at excessive speed; or
(d) a violent swing or large rise in the loop of a balance rope occurs. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 226 (7).
(8) The devices required for the purposes of clause (7) (c) shall be installed in the mine shaft. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 226 (8).
(9) On a friction hoist, a device shall be installed that synchronizes the position of the shaft conveyance with safety devices driven from the drum. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 226 (9).
(10) A hoist that is electrically powered shall,
(a) have an ammeter within plain view of the hoist operator to indicate the hoist motor current;
(b) except when the slowdown control at the limits of travel is automatic, have a device to warn the operator, audibly, that the hoist is approaching the limit where a reduction in speed is necessary for safe manual braking; and
(c) have a speed indicator if the normal speed exceeds 2.5 metres per second;
(d) have a device from which a voltage signal that is proportioned to the speed of the hoist can be obtained;
(e) have a backout device as prescribed in subsection (11) by which a shaft conveyance or counterweight can be removed from an overwound or underwound position;
(f) if equipped with an underwind by-pass device, have such device,
(i) manually operable only, and
(ii) restrict the hoist operation to slow speed;
(g) have overwind by-pass devices that,
(i) are manually operable only,
(ii) when in use restrict hoist operation to slow speed, and
(iii) allow hoist travel beyond the first device providing overwind protection;
(h) have a master controller that has a neutral or brake reset position;
(i) have any brake operating levers arranged so that upon an interruption of the safety circuit the power to the hoist cannot be restored until the levers are in the brake applied position;
(j) have accurate and sensitive safety controllers; and
(k) have each safety-related device capable of being effective under the environmental conditions in which it is installed. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 226 (10).
(11) A backout device shall,
(a) be manually operable only; and
(b) prevent the brake or brakes from being released until sufficient torque has been developed to ensure movement in the correct direction. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 226 (11).
(12) The adjustment of a protective device shall be altered only by a competent person authorized to do so. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 226 (12).
227. (1) A device that permits changing from manual to automatic control shall be installed on an automatic hoist and the device shall be,
(a) located where it is readily accessible to the manual controls; and
(b) operated only by an authorized worker. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 227 (1).
(2) Where a hoist is designed to be operated from control stations located at shaft levels and within a shaft conveyance, the switch for affecting the change-over of the control mode between that at the shaft levels and at the shaft conveyance shall be effective only at the shaft level at which the shaft conveyance is stopped. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 227 (2).
(3) Devices installed on the levels for the purpose of selecting the shaft conveyance destination and initiating hoist movement shall be effective only when,
(a) the shaft conveyance is stopped at that level; and
(b) the installation is designed for call operation. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 227 (3).
(4) When an executive signal for hoist motion is given from controls at a level, at least five seconds shall lapse before the hoist moves. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 227 (4).
(5) Except for jogging, devices at shaft level control stations for initiating hoist motion shall be effective only when the shaft gate at the level where the conveyance is stopped is closed. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 227 (5).
(6) Except for jogging, devices located within a cage for initiating hoist motion shall be effective only when the door of the cage and the gate of the shaft are closed. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 227 (6).
(7) Where the controls for initiating hoist motion are located within a cage, a device shall be installed in the cage by which the safety circuit of the hoist can be interrupted. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 227 (7).
228. (1) A shaft rope shall not be used unless,
(a) a 2.5 metre representative sample has been subjected to a destructive test in accordance with CSA Standard G4-00 “Steel Wire Rope for General Purpose and for Mine Hoisting and Mine Haulage”; and
(b) a Certificate of Test has been obtained from a cable testing laboratory approved by the Minister. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 228 (1); O. Reg. 31/04, s. 14 (1).
(2) The test described in subsection (2.1) shall be performed not more than six months after a hoisting rope is first used on a drum hoist, and afterwards at intervals of not more than six months. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 10 (1).
(2.1) A piece of the rope at least 2.5 metres long located at the lower end above the attachment to the conveyance shall be cut off, have its ends fastened to prevent unravelling and be tested in accordance with CSA Standard G4-00 “Steel Wire Rope for General Purpose and for Mine Hoisting and Mine Haulage”. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 14 (2).
(2.2) The date of each test under subsections (1) and (2.1) and the results obtained shall be recorded in the Rope Record Book for the rope. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 14 (2).
(3) A Certificate of Test issued under section 20 shall be kept available for inspection, and a copy shall be given to the joint health and safety committee or health and safety representative, if any. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 14 (2).
(4) A hoisting rope being used as a shaft rope shall be tested throughout its working length by a competent person using an electromagnetic testing device designed, built and tested according to appropriate engineering standards,
(a) within six months of being put into service; and
(b) thereafter at regular intervals not exceeding four months; or
(c) at intervals shorter than four months where, by extrapolation from past tests, the loss in breaking strength will exceed 10 per cent before the next prescribed test. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 228 (4); O. Reg. 779/94, s. 10 (2); O. Reg. 272/97, s. 40 (1).
(5) A balance rope and, where practical, a guide and a rubbing rope in use, shall be tested throughout its working length by a competent person using an electromagnetic testing device designed, built and tested according to appropriate engineering standards,
(a) within twelve months of being put into service; and
(b) thereafter at regular intervals not exceeding eight months except where a test discloses a loss exceeding 5 per cent of the breaking strength recorded on the Certificate of Test, in which case the regular intervals shall not exceed four months. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 228 (5); O. Reg. 272/97, s. 40 (2).
(6) The date of each electromagnetic test and the results obtained shall be recorded in the Rope Record Book for the rope. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 228 (6).
(7) A person competent to do so shall interpret the electromagnetic test and graphs and shall sign the record consisting of the test, the graphs and the interpretation. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 40 (3).
(8) The record shall be kept readily available at the mine site while the rope is in service. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 40 (3).
(9) If a test shows a loss exceeding 7.5 per cent of the breaking strength recorded on the Certificate of Test, the person who signs the record shall send a copy of the record of the test to the owner and the joint health and safety committee or health and safety representative, if any, within 14 days after the test is completed. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 40 (3).
(10) A rope shall not be used as a shaft rope if it has been spliced. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 10 (3).
(10.1) A shaft rope shall not be reversed unless it is used on a friction hoist. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 10 (3).
(11) The minimum nominal diameter of a hoisting rope shall exceed,
(a) 15.9 millimetres where only one rope supports a shaft conveyance or counterweight; and
(b) 12.7 millimetres where more than one rope supports a shaft conveyance or counterweight. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 228 (11).
(12) The factor of safety of a hoisting rope installed on a drum hoist shall not be less than,
(a) 8.5 at the point the rope is attached to a shaft conveyance or counterweight, subject to clause (b);
(b) 7.5 at the point the rope is attached to a skip or counterweight where the material load was accurately weighed; and
(c) 5.0 at the point the rope leaves the head sheave when the shaft conveyance or counterweight is at its lowest point of normal travel, subject to subsection (12.1). O. Reg. 31/04, s. 14 (3).
(12.1) Clause (12) (c) does not apply if,
(a) the drum hoist is being used in a vertical shaft;
(b) at the point that the rope leaves the head sheave when the shaft conveyance or counterweight is at its lowest point of normal travel, the rope has a breaking strength at the time of installation of not less than that obtained from the formula, 25,000 divided by the quantity (4,000 plus L) multiplied by the maximum suspended load to be carried by the rope, including the load represented by the weight of the rope itself, where L is the maximum length of the rope in metres, in the shaft compartment below the head sheave;
(c) the mine hoisting plant meets the standards set out in SABS Code of Practice 0294, Ed. 1, “The performance, operation, testing and maintenance of drum winders relating to rope safety”, as approved according to procedures of SABS on August 4, 2000; and
(d) the rope is used, maintained and examined according to the requirements set out in SABS Code of Practice 0293:1996, “Condition assessment of steel wire ropes on mine winders”, as approved by the President of SABS on September 16, 1996. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 14 (3).
(13) The factor of safety of a hoisting rope installed on a friction hoist shall not be less than the greater of,
(a) the factor obtained from the formula 8.0 minus 0.00164 L, where L is the maximum length of the rope in metres, in the shaft compartment below the head sheave or the drum of a friction hoist; or
(b) 5.5. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 228 (13); O. Reg. 31/04, s. 14 (4).
(14) The factor of safety of a tail or balance rope shall not be less than 7. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 228 (14).
(15) The factor of safety of a guide or a rubbing rope shall not be less than 5. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 228 (15).
(16) Notice in duplicate in the form set out in the Rope Record Book of the installation of a shaft rope and containing the information set out in the said Book shall be kept readily available at the mine site. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 228 (16); O. Reg. 272/97, s. 40 (4).
(17) When a shaft rope is removed from service notice thereof shall be kept readily available at the mine site for one year and the notice shall,
(a) state,
(i) the date of removal,
(ii) the reason for removal, and
(iii) the disposition of the removed rope; and
(b) be in the form of the detachable part of the white Rope Installation Sheet in the Rope Record Book. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 228 (17); O. Reg. 272/97, s. 40 (5).
(18) No rope shall be used as a shaft rope where the breaking strength of the rope has dropped below the breaking strength set out in the Certificate of Test as follows:
1. In any part of a hoisting rope, 90 per cent.
2. In any part of a multi-layer, multi-strand balance rope, 90 per cent.
3. In any part of a single layer stranded balance rope, 85 per cent.
4. In any part of a guide or rubbing rope, 75 per cent. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 228 (18).
(19) Despite subsection (18), no rope shall be used as a shaft rope where,
(a) the extension of a test piece has decreased to less than 60 per cent of its original extension when tested to destruction and marked corrosion or considerable loss in wire torsions has occurred;
(b) the number of broken wires, excluding filler wires, in any section equal to one lay length exceeds 5 per cent of the total; or
(c) the rate of stretch in a friction hoisting rope shows a rapid increase over its normal stretch recorded during its service. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 228 (19).
(20) If hoisting is discontinued or suspended in a shaft compartment, each shaft rope shall be removed from the shaft immediately. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 10 (4).
(21) Despite subsection (20), shaft ropes may be left in a shaft compartment if the ropes are continually maintained and tested in accordance with this Regulation. O. Reg. 779/94, s. 10 (4).
229. (1) Shaft ropes shall be attached by closed type devices that will not inadvertently disconnect. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 229 (1).
(2) In a drum hoist installation, the hoisting rope from a shaft conveyance and counterweight shall be attached to the drum of the hoist. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 229 (2).
(3) No wedge type attachments shall be used unless the attachments are,
(a) in sound condition; and
(b) certified at least once every six years of use as being in sound condition by a competent person or by the manufacturer. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 229 (3).
(4) When the attachments for a shaft hoisting rope are first installed, or re-installed after disassembling, the following measures and procedures shall be taken before the hoist is put to use:
1. Two test trips of the conveyance or counterweight through the working part of the shaft, while the conveyance or counterweight is carrying normal load shall be performed.
2. An examination of the attachments upon the completion of the two test trips shall be made.
3. Any necessary adjustments shall be made.
4. A record of any adjustments, examinations and test trips shall be made in the Hoisting Machinery Record Book by the person or persons making the adjustments, examinations and test trips. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 229 (4).
(5) Where shaft rope attachments are made using rope clips, the number of clips to be used and their torque shall be in accordance with good engineering standards. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 229 (5).
(6) A socket attachment used between a shaft conveyance or counterweight and a shaft rope shall be,
(a) designed to be suitable for mine hoisting;
(b) installed by a person who,
(i) is competent in the installation of the type of socket being used, and
(ii) complies with the manufacturer’s current installation standard; and
(c) if it is used for hoisting ropes, made with a socket long enough to ensure that the embedded length of wire in the socket is greater than seven times the rope diameter. O. Reg. 486/99, s. 14.
(7) Each component of an attachment between a shaft conveyance or counterweight and a shaft rope, except for a rope clip, shall be designed to ensure that when in service and carrying the rated load, the component is capable of withstanding at least four times the maximum allowable design stresses without permanent distortion. O. Reg. 486/99, s. 14.
(8) For the purpose of subsection (7), the maximum allowable design stresses are those established by good engineering practice and shall take into account the effects of,
(a) the weight of the conveyance or counterweight;
(b) the rated load;
(c) any impact load;
(d) any dynamic load;
(e) stress concentration factors;
(f) corrosion;
(g) metal fatigue; and
(h) dissimilar materials. O. Reg. 486/99, s. 14.
(9) The rope attachments, other than rope clips, installed after October 7, 1999 shall be identified and load rated by the manufacturer or a professional engineer. O. Reg. 486/99, s. 14.
230. (1) A certificate shall be obtained for each shaft conveyance or counterweight showing its,
(a) rated load, as certified by a professional engineer; and
(b) serial number, date of manufacture and the name of the manufacturer. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 230 (1).
(2) Each shaft conveyance and counterweight shall be examined and inspected at least once in every five years of use by a competent person and a record of such examination and inspection shall be kept available for inspection. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 230 (2).
(3) All parts of a shaft conveyance or counterweight when in service and carrying the rated load shall be capable of withstanding at least four times the maximum allowable design stresses without permanent distortion. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 230 (3).
(4) The maximum allowable design stresses shall be those established by good engineering practice and include the effects of,
(a) the weight of the conveyance or counterweight;
(b) the rated load;
(c) any impact load;
(d) any dynamic load;
(e) stress concentration factors;
(f) corrosion;
(g) metal fatigue; and
(h) dissimilar materials. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 230 (4).
(5) Where a worker performs work from the top of a shaft conveyance or counterweight, there shall be provided for the worker,
(a) a safe footing; and
(b) overhead protection, except when changing shaft guides. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 230 (5).
(6) Devices shall be provided in a shaft conveyance by which any equipment or supplies within the conveyance may be safely secured. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 230 (6).
231. (1) This section applies when a suspended or movable work platform that is not a shaft conveyance is used to transport or support a worker who is performing work in a shaft or in a raise. O. Reg. 68/96, s. 5.
(1.1) The work platform shall be designed by a professional engineer in accordance with good engineering practices and shall be built in accordance with the design. O. Reg. 68/96, s. 5.
(2) Before the initial use of a work platform, the employer shall give notice to the joint health and safety committee or to the health and safety representative, if any. O. Reg. 236/99, s. 8.
232. (1) A cage, being used to transport persons, shall,
(a) where it is supported by only a single rope or attachment point have the safety catches and mechanisms prescribed in subsection (6);
(b) except on any side which has a door, be enclosed by sheet steel at least three millimetres thick;
(c) have ventilation, adequate for the persons being transported;
(d) have a hood of steel plate, at least five millimetres thick;
(e) have a door or doors as prescribed in subsection (2);
(f) have an internal height greater than 2.1 metres;
(g) have a clearance at the door that is greater than 1.8 metres; and
(h) have where practical, an exit for the persons in the roof which can be opened from inside or outside the cage. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 232 (1).
(2) The door or doors on a cage shall,
(a) be at least 1.5 metres high;
(b) be mounted and arranged so they cannot be opened outward from the cage;
(c) have devices for positive latching in the closed position;
(d) be of solid materials, except for a viewing window;
(e) be so arranged that they may be closed at all times that persons or materials, except rolling stock, are being transported in the cage;
(f) be mounted so as to provide only enough clearance at the floor to permit free closing or opening; and
(g) be of adequate strength to withstand normal shock loads. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 232 (2).
(3) A skip used to transport workers in a shaft shall meet the following requirements unless it is being used to transport workers for shaft inspection or shaft maintenance or unless it is being used in an emergency:
1. The skip must have the safety catches and mechanisms required by subsection (6) if the skip is supported by only a single rope or attachment point.
2. The skip must provide an enclosure at least 1.07 metres high for the persons being transported.
3. The skip must have ventilation that is adequate for the persons being transported.
4. The skip must have a suitable floor that is adequately fastened.
5. The skip must have a means for safe entry and exit. O. Reg. 571/92, s. 19.
(3.1) For the purposes of subsection (3), a skip is considered to be being used in an emergency if it is being used to hoist injured people, to evacuate people, to fight fire or to enable people to perform emergency repair work necessary to maintain the mine or the mine dewatering system, electrical system or ventilation system. O. Reg. 571/92, s. 19.
(4) The openings between a shaft and a skip box over which persons must pass to enter or leave a skip shall be closed off sufficiently to prevent a person from falling through the opening. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 232 (4).
(5) The shaft signal pull cord shall be located in a convenient place for the skip tender. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 232 (5).
(6) Safety catches and mechanisms on a cage or skip shall,
(a) be of a type and design that meets good engineering practice;
(b) stop and hold a cage or skip transporting persons should the supporting rope or attachment break; and
(c) be subjected to the tests prescribed in subsection (7) and successfully pass the free fall test prescribed in subsection (8),
(i) prior to the cage or skip first being used to transport persons, and
(ii) prior to the cage or skip first being used after repairs to correct distortion of the safety catches and mechanisms. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 232 (6); O. Reg. 272/97, s. 42 (1).
(7) Free fall tests shall be performed under the following conditions:
1. The cage or skip must carry a weight equal to its maximum permitted load of persons and any material permitted to be carried at the same time.
2. The cage or skip must travel at a speed equal to,
i. the normal hoisting speed when transporting persons, or
ii. the speed attained by a free fall of 1.5 metres.
3. The guides on which the test is made must be of the same specifications as those in the shaft in which the conveyance will operate. O. Reg. 68/96, s. 6 (1).
(7.1) A free fall test shall not be performed at the speed attained by a free fall of 1.5 metres unless the design and configuration of the safety dogs and loading on the cage or skip have been tested at normal hoisting speed before the free fall test. O. Reg. 68/96, s. 6 (1).
(7.2) If a free fall test is to be performed at the speed attained by a free fall of 1.5 metres, the person performing the test shall record the rate of deceleration and the rate of change in deceleration of the cage or skip on a chart suitable for determining the deceleration of the conveyance. O. Reg. 68/96, s. 6 (1).
(8) A free fall test shall be successfully passed if,
(a) the skip or cage decelerates to a stop at an average rate that is not less than nine or greater than 20 metres per second per second.
(b) there is no damage to the safety dogs and mechanisms;
(c) the safety dogs engage the guides continuously during deceleration; and
(d) a calculation shows that the safety dogs will stop the cage or skip when it is carrying its maximum material load. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 232 (8); O. Reg. 68/96, s. 6 (2).
(9) A report of a free fall test shall be made in the Hoisting Machinery Record Book for the hoist. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 42 (2).
233. (1) A system for communicating by voice shall be installed and maintained at an underground mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 233 (1).
(2) The communication system required by subsection (1) shall permit communication between persons at,
(a) the collar of the shaft, including the collar of an internal shaft;
(b) the landing stations in use in a shaft;
(c) the hoist room for the shaft including the hoist room for an internal shaft;
(d) an underground refuge station; and
(e) an attended place on surface. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 233 (2).
234. Where a call system is installed for a cage, the call system shall,
(a) not be operated in excess of 150 volts; and
(b) be arranged so that the call signals are inaudible to the hoist operator. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 234.
235. (1) A signalling system shall be installed at an underground mine by which signals may be exchanged between the tender of a shaft conveyance and the hoist operator for the purpose of controlling the hoist. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 235 (1).
(2) The system prescribed in subsection (1) shall,
(a) not be operated in excess of 150 volts;
(b) be supplied with power from a transformer which supplies no other load;
(c) where the primary voltage of the transformer exceeds 750 volts,
(i) have one conductor of the power supply grounded, or
(ii) have the conductors ungrounded if,
(A) an isolating transformer with a 1 to 1 ratio supplies the power for the signal, and
(B) the circuit has a device to indicate a ground fault;
(d) have the non-current carrying metal parts of the signalling unit grounded unless the unit is mounted at least 2.4 metres above the floor;
(e) except as prescribed in subsection (3), be capable of providing signals that are,
(i) audible and clear,
(ii) separate for each shaft compartment, and
(iii) distinctive in sound for each compartment;
(f) be arranged so that the hoist operator can return a signal to the worker signalling; and
(g) be installed at every working level, landing deck and any other necessary shaft location. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 235 (2).
(3) The system shall be capable of providing a signal that is both audible and visible when installed on a multi-deck sinking stage. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 235 (3).
(4) Signalling systems using radio frequencies for transmitting signals shall comply with section 174. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 235 (4).
236. (1) A signal for hoist movement shall be given only,
(a) by an authorized worker; and
(b) when the shaft conveyance or counterweight is at the same location as the worker signalling, except during,
(i) shaft sinking and preliminary shaft development, or
(ii) maintenance work in a shaft. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 236 (1).
(2) No hoist shall be moved on manual control unless,
(a) the signal prescribed under this section is given;
(b) the signal is returned by the hoist operator; and
(c) at least four seconds have elapsed after the executive signal has been given. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 236 (2).
(3) Signals shall be given in the following sequence:
1. Cautionary.
2. Destination.
3. Executive. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 236 (3).
(4) The following basic code of signals to a hoist operator shall be used:
|
1. |
Stop immediately |
1 signal |
|
2. |
Where the shaft conveyance is stationary, hoist |
1 signal |
|
3. |
Lower |
2 signals |
|
4. |
Persons entering or leaving a shaft conveyance |
3 signals |
|
5. |
Caution — blasting to take place |
4 signals |
|
6. |
Release of shaft conveyance |
5 signals |
|
7. |
Danger |
9 signals |
|
8. |
Chairing |
1 signal followed by 2 signals |
|
9. |
Hoist slowly |
3 signals, followed by 3 signals, followed by 1 signal |
|
10. |
Lower slowly |
3 signals, followed by 3 signals, followed by 2 signals |
R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 236 (4).
(5) In addition to the basic code of signals prescribed by subsection (4), the tender of a shaft conveyance shall comply with the Code of Standard Signals issued by the Ministry. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 236 (5).
(6) Where it is necessary for the operation of a shaft conveyance, the supervisor in charge of an underground mine may establish signals in addition to those prescribed by subsections (4) and (5). R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 236 (6).
(7) The basic code of signals and destination signals shall be posted in every hoistroom, working level and landing deck. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 236 (7).
237. (1) This section applies during shaft sinking and preliminary development work during shaft sinking at an underground mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 237 (1).
(2) A bucket used to transport persons shall,
(a) be provided when the vertical depth of a shaft below the collar exceeds fifty metres;
(b) be at least 1.07 metres high; and
(c) be designed as prescribed by subsections 230 (3) and (4). R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 237 (2).
(3) Where the distance between a head sheave and the shaft bottom exceeds 100 metres a crosshead shall be used with a bucket. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 237 (3).
(4) A crosshead shall be,
(a) landed on at least two chairs at the bottom crosshead stop to prevent distortion;
(b) attached to the rope by a safety appliance in such manner that where the crosshead jams in the shaft compartment, the bucket is stopped; and
(c) of a type that encloses the bucket unless,
(i) the shaft compartment is tightly lined, and
(ii) the bucket is barrel-shaped. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 237 (4).
(5) Dual lights shall be installed to indicate to the hoist operator that,
(a) the crosshead and bucket are descending together from the bucket dumping position;
(b) the service doors are in or out of the shaft compartment; and
(c) the dump doors are in or out of the shaft compartment. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 237 (5).
(6) A service door or doors as prescribed by subsection (7), to cover the sinking compartment of a shaft, shall be provided. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 237 (6).
(7) The service door or doors required by subsection (6) shall,
(a) be installed at the collar and any place in the shaft where tools and other materials are loaded or unloaded into or from the bucket;
(b) be automatically latched out by mechanical devices when out of the shaft compartment;
(c) be closed when a bucket is being loaded or unloaded with tools and other materials; and
(d) be closed when persons are entering or leaving a bucket, except where the closed crosshead provides equal protection for persons. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 237 (7).
(8) Dump doors shall be installed and maintained that,
(a) prevent a bucket from being dumped when the dump doors are open;
(b) prevent any material from falling down the shaft while the bucket is being dumped; and
(c) are provided with devices that securely latch the dump doors out of the shaft compartment automatically. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 237 (8).
(9) Where a multi-deck stage is being used, the stage shall be,
(a) designed by a professional engineer in accordance with good engineering practice; and
(b) built in accordance with the design. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 237 (9).
(10) Before the initial use of a multi-deck stage, the employer shall give notice to the joint health and safety committee or to the health and safety representative, if any. O. Reg. 236/99, s. 9.
(11) A bucket shall be filled so that no piece of loose rock projects above the level of the rim. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 237 (11).
(12) Except during shaft maintenance, repairs and inspections, a person being transported by a bucket shall ride in the bucket when it is travelling above the bottom crosshead stop. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 237 (12).
(13) The worker authorized to give signals for hoist movement shall,
(a) maintain proper discipline of persons riding in the bucket; and
(b) enforce the loading restrictions of the conveyance permit. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 237 (13).
(14) No person shall obstruct the worker mentioned in subsection (13) from performing his or her prescribed duties. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 237 (14).
(15) A bucket shall not be allowed to leave the top or bottom of the shaft until the bucket has been steadied. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 237 (15).
(16) A bucket returning to the shaft bottom shall be,
(a) stopped at a distance at least five metres and not more than ten metres above the bottom of the shaft; and
(b) lowered slowly below the point described in clause (a) only on a separate signal. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 237 (16).
(17) On the initial trip following a blasting operation, no bucket transporting workers shall be lowered below a point,
(a) less than fifteen metres above the blasting set or bulkhead; or
(b) where the health and safety of workers is likely to be endangered. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 237 (17).
(18) Below the point prescribed in subsection (17), the bucket shall be lowered slowly on the signal of the workers being transported and only a sufficient number of workers shall be transported on the initial trip as are required to conduct a proper examination of the part of the shaft that may be affected by the blast. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 237 (18).
(19) Persons may be at the bottom of the shaft during the dumping cycle of the shaft conveyance. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 237 (19).
238. (1) No person shall operate, or be permitted to operate, a hoist, unless that person,
(a) is in possession of a subsisting hoist operator’s medical certificate;
(b) is over eighteen years of age;
(c) Revoked: O. Reg. 60/94, s. 13.
(d) is a competent person or, in the case of a worker being trained to operate the hoist, is under the direct supervision of a competent person; and
(e) is physically and mentally fit to discharge the duties of a hoist operator. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 238 (1); O. Reg. 60/94, s. 13.
(2) A person operating a hoist shall,
(a) undergo a medical examination by a physician before commencing work as a hoist operator and every twelve months thereafter; and
(b) obtain a hoist operator’s medical certificate from the physician certifying that the person is physically fit to operate a hoist and is not subject to any infirmity of body and mind that may interfere with the duties of a hoist operator. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 238 (2).
(3) A hoist operator’s medical certificate shall,
(a) be kept available for inspection; and
(b) expire twelve months after its date. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 238 (3).
(4) A hoist operator’s medical certificate shall be in the following form:
Occupational Health and Safety Act
HOIST OPERATOR’S MEDICAL CERTIFICATE
|
I have this day examined |
|
|
|
|
|
Name ……………………………………….………….. |
|
|
and certify he/she is physically fit to operate a hoist and is not subject to any infirmity of body or mind that may interfere with the duties of a hoist operator. |
|
|
|
|
|
……………………………………………..…………… |
|
|
Signature of legally qualified medical practitioner |
|
|
|
|
|
…………………………… |
|
|
(date) |
|
R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 238 (4).
239. (1) A report shall be made by the hoist operator in the Hoist Operator’s Log Book for each shift performed by him or her of,
(a) the working condition of,
(i) the hoist brakes, clutches and clutch brake interlocks,
(ii) the depth indicator,
(iii) the signal system,
(iv) the hoist controls,
(v) the overwind and underwind devices, and
(vi) other devices which may affect safe hoist operation;
(b) any instructions given to him or her affecting hoist operations;
(c) any unusual circumstances in connection with the operation of the hoist;
(d) the results of any tests prescribed by this Regulation;
(e) any trial trips;
(f) any inadvertent stoppages; and
(g) his or her actual starting and finishing time. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 239 (1).
(2) The hoist operator shall,
(a) review and countersign all entries in the Hoist Operator’s Log Book for the preceding two shifts; and
(b) sign in the Hoist Operator’s Log Book for his or her period of duty. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 239 (2).
(3) A person issuing instructions to the hoist operator shall record and sign such instructions in the Hoist Operator’s Log Book. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 239 (3).
(4) The supervisor in charge of a mine hoist shall review and countersign each working day the entries in the Hoist Operator’s Log Book for the preceding twenty-four hour work period. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 239 (4).
(5) The Hoist Operator’s Log Book shall be kept in the hoistroom and available for inspection. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 239 (5).
240. (1) A hoist operator shall,
(a) at least once during his or her shift, in accordance with subsection (2),
(i) test for the satisfactory working conditions and holding capacity of the hoist brakes, and
(ii) test the holding capacity of any friction clutch;
(b) at least once in twenty-four hours of use of a hoist, test the overwind and underwind protective devices by operating the hoist into them;
(c) make a return trip of a shaft conveyance,
(i) through the working part of a shaft if hoisting has been stopped for a period exceeding two hours and the hoist operator has reason to believe that an event may have occurred to cause damage or obstruction to the free and normal movement of the conveyances in the shaft, and
(ii) below any part of a shaft that has been under repair, after the repairs have been completed;
(d) remain at the hoist controls when the hoist is in motion under manual control;
(e) except when the hoist is on automatic control due to a temporary absence of the operator from the hoist controls, set the brakes and controls so that at least two separate and distinct actions are required to put the hoist in motion;
(f) not be in voice communication when the hoist is in motion and under his or her manual control, except during an emergency or during maintenance and examination;
(g) not operate the hoist to transport any person unless at least two brakes can be applied to stop the hoist drum;
(h) not lower persons on an unclutched drum;
(i) when heavy loads or irregularly shaped loads are on or under the shaft conveyance, operate the hoist with caution;
(j) complete the hoist movement required by an executive signal after the hoist movement is begun unless there is a signal to stop or an emergency signal; and
(k) upon receiving three signals, remain at the hoist controls unless advised orally by the person in charge of the conveyance that hoist movement will not be required. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 240; O. Reg. 584/91, s. 6; O. Reg. 31/04, s. 15 (1).
(2) The following applies with respect to the tests required by clause (1) (a):
1. The tests shall be conducted in accordance with a procedure established for the hoist.
2. The hoist operator shall conduct the tests immediately before the hoist is used to move a shaft conveyance that is transporting persons.
3. If the tests have been conducted under paragraph 2 during a shift, it is not necessary to conduct them again during the same shift. O. Reg. 31/04, s. 15 (2).
241. No person shall,
(a) operate or interfere with devices or controls for operating a hoist unless authorized;
(b) speak to the hoist operator while he or she is operating the hoist on manual control, except in an emergency or when the hoist is being repaired, maintained or adjusted;
(c) be on a cage while it is being placed onto or removed from chairs;
(d) be in, on or under a shaft conveyance or counterweight which is supported by an unclutched drum unless the conveyance or counterweight is secured in position or unless permitted by subsection 237 (19);
(e) leave a shaft conveyance that has inadvertently stopped at a point other than a shaft station, except upon instruction from an authorized person outside the conveyance;
(f) put to use any chairs for landing a cage, unless,
(i) a signal for chairing has been made and returned, or
(ii) special arrangements have been made to operate a cage with a car, in balance, from that location;
(g) permit the normal operation of a mine hoist if an object which may be a hazard to the operation of a shaft conveyance or counterweight has fallen down a mine shaft until,
(i) a shaft inspection or a trial run through the affected part has been made,
(ii) any obstructions have been removed, and
(iii) any damage affecting safe operation has been repaired. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 241.
242. (1) The hoist operator shall be instructed in the procedures to follow in operating the hoist where there is,
(a) an intermediate shaft obstruction;
(b) an emergency; and
(c) an inadvertent hoist stoppage,
and shall be instructed in the procedures for operating any safety devices for people. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 242 (1).
(2) A notice shall be posted in the hoistroom warning that no person shall speak to the hoist operator while the hoist operator is operating the hoist on manual control, except in an emergency or when the hoist is being repaired, maintained or adjusted. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 242 (2).
(3) A hoist operator shall be available at a mine to manually operate an automatically controlled mine hoist when persons are underground. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 242 (3).
(4) A competent person or persons shall be designated to,
(a) give mine shaft signals;
(b) be in charge of a shaft conveyance;
(c) maintain discipline of persons riding in a shaft conveyance;
(d) enforce the load limits for the shaft conveyance; and
(e) notify the hoist operator of heavy loads or irregular shaped loads on or under the shaft conveyance. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 242 (4).
(5) Procedures shall be adopted for removing persons from a shaft conveyance which has stopped inadvertently at a place in a shaft other than a shaft station. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 242 (5).
(6) The person or persons designated to carry out the functions set out in subsection (4) shall be readily available to perform those functions. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 242 (6).
243. (1) When equipment or supplies are being transported in a shaft, they shall,
(a) when in a shaft conveyance, be loaded and secured in a manner to prevent shifting;
(b) when secured to a hoisting rope of the conveyance, be secured in a manner to prevent damage to the rope and permit the safety mechanisms of the conveyance to operate; and
(c) when transported below the shaft conveyance or crosshead, be suspended in a manner to prevent contact with shaft furnishings. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 243 (1).
(2) The suspension system or arrangement used to transport equipment or supplies below the shaft conveyance or crosshead shall be capable of withstanding at least four times the maximum allowable design stresses without permanent distortion to any component of the system or arrangement and shall meet the requirements prescribed by subsection 230 (4). R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 243 (2).
244. (1) No person shall be transported in a shaft conveyance,
(a) that is a cage, unless the cage doors are closed;
(b) while the hoist that is raising or lowering the shaft conveyance is being used to transport ore or waste;
(c) that is a multi-deck cage, where supplies or service rolling stock are being transported, except that persons may be carried on the top deck when,
(i) such materials are carried on another deck,
(ii) the materials are adequately secured,
(iii) the doors of the top deck are closed,
(iv) the combined load does not exceed 85 per cent of the material load limit of the conveyance, and
(v) the scheduled trips for persons have been completed;
(d) where personal hand tools or equipment are being transported, unless such tools or equipment are,
(i) protected by guards,
(ii) secured, and
(iii) the combined load does not exceed 85 per cent of the material load limit of the conveyance;
(e) unless a worker authorized to give signals is in charge of the conveyance; and
(f) with explosives, supplies or service rolling stock. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 244 (1).
(2) Despite clause (1) (f), those workers required to handle explosives, supplies or service rolling stock may be transported with the explosives, supplies or service rolling stock if space is provided for the safety of the workers and the combined load does not exceed 85 per cent of the material load limit of the conveyance. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 244 (2).
245. Where a mine shaft exceeds 100 metres in vertical depth, a shaft conveyance shall be provided for the raising and lowering of workers. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 245.
246. No mine hoisting plant shall be put to, or continued in, normal service if it is or ought to be known to have a defect or be in an improper state of repair except for the purpose of correcting the defect or improper state of repair. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 246.
247. (1) One or more competent persons shall be appointed to examine the following parts of an electrically-powered or electrically-controlled hoist:
1. Hoist motors.
2. Hoist controls.
3. Electrical safety devices.
4. Signalling devices. O. Reg. 68/96, s. 7 (1).
(2) The examination shall be done at least once each week when the hoist is being used. O. Reg. 68/96, s. 7 (1).
(2.1) If the parts were not examined during the week before the hoist is to be used, the examination shall be done immediately before it is used. O. Reg. 68/96, s. 7 (1).
(3) A record of the examination, servicing and repair shall be made in the Electrical Hoisting Equipment Record Book. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 247 (3).
(4) The entries in the Electrical Hoisting Equipment Record Book shall be dated and signed by the person performing the examination, servicing or repairs. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 247 (4).
(5) A record of a failure or accident involving an electrical component of a hoist motor and controls, electrical safety and signalling devices shall be made in the Electrical Hoisting Equipment Record Book by the supervisor in charge of electrical hoisting equipment. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 247 (5).
(6) The supervisor in charge of the mine hoisting plant shall,
(a) review the entries made in the Electrical Hoisting Equipment Record Book within one week after each entry is made;
(b) ascertain that the examinations required by this section and all necessary work have been done; and
(c) upon completion of each review required by clause (a), certify in the Electrical Hoisting Equipment Record Book that he or she has complied with clauses (a) and (b). R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 247 (6); O. Reg. 68/96, s. 7 (2).
248. (1) A competent person or persons shall be appointed to examine the mechanical parts of a mine hoisting plant in accordance with subsections (2), (2.1) and (2.2). R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 248 (1); O. Reg. 68/96, s. 8 (1).
(2) An examination shall be made,
(a) immediately before the hoisting plant is used if it was not examined the previous day, and at least once each day thereafter that it is in use,
(i) of the exterior of each hoisting and tail rope to detect the presence of kinks or other damage and to note the appearance of the rope dressing, and
(ii) of the safety catches of the shaft conveyance for any defects;
(b) Revoked: O. Reg. 68//96, s. 8 (2).
(c) if the hoist is being used, at least once every month of,
(i) the shaft ropes to determine,
(A) the amount of wear, distortion and corrosion,
(B) the need for lubrication,
(C) the need for changing the wear patterns,
(ii) the hoisting ropes for the number and location of broken wires, and
(iii) the friction treads of a friction hoist;
(d) at least once every six months of service of,
(i) the hoisting rope of a drum hoist within the attachments at the drum and at the drum sprout, and
(ii) the hoisting rope of a friction hoist within attachments at the shaft conveyance or counterweight in accordance with an established procedure; and
(e) at least once every twelve months of,
(i) bolt locking devices, foundation bolts and all bolts critical to hoist safety, and
(ii) the bails, suspension gear and structure of the shaft conveyance and counterweight. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 248 (2); O. Reg. 68/96, s. 8 (2); O. Reg. 272/97, s. 44 (1); O. Reg. 486/99, s. 15 (1).
(2.0.1) If any of the equipment described in clause (c) was not examined in accordance with that clause during the month before the hoist is to be used, the examination shall be done immediately before the hoist is to be used. O. Reg. 486/99, s. 15 (2).
(2.1) The following parts shall be examined at least once a week when they are in use:
1. Any conveyance safety mechanisms for proper adjustment and freedom of movement.
2. Any head, deflection or idler sheaves, their shafting and bearer and sole plates.
3. The attachments of each shaft rope.
4. The attachments on any shaft conveyance or counterweight.
5. Any shaft conveyance, counterweight and work platform.
6. The hoist parts, brakes, clutch, brake-clutch interlocks and depth indicators.
7. Any hoisting equipment being used for shaft sinking.
8. Any auxiliary brake operating weights, to assure their freedom of movement and holding capacity. O. Reg. 68/96, s. 8 (3); O. Reg. 236/99, s. 10 (1).
(2.2) If the parts listed in subsection (2.1) were not examined during the week before they are to be used, the examination shall be done immediately before they are used. O. Reg. 68/96, s. 8 (3).
(2.3) An examination of the clutch and brake-clutch interlocks under subsection (2.1) shall include an operational check to ensure their performance. O. Reg. 236/99, s. 10 (2).
(3) At least once every three months, the safety catches and mechanisms of the cage or other shaft conveyance shall be tested and such tests shall consist of releasing the empty conveyance suddenly in some suitable manner from rest, so that the safety catches have the opportunity to grip the guides and, where the safety catches do not act satisfactorily, the cage or other shaft conveyance shall not be used for lowering or raising workers until the safety catches have been repaired and tested and shown to act satisfactorily. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 248 (3).
(4) Hoisting ropes in use on a drum hoist shall be cleaned when necessary and shall be dressed with lubricant at least once each month so as to maintain a good coating and a record of the cleaning and dressing shall be entered in the Hoisting Machinery Record Book and the entry shall be dated and signed by the supervisor in charge of the work. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 248 (4).
(5) Revoked: O. Reg. 779/94, s. 11.
(6) After every eighteen months of service on a friction hoist, the portion of the hoisting rope and tail rope that is within the wedge and socket attachments shall be cut off unless that portion of the rope is visually examined and it is found that,
(a) there are no broken wires;
(b) there is no advanced corrosion;
(c) there is no excessive pitting; and
(d) there is no excessive deformation of wires. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 248 (6).
(7) An examination shall be made by a competent person, using non-destructive methods acceptable to a professional engineer, to determine the condition of the,
(a) mine hoist shafting, brake pins and linkages; and
(b) structural parts, attachment pins and draw bars of a shaft conveyance and counterweight. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 44 (2).
(7.1) The examination shall be made before the parts are first used and at regular intervals that are no greater than those recommended by the competent person performing the examination. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 44 (2).
(8) Drawings of the parts to be examined under subsection (7) shall be made available, upon request, to the person performing the examination. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 248 (8).
(9) A record of the examinations required by this section and any servicing and repairs shall be entered in the Hoisting Machinery Record Book and the entries in the Record Book shall be dated and signed by the person performing the examination, servicing or repairs. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 248 (9).
(10) A record of a failure and accident involving a mechanical part of a mine hoisting plant shall be made in the Hoisting Machinery Record Book by the supervisor in charge of the mechanical hoisting equipment. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 248 (10).
(11) The supervisor in charge of the mechanical parts of the mine hoisting plant shall countersign each entry made in the Hoisting Machinery Record Book with respect to examinations made under subsection (7). R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 248 (11).
(12) The supervisor in charge of the mine hoisting plant shall,
(a) review the entries made in the Hoisting Machinery Record Book within one week after each entry is made;
(b) ascertain that the examinations required by this section have been made and all necessary work done; and
(c) upon completion of the review required by clause (a), certify in the Hoisting Machinery Record Book that he or she has complied with clauses (a) and (b). R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 248 (12); O. Reg. 68/96, s. 8 (4).
249. (1) An examination shall be made by a competent person of,
(a) the mine shaft, at least once a week when it is being used;
(b) if the hoist is being used, the shaft guides, timbers, walls, and compartments used for hoisting, at least once every month;
(c) the headframe, headframe foundation and backlegs, sheave deck, dump, bin and bin supports, at least once every year;
(d) the shaft sump, at such frequency as is necessary to assure that the tail, guide and rubbing rope connections are clear of water and spillage; and
(e) water in the shaft sump at least once every year to determine its pH. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 249 (1); O. Reg. 68/96, s. 9 (1); O. Reg. 486/99, s. 16 (1).
(1.1) If the mine shaft is not examined during the week before it is to be used, the examination shall be done immediately before it is used. O. Reg. 68/96, s. 9 (2).
(1.2) If the shaft guides, timbers, walls and compartments used for hoisting are not examined during the month before the hoist is used, the examination shall be done immediately before the hoist is used. O. Reg. 486/99, s. 16 (2).
(2) A record of the examinations required by subsection (1) and any servicing and repairs shall be entered in the Shaft Inspection Record Book and such entries shall be dated and signed by the person performing the examination, servicing or repairs. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 249 (2).
(3) The supervisor in charge of the mine shaft and headframe shall,
(a) review the entries made in the Shaft Inspection Record Book within one week after each entry is made;
(b) ascertain that the examinations required by subsection (1) have been made and all necessary work done;
(c) upon completion of the review required by clause (a), certify in the Shaft Inspection Record Book that he or she has complied with clauses (a) and (b). R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 249 (3); O. Reg. 68/96, s. 9 (3).
250. The ropes, sheaves, brakes, attachments and other parts of a utility or tugger hoist shall be regularly examined by a competent person and kept in safe condition. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 250.
251. (1) Revoked: O. Reg. 272/97, s. 45.
(2) A direct gas fired non-recirculating make-up heater being used for heating a mine or a mining plant shall be installed, operated and maintained to conform to National Standard of Canada CAN1-3.7-77. O. Reg. 584/91, s. 7.
(3) All liquid or gas fuel for a heating system shall be piped and stored so that any leakage will not accumulate at or enter an underground mine. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 251 (3).
(4) A heating system shall be operated and maintained so as to eliminate the risk of fire or explosion. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 251 (4).
(5) A record of service, maintenance and tests on the heating system shall be kept in a log book. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 251 (5).
252. (1) In a mining plant building, a ventilation system shall be provided, maintained and used, that will,
(a) provide a partial pressure of oxygen in the atmosphere of more than eighteen kilopascals to all workplaces therein; and
(b) except as provided by a regulation made in respect of a designated substance, dilute and remove contaminants from all workplaces therein to prevent exposure of a worker to contaminants in excess of the values,
(i) prescribed under section 4 of Regulation 833 of the Revised Regulations of Ontario, 1990 (Control of Exposure to Biological or Chemical Agents), or
(ii) if no values are prescribed under the said section 4, adopted as criteria or guides under section 283 of this Regulation. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 252 (1); O. Reg. 272/97, s. 46.
(2) Accurate plans and records of a mining plant building ventilation system shall be kept and maintained, showing,
(a) the location of all ventilation openings;
(b) the location of all ventilation fans;
(c) the volumes of air in cubic metres per second handled by the fans and openings;
(d) the volumes of air in cubic metres per second withdrawn by processing equipment; and
(e) the location and functions of all ventilation regulating doors, louvres or other devices. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 252 (2).
(3) Where in a mining plant the atmosphere may contain chemical or physical agents that are likely to endanger the health and safety of a worker, equipment for the detection of such agents shall be provided and such equipment shall be readily accessible. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 252 (3).
253. (1) In an underground mine, a mechanical ventilation system shall be provided, maintained and used that will,
(a) provide a partial pressure of oxygen of more than eighteen kilopascals; and
(b) except as provided by a regulation made in respect of a designated substance, dilute and remove contaminants from all workplaces therein to prevent exposure of a worker to contaminants in excess of the values,
(i) prescribed under section 4 of Regulation 833 of the Revised Regulations of Ontario, 1990 (Control of Exposure to Biological or Chemical Agents), or
(ii) if no values are prescribed under the said section 4, adopted as criteria or guides under section 283 of this Regulation. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 253 (1); O. Reg. 272/97, s. 47.
(2) Accurate plans and records of a mechanical ventilation system in an underground mine shall be kept and maintained showing,
(a) the location of all ventilation fans;
(b) the volumes of air in cubic metres per second handled by the ventilation fans;
(c) the fan operating gauge pressure;
(d) the direction of flow of main ventilating airflows;
(e) the location and function of all fire doors; and
(f) the location and function of all ventilation doors, brattices, stoppings and regulators controlling airflows. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 253 (2).
254. (1) In an underground mine,
(a) subject to clause (b), a development, exploration or production workplace shall be ventilated throughout by an auxiliary ventilation system for any advance in excess of sixty metres from a mechanical mine ventilation system; and
(b) a continuous supply of fresh air shall be provided and used to dilute and remove contaminants,
(i) in a raise, and
(ii) in a sub-drift for any advance in excess of ten metres from a mechanical mine ventilation system,
to prevent exposure of a worker to contaminants in excess of the values,
(iii) prescribed under section 4 of Regulation 833 of the Revised Regulations of Ontario, 1990 (Control of Exposure to Biological or Chemical Agents), or
(iv) if no values are prescribed under the said section 4, adopted as criteria or guides under section 283 of this Regulation. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 254 (1); O. Reg. 272/97, s. 48.
(2) The fresh air supply prescribed by clause (1) (b) shall be,
(a) independent of the air supplied by any drill or machine used;
(b) controlled only at the beginning of the raise or sub-drift; and
(c) operating when a blast is detonated. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 254 (2).
255. (1) An underground area that is not part of an underground mine ventilation system shall,
(a) be effectively barricaded to prevent inadvertent entry;
(b) be posted with signs to warn a person that entry is prohibited; and
(c) subject to subsection (3), be examined by a competent person before any other person enters or is permitted to enter the underground area. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 255 (1).
(2) The examination prescribed in clause (1) (c) shall consist of an examination for,
(a) oxygen deficiency due to a partial pressure of oxygen in the atmosphere less than eighteen kilopascals;
(b) the presence of a toxic gas, vapour, dust, mist or fume; and
(c) any other dangerous condition. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 255 (2).
(3) Before a competent person examines the underground area he or she shall be provided with instructions in writing setting out,
(a) the hazard involved;
(b) the use of testing equipment required;
(c) the personal protective devices he or she is required to use or wear; and
(d) any other precautions and procedures to be taken for his or her protection. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 255 (3).
256. (1) Before material containing cyanide is used for back fill in an underground mine, an assessment shall be conducted to determine the precautions to be taken to protect the health and safety of workers. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 49.
(2) The assessment shall be done in consultation with the joint health and safety committee or the health and safety representative, if any. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 49.
257. In an underground mine, clean water under pressure shall be made available for dust control purposes in a workplace where rock or ore is drilled, blasted, loaded or transported. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 257.
258. In an underground mine, broken rock or ore shall be thoroughly wetted by water,
(a) during blasting operations or immediately thereafter; and
(b) when the ore or rock is being loaded or scraped. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 258.
259. Sections 257 and 258 do not apply at a salt mine or any other operation where the ore or rock is hygroscopic. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 259.
260. No person shall enter or remain, or be permitted to enter or remain, in a workplace affected by blasting contaminants until the ventilation system has removed the contaminants or rendered them harmless. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 260.
261. In an underground mine a battery-charging station shall be ventilated to prevent the accumulation of an explosive mixture of gases. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 261.
262. (1) Effective illumination by means of stationary lighting shall be provided in an underground mine,
(a) at all active shaft stations and shaft conveyance landings where workers are required to travel or work; and
(b) where the nature of the equipment or the operation may create a hazard due to insufficient illumination. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 262.
(2) Every worker in an underground mine shall wear retroreflective material on headgear and outer clothing. O. Reg. 174/01, s. 7.
263. (1) Effective illumination appropriate for the task shall be provided at all workplaces on the surface, including,
(a) in those areas adjacent to the workplace where workers are required to travel; and
(b) in those circumstances where the nature of the equipment or the operation may create a hazard to a worker due to insufficient lighting. O. Reg. 174/01, s. 8.
(2) Subject to subsection (3), between sunset and sunrise, every worker shall wear retroreflective material on headgear and outer clothing that enables the worker to be seen. O. Reg. 291/02, s. 8.
(3) A worker is not required to comply with subsection (2) if the worker is in a booth, vehicle cab or another protective enclosure or if a work area is provided with fixed lighting that enables the worker to be seen. O. Reg. 291/02, s. 8.
264. In a workplace in a building which is solely dependent on artificial lighting and where a failure of the regular lighting system would create conditions that might endanger the safety of any person in the building, emergency lighting shall be provided which,
(a) turns on automatically when the regular lighting fails;
(b) is independent of the regular lighting source;
(c) provides adequate lighting for evacuation of the building; and
(d) shall be tested as frequently as necessary to ensure the system will function in an emergency but not less frequently than recommended by the manufacturer. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 264.
265. Compressed air for breathing purposes in air supplied respirators shall conform to CSA Standard CAN 3-Z180.1-M85, “Compressed Breathing Air and Systems”. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 265; O. Reg. 571/92, s. 20.
266. Where dust or other material is likely to cause a hazard by becoming airborne, the dust, or other material, shall be removed with a minimum of delay by,
(a) vacuuming;
(b) wet sweeping;
(c) wet shovelling; or
(d) other suitable means. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 266.
267. (1) An annual survey of potentially hazardous minor elements shall be conducted on all feed streams to and concentrates coming from a mining plant. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 267 (1).
(2) An assessment shall be made of the potential hazard from the elements detected in the survey required by subsection (1) due to the processes used in the mining plant. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 267 (2).
(3) Workplaces in the mining plant shall be monitored for the hazardous elements and compounds revealed by the assessment required by subsection (2). R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 267 (3).
(4) The results of the survey, the assessment and description and results of the monitoring program shall be reported annually to the joint health and safety committee or health and safety representative, if any. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 50.
(5) This section does not apply to a mining plant at a gravel pit or quarry. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 267 (5).
268. An annual survey of use by mass of potentially hazardous chemical reagents shall be made in a mining plant. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 268.
269. Where a potentially hazardous chemical reagent has caused a medical or compensable injury,
(a) an annual record shall be maintained for the reagent,
(i) specifying its trade name and chemical composition, and
(ii) identifying all possible toxic chemical elements and compounds of the reagent;
(b) a record of the injury caused by the reagent shall be kept. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 269.
270. A copy of the records and the surveys required under sections 267, 268 and 269 shall be sent to the joint health and safety committee or health and safety representative, if any, annually. O. Reg. 272/97, s. 51.
271. Subject to section 273, a confined space shall be entered only where,
(a) there is an easy egress from all accessible parts of the confined space;
(b) mechanical equipment in the confined space is,
(i) disconnected from its power source, and
(ii) locked out;
(c) all pipes and other supply lines except those required for the work therein are blanked off; and
(d) the confined space is tested and evaluated by a competent person who,
(i) records the results of each test in a permanent record, and
(ii) certifies in writing in the permanent record that the confined space,
(A) is free from hazard, and
(B) will remain free from hazard while any person is in the confined space having regard to the nature and duration of the work to be performed. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 271.
Note: On September 30, 2006, section 271 is revoked. See: O. Reg. 630/05, ss. 2, 5.
272. Subject to section 273, a confined space in which there exists or is likely to exist,
(a) a toxic gas, vapour, dust or fume; or
(b) a partial pressure of oxygen in the atmosphere of less than eighteen kilopascals or more than twenty-three kilopascals,
shall not be entered unless,
(c) the requirements of section 271 are complied with;
(d) the space is purged and ventilated to provide a safe atmosphere;
(e) the measures necessary to maintain a safe atmosphere have been taken;
(f) another person is stationed outside the confined space;
(g) suitable arrangements have been made to remove the person from the confined space should he or she require assistance; and
(h) a person adequately trained in artificial respiration is conveniently available. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 272.
Note: On September 30, 2006, section 272 is revoked. See: O. Reg. 630/05, ss. 2, 5.
273. Despite sections 271 and 272, confined space in which there exists or is likely to exist,
(a) a toxic gas, vapour, dust or fume; or
(b) a partial pressure of oxygen in the atmosphere when measured and corrected to standard atmospheric pressure of less than eighteen kilopascals or more than twenty-three kilopascals,
and that cannot be purged and ventilated to provide and maintain a safe atmosphere may be entered if,
(c) all the requirements of the said section 271, except of subclause (d) (ii) thereof, are complied with;
(d) the person entering is using a suitable breathing apparatus and a safety harness or other similar equipment to which is securely attached a rope, the free end of which is held by a person equipped with an alarm who is keeping watch outside the confined space;
(e) the person entering is using such other equipment as is necessary to ensure his or her safety;
(f) the safety harness, rope and other equipment mentioned in clause (d) have been inspected by a competent person and are in good working order; and
(g) a person adequately trained in artificial respiration is conveniently available. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 273.
Note: On September 30, 2006, section 273 is revoked. See: O. Reg. 630/05, ss. 2, 5.
274. (1) Subject to subsection (2), where the gas or vapour in a confined space is or is likely to be explosive or flammable, the confined space shall be entered only where,
(a) the concentration of the gas or vapour does not or is not likely to exceed 50 per cent of the lower explosive limit of the gas or vapour; and
(b) the only work to be performed is that of cleaning or inspection and of such a nature that it does not create any source of ignition. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 274 (1).
(2) Cold work may be performed in a confined space in which there exists or is likely to exist an explosive or flammable gas or vapour where the concentration does not, and is not likely to, exceed 10 per cent of the lower explosive limit of the gas or vapour. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 274 (2).
Note: On September 30, 2006, section 274 is revoked. See: O. Reg. 630/05, ss. 2, 5.
275. (1) The requirements of sections 271, 272, 273 and 274 apply with all necessary modifications to any confined space while any person remains in that space. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 275 (1).
(2) Sections 271, 272, 273 and 274 do not apply to the workings of an underground mine including drifts, levels, shafts, stopes and raises. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 275 (2).
Note: On September 30, 2006, section 275 is revoked. See: O. Reg. 630/05, ss. 2, 5.
276. (1) Subject to subsections (3), (4) and (5), toilets and wash-basins in a mining plant shall be provided in accordance with the following Table:
TABLE
|
|
Number of facilities |
|
|
Number of Workers |
Toilets |
Washbasins |
|
1 to 9 |
1 |
1 |
|
10 to 24 |
2 |
2 |
|
25 to 49 |
3 |
3 |
|
50 to 74 |
4 |
4 |
|
75 to 100 |
5 |
5 |
|
Add one toilet and one washbasin for each additional thirty workers or fraction thereof. |
|
|
R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 276 (1).
(2) In a washroom,
(a) a toilet shall be enclosed by walls or partitions and a door that is capable of being locked from the inside to provide privacy to a person using the toilet;
(b) hot and cold water shall be supplied to each washbasin;
(c) ventilation to the outdoors capable of providing ten changes of air per hour shall be provided;
(d) a reasonable supply of personal hygiene supplies and equipment shall be provided,
and where separate washrooms are provided for each sex, a legible sign indicating the sex by which the washroom is to be used shall be posted at the door. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 276 (2).
(3) In calculating the number of toilets and washbasins required by the Table in subsection (1), the number of workers in the Table in subsection (1) shall be that number of workers who are normally present on the premises for more than 25 per cent of their working shift. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 276 (3).
(4) Urinals may be substituted for one-half of the required number of toilets for males and for this purpose each 600 millimetres of straight trough urinal may be counted as one urinal. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 276 (4).
(5) For the purpose of this section, each 500 millimetres of circumference of a circular wash fountain or length of straight trough washbasin may be counted as one washbasin. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 276 (5).
(6) Water that is to be used for personal washing purposes shall not,
(a) exceed 60° Celsius at any outlet; or
(b) be directly mixed with steam. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 276 (6).
277. (1) Suitable sanitary conveniences must be provided at a mine in accordance with this section. O. Reg. 60/94, s. 14.
(2) If workers are employed in an underground mine, one toilet must be provided for each group of twenty-five workers or less employed on a shift. O. Reg. 60/94, s. 14.
(3) If workers are employed at a surface mine, one toilet and one urinal must be provided for each group of twenty-five workers or less employed on a shift. O. Reg. 60/94, s. 14.
(4) A toilet at a mine must meet the following requirements:
1. It must be the water-flushing type or of a sanitary design.
2. It must be located in an individual compartment that has a suitable floor and a door that can be locked.
3. It must be provided with clothes hooks.
4. It must be provided with a means for cleansing hands.
5. It must be supplied with toilet paper and, if any of the workers using it are women, with a means for disposing of feminine hygiene products.
6. If electricity is available, the toilet must be provided with lighting.
7. If electricity is available, the toilet must be provided with heating if the toilet is in a location that is colder than 10º Celsius or is in an area that is cold, damp and drafty. O. Reg. 60/94, s. 14.
(5) A toilet in an underground mine must be located in a well-ventilated part of the mine and must be conveniently placed having regard to the number of workers employed on the different levels of the mine. O. Reg. 60/94, s. 14.
(6) A toilet at a mine must be provided with disinfectant and cleansers and must be cleaned and maintained as often as is required to keep it sanitary and at least once a week. O. Reg. 60/94, s. 14.
(7) The waste from a toilet at a surface mine must be disposed of on a regular basis. O. Reg. 60/94, s. 14.
(8) The waste from a toilet in an underground mine must on a regular basis be removed, placed in a sturdy leak-proof container and brought to the surface for disposal. O. Reg. 60/94, s. 14.
(9) Despite subsection (8), the employer may use a different hygienic underground disposal system for wastes from a toilet in an underground mine with the agreement of the joint health and safety committee or the health and safety representative, if any, for the workplace. O. Reg. 60/94, s. 14.
278. (1) Suitable and adequate facilities to wash and shower and to change and dry their clothing shall be provided for workers,
(a) at an underground mine; and
(b) at a surface mine, where the workers are subject to dusty, dirty or wet conditions. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 278 (1).
(2) At an underground mine, the facilities required by subsection (1) shall be located,
(a) when above ground, near the principal entrance of the mine;
(b) unless of non-combustible construction, not nearer than fifteen metres to a shafthouse or portal house; and
(c) not in a hoistroom or boilerhouse, unless a separate, properly constructed room is provided. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 278 (2).
(3) At a surface mine, where the facilities required by subsection (1) are located at a considerable distance from the place of work, adequate transportation to the facilities from the workplace shall be provided to the workers in inclement weather. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 278 (3).
(4) Where practical, protection from the elements between the shaft entrance and the change rooms shall be provided. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 278 (4).
279. Where the clothing of a worker is likely to be contaminated by a biological or chemical agent that may be a hazard to health suitable facilities shall be provided for,
(a) laundering work clothing; and
(b) keeping work clothes separate from street clothes. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 279.
280. (1) Cool potable drinking water shall be provided in mining plants,
(a) from,
(i) a fountain with an upward jet, or
(ii) a tap from a piped water supply or a covered vessel, together with a supply of single-use cups in a sanitary container located near the tap;
(b) on every floor where work is regularly performed; and
(c) within 100 metres of any area where work is regularly performed. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 280 (1).
(2) In underground mines cool potable drinking water shall be provided at locations that,
(a) are reasonably accessible to a worker; and
(b) shall be kept in a clean and sanitary condition. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 280 (2).
(3) The employer shall ensure that all potable drinking water in a mine or mining plant complies with,
(a) the Ontario Drinking Water Standards referred to in Ontario Regulation 459/00 (Drinking Water Protection — Larger Water Works); or
(b) the regulations governing pre-packaged water made under the Food and Drugs Act (Canada). O. Reg. 291/02, s. 9.
281. (1) Where fifteen or more persons congregate to eat, a lunchroom shall be provided which,
(a) is of sufficient size to accommodate all the persons therein;
(b) is heated, lighted and ventilated;
(c) has hand washing and drying facilities;
(d) has hot and cold water;
(e) has facilities for warming of food;
(f) has suitable seating facilities; and
(g) has a non-combustible, covered receptacle for waste disposal. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 281 (1).
(2) An employer shall ensure that all workers have access to an eating area with,
(a) hand cleaning facilities;
(b) potable water;
(c) suitable seating facilities;
(d) lighting;
(e) ventilation;
(f) facilities to keep food from freezing;
(g) heating, if working conditions are wet or cold or both; and
(h) a fire retardant receptacle for waste disposal. O. Reg. 571/92, s. 21.
(3) All lunchrooms and eating areas shall be kept sanitary, clean and dry. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 281 (3).
281.1 (1) Every employer shall equip and maintain a first aid room close to the entrance of an underground mine. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 6.
(2) A first aid room shall be equipped with at least the items listed in the Schedule. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 6.
(3) A first aid room shall be in the charge of a person,
(a) who is certified in Advanced St. John Ambulance First Aid and in cardio-pulmonary resuscitation or who holds an equivalent qualification;
(b) who is readily available; and
(c) who does not perform other work of a nature that is likely to adversely affect the person’s availability to administer first aid. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 6.
281.2 (1) Every employer shall ensure that a person trained in extrication and in rescue methods and equipment pertinent to underground mines is readily available. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 6.
(2) An employer shall keep at a location near a work area in an underground mine,
(a) equipment enabling voice communication with the surface;
(b) a basket stretcher with a spine board and stretcher straps and ropes for lowering and hoisting the basket stretcher;
(c) two blankets, six triangular bandages and three pressure dressings, all of which are sealed in a container that keeps them clean, dry and serviceable;
(d) a splint; and
(e) a cervical collar. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 6.
(3) An employer shall consult with the joint health and safety committee or the health and safety representative or, if there is no committee or representative, with the workers to determine what equipment is necessary to rescue injured workers. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 6.
(4) An employer shall keep the equipment determined under subsection (3) to be necessary and a list of the equipment at suitable locations at an underground mine. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 6.
281.3 (1) An employer shall ensure that all first aid and rescue equipment is inspected at regular intervals as determined by the employer in consultation with the joint health and safety committee or the health and safety representative or, if there is no committee or representative, with the workers. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 6.
(2) An employer shall keep a record of all inspections of first aid and rescue equipment. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 6.
282. (1) Revoked: O. Reg. 583/91, s. 7.
(2) At every mining plant where poisonous or dangerous compounds, solutions or gases are present, there shall be kept or installed in a conspicuous place, as near the compounds, solutions or gases as is practical,
(a) antidotes and washes;
(b) eye wash fountains; and
(c) where necessary, showers for treating injuries received from such compounds, solutions or gases. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 282 (2).
(3) Antidotes and washes required under subsection (2) shall be properly labelled and explicit directions for their use shall be affixed to the boxes containing them. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 282 (3).
283. As a factor to be considered under clause 33 (8) (f) of the Act, the threshold limit values for chemical substances and physical agents set out in “TLVs Threshold Limit Values and Biological Exposure Indices for 1986-87” issued by the American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists are adopted as criteria or guides. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 283.
284. Revoked: O. Reg. 272/97, s. 52.
285. Where a box, drum or other container contains a biological or chemical agent which is likely to affect the health or safety of a worker, the box, drum or other container shall be labelled in clear legible print to identify the agent and the label shall state the precautions to be taken in the handling, use, storage and disposal of the agent. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 285.
286. Where a local exhaust ventilation system recirculates air to the workplace, provision shall be made for a make-up air supply system having sufficient volume to keep any contaminants below the values,
(a) prescribed under section 4 of Regulation 833 of the Revised Regulations of Ontario, 1990; or
(b) if no values are prescribed under the said section 4, adopted as criteria or guides under section 283 of this Regulation,
and the contaminant level in the recirculated air shall not exceed 20 per cent of such values. R.R.O. 1990, Reg. 854, s. 286; O. Reg. 236/99, s. 11.
287. In sections 288 to 293,
“radon daughters” means polonium-218 (RaA), lead-214 (RaB), bismuth-214 (RaC) and polonium-214 (RaC’);
“WL” means working level of radon daughters as determined in accordance with subsection 288 (1);
“WLM” means working level month of radon daughters as determined in accordance with subsection 288 (2). O. Reg. 583/91, s. 8.
288. (1) One working level of radon daughters is the amount of any combination of radon daughters in one litre of air that will release 1.3 × 105 mega electron volts of alpha particle energy during their radioactive decay to lead-210 (RaD). O. Reg. 583/91, s. 8.
(2) One working level month of radon daughters is the amount of a person’s exposure to radon daughters resulting from breathing air that contains one WL for a period of 170 hours. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 8.
289. (1) Samples of air to which workers may be exposed in an underground mine shall be tested for the presence of radon daughters by a competent person. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 8.
(2) The air to which workers may be exposed in an underground mine shall be tested,
(a) before work begins in a mine that is being reopened; and
(b) within six months after the commencement of excavation of a new mine. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 8.
(3) The air to which workers may be exposed in an underground mine shall be retested,
(a) at least monthly, if the concentration of radon daughters in a sample exceeds 0.1 WL; and
(b) at least quarterly, if the concentration of radon daughters in a sample is greater than 0.06 WL up to and including 0.1 WL. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 8.
(4) If the concentration of radon daughters in a sample is less than or equal to 0.06 WL, a competent person shall assess once a year whether to retest the air in the work area in the underground mine and in making the assessment shall consider previous test results and changes in the mine or its operations. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 8.
(5) An employer shall keep a record of the results of all tests of samples of air in an underground mine and shall give a copy of all results to the joint health and safety committee or the health and safety representative, if any. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 8.
(6) An employer shall post the results of all testing in a place where they are likely to come to the attention of workers as soon as the results become available and shall keep them posted for at least fourteen days. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 8.
(7) Samples of air in an underground mine shall be tested for the presence of radon daughters by a competent person within one year after the date that this section comes into force. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 8.
(8) Subsection (7) does not apply with respect to an underground mine if in a previous test the concentration of radon daughters was less than or equal to 0.06 WL, if a competent person considers that a test is not necessary in the circumstances, having assessed previous test results and changes in the mine or its operations. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 8.
290. (1) Every employer shall ensure that the airborne concentration of radon daughters to which workers may be exposed in an underground mine is reduced to the lowest practical level in accordance with good industrial hygiene practice. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 8.
(2) An employer shall ensure that no worker who is continuously employed by the employer during a year inhales air which exposes the worker to more than one WLM. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 8.
291. If the concentration of radon daughters to which a worker may be exposed in an underground mine exceeds 0.33 WL, the employer,
(a) shall immediately remove all workers from the affected area of the mine;
(b) shall give written notice of the occurrence to the joint health and safety committee or health and safety representative, if any;
(c) shall implement the measures and procedures required by subsection 255 (1);
(d) shall provide the written instructions required by subsection 255 (3) to all workers assigned to do remedial work; and
(e) shall provide to workers doing remedial work and require the use of respiratory equipment appropriate to prevent or limit the workers’ exposure to radon daughters. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 8; O. Reg. 272/97, s. 53.
292. (1) An employer shall develop and implement in consultation with the joint health and safety committee or the health and safety representative, if any, a written description of work practices for a workplace at which the airborne concentration of radon daughters exceeds 0.1 WL. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 8; O. Reg. 291/02, s. 10 (1).
(2) The written description of work practices shall include procedures for investigating the cause of and reducing the level of the airborne concentration of radon daughters to the lowest practical level in accordance with good industrial hygiene practice. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 8; O. Reg. 291/02, s. 10 (2).
(3) An employer shall post the written description of work practices in a place where it is likely to come to the attention of all workers who may be affected by exposure to radon daughters. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 8; O. Reg. 291/02, s. 10 (3).
(4) Revoked: O. Reg. 272/97, s. 54.
293. (1) This section applies with respect to a workplace where a written description of work practices referred to in section 292 has been implemented. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 8; O. Reg. 291/02, s. 11.
(2) An employer shall train workers in radiation hazards and protection practices. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 8.
(3) An employer shall calculate in WLMs the annual cumulative level of exposure of a worker who is exposed to an average concentration of radon daughters greater than 0.1 WL over a period of eight hours. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 8.
(4) An employer shall keep a record of the information calculated under subsection (3) and shall give a copy of the record,
(a) to the worker or the next of kin or personal representative of a deceased worker, on receipt of a written request; and
(b) to the joint health and safety committee or the health and safety representative, if any. O. Reg. 583/91, s. 8.
(5) An employer shall forward a copy of a record kept under subsection (4) to the National Dose Register established under the Atomic Energy Control Act (Canada). O. Reg. 583/91, s. 8.
Note: On September 30, 2006, the Regulation is amended by adding the following Part:
294. In this Part,
“acceptable atmospheric levels” means that,
(a) the atmospheric concentration of any explosive or flammable gas or vapour is less than,
(i) 25 per cent of its lower explosive limit, if paragraph 1 of subsection 311 (4) applies,
(ii) 10 per cent of its lower explosive limit, if paragraph 2 of subsection 311 (4) applies,
(iii) 5 per cent of its lower explosive limit, if paragraph 3 of subsection 311 (4) applies,
(b) the oxygen content of the atmosphere is at least 19.5 per cent but not more than 23 per cent by volume, and
(c) the exposure to atmospheric contaminants does not exceed any applicable level set out in a regulation made under the Act and listed in Table 1;
“assessment” means an assessment of hazards with respect to one or more confined spaces in a workplace, as described in section 298;
“atmospheric hazards” means,
(a) the accumulation of flammable, combustible or explosive agents,
(b) an oxygen content in the atmosphere that is less than 19.5 per cent or more than 23 per cent by volume, or
(c) the accumulation of atmospheric contaminants, including gases, vapours, fumes, dusts or mists, that could,
(i) result in acute health effects that pose an immediate threat to life, or
(ii) interfere with a person’s ability to escape unaided from a confined space;
“cold work” means work that is not capable of producing a source of ignition;
“confined space” means a fully or partially enclosed space,
(a) that is not both designed and constructed for continuous human occupancy, and
(b) in which atmospheric hazards may occur because of its construction, location or contents or because of work that is done in it;
“emergency work” means work performed in connection with an unforeseen event that involves an imminent danger to the life, health or safety of any person;
“hot work” means work that is capable of producing a source of ignition;
“lead employer” means an employer who contracts for the services of one or more other employers or independent contractors in relation to one or more confined spaces that are located,
(a) in the lead employer’s own workplace, or
(b) in another employer’s workplace;
“plan” means a plan for one or more confined spaces in a workplace, as described in section 299;
“program” means a program for one or more confined spaces in a workplace, as described in section 297;
“purging” means displacing contaminants from a confined space;
“related work” means work that is performed near a confined space in direct support of work inside the confined space. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
295. (1) Sections 296 to 299 and 301 to 313 of this Regulation do not apply to emergency work performed by,
(a) a firefighter as defined in the Fire Protection and Prevention Act, 1997; or
(b) a person who,
(i) holds a certificate under the Technical Standards and Safety Act, 2000 designating him or her as a gas technician, and
(ii) is working under the direction of a fire department, as defined in the Fire Protection and Prevention Act, 1997. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(2) A worker described in subsection (1) who performs emergency work shall be adequately protected by,
(a) personal protective equipment, clothing and devices provided by the worker’s employer;
(b) training under section 300 provided by that employer; and
(c) written procedures and other measures developed by that employer. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(3) This Part does not apply to work performed underwater by a diver during a diving operation as defined in Ontario Regulation 629/94 (Diving Operations) made under the Act. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
296. (1) This section applies if the workers of more than one employer perform work in the same confined space or related work with respect to the same confined space. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(2) Before any worker enters the confined space or begins related work with respect to the confined space, the lead employer shall prepare a co-ordination document to ensure that the duties imposed on employers by sections 297 to 299, 301 to 304 and 306 to 312 are performed in a way that protects the health and safety of all workers who perform work in the confined space or related work with respect to the confined space. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(3) Without restricting the generality of subsection (2), the co-ordination document may provide for the performance of a duty or duties referred to in that subsection by one or more employers on behalf of one or more other employers, with respect to some or all of the workers. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(4) A copy of the co-ordination document shall be provided to,
(a) each employer of workers who perform work in the same confined space or related work with respect to the same confined space; and
(b) the joint health and safety committee or health and safety representative, if any, for each employer of workers who perform work in the same confined space or related work with respect to the same confined space. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
297. (1) If an employer’s workplace includes a confined space that workers may enter to perform work, the employer shall ensure that a written program for the confined space is developed and maintained in accordance with this Part before a worker enters the confined space. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(2) The program may apply to one or more confined spaces. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(3) The program shall be developed and maintained in consultation with the joint health and safety committee or the health and safety representative, if any. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(4) The program shall be adequate and shall provide for,
(a) a method for recognizing each confined space to which the program applies;
(b) a method for assessing the hazards to which workers may be exposed, in accordance with section 298;
(c) a method for the development of one or more plans, in accordance with section 299;
(d) a method for general training of workers, in accordance with section 300; and
(e) an entry permit system that sets out the measures and procedures to be followed when work is to be performed in a confined space to which the program applies. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(5) The employer shall provide a copy of the program to the joint health and safety committee or the health and safety representative, if any. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(6) The employer shall ensure that a copy of the program is available to,
(a) any other employer of workers who perform work to which the program relates; and
(b) every worker who performs work to which the program relates, if the workplace has no joint health and safety committee or health and safety representative. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
298. (1) Before any worker enters a confined space, the employer shall ensure that an adequate assessment of the hazards related to the confined space has been carried out. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(2) The assessment shall be recorded in writing and shall consider, with respect to each confined space,
(a) the hazards that may exist due to the design, construction, location, use or contents of the confined space; and
(b) the hazards that may develop while work is done inside the confined space. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(3) The record of the assessment may be incorporated into an entry permit under section 302. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(4) If two or more confined spaces are of similar construction and present the same hazards, their assessments may be recorded in a single document, but each confined space shall be clearly identified in the assessment. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(5) The employer shall appoint a person with adequate knowledge, training and experience to carry out the assessment and shall maintain a record containing details of the person’s knowledge, training and experience. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(6) The assessment shall contain the name of the person who carries out the assessment. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(7) The person shall sign and date the assessment and provide it to the employer. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(8) On request, the employer shall provide copies of the assessment and of the record mentioned in subsection (5) to,
(a) the joint health and safety committee or the health and safety representative, if any; or
(b) every worker who performs work to which the assessment relates, if the workplace has no joint health and safety committee or health and safety representative. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(9) The employer shall ensure that the assessment is reviewed as often as is necessary to ensure that the relevant plan remains adequate. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
299. (1) Before any worker enters a confined space, the employer shall ensure that an adequate written plan, including procedures for the control of hazards identified in the assessment, has been developed and implemented by a competent person for the confined space. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(2) The plan may be incorporated into an entry permit under section 302. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(3) The plan shall contain provisions for,
(a) the duties of workers;
(b) co-ordination in accordance with section 296, if applicable;
(c) on-site rescue procedures, in accordance with section 303;
(d) rescue equipment and methods of communication, in accordance with section 304;
(e) personal protective equipment, clothing and devices, in accordance with section 305;
(f) isolation of energy and control of materials movement, in accordance with section 306;
(g) attendants, in accordance with section 307;
(h) adequate means for entering and exiting, in accordance with section 308;
(i) atmospheric testing, in accordance with section 310;
(j) adequate procedures for working in the presence of explosive or flammable substances, in accordance with section 311; and
(k) ventilation and purging, in accordance with section 312. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(4) One plan may deal with two or more confined spaces that are of similar construction and present the same hazards as identified by the assessment. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(5) The employer shall ensure that the plan is reviewed as often as is necessary to ensure that it remains adequate. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
300. (1) Every worker who enters a confined space or who performs related work shall be given adequate training for safe work practices for working in confined spaces and for performing related work, including training in the recognition of hazards associated with confined spaces. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(2) The employer shall appoint a person with adequate knowledge, training and experience to conduct the training. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(3) The employer shall ensure that training under this section is developed in consultation with the joint health and safety committee or the health and safety representative, if any. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(4) The employer shall ensure that training under this section is reviewed, in consultation with the joint health and safety committee or the health and safety representative, if any, whenever there is a change in circumstances that may affect the safety of a worker who enters a confined space in the workplace, and in any case at least once annually. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(5) The employer shall maintain up-to-date written records showing who provided and who received training under this section, the nature of the training and the date when it was provided. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(6) The records may be incorporated into an entry permit under section 302. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(7) Training under this section may be combined with training under section 301. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
301. (1) The employer shall ensure that every worker who enters a confined space or who performs related work,
(a) receives adequate training, in accordance with the relevant plan, to work safely and properly; and
(b) follows the plan. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(2) The employer shall maintain up-to-date written records showing who provided and who received training under this section, and the date when it was provided. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(3) The records may be incorporated into an entry permit under section 302. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(4) Training under this section may be combined with training under section 300. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
302. (1) The employer shall ensure that a separate entry permit is issued each time work is to be performed in a confined space, before any worker enters the confined space. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(2) An entry permit shall be adequate and shall include at least the following:
1. The location of the confined space.
2. A description of the work to be performed there.
3. A description of the hazards and the corresponding control measures.
4. The time period for which the entry permit applies.
5. The name of the attendant described in section 307.
6. A record of each worker’s entries and exits.
7. A list of the equipment required for entry and rescue, and verification that the equipment is in good working order.
8. Results obtained in atmospheric testing under section 310.
9. If the work to be performed in the confined space includes hot work, adequate provisions for the hot work and corresponding control measures. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(3) Before each shift, a competent person shall verify that the entry permit complies with the relevant plan. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(4) The employer shall ensure that the entry permit, during the time period for which it applies, is readily available to every person who enters the confined space and to every person who performs related work with respect to the confined space. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
303. (1) The employer shall ensure that no worker enters or remains in a confined space unless, in accordance with the relevant plan, adequate written on-site rescue procedures that apply to the confined space have been developed and are ready for immediate implementation. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(2) Before a worker enters a confined space, the employer shall ensure that an adequate number of persons trained in the matters listed in subsection (3) are available for immediate implementation of the on-site rescue procedures mentioned in subsection (1). O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(3) The persons shall be trained in,
(a) the on-site rescue procedures mentioned in subsection (1);
(b) first aid and cardio-pulmonary resuscitation; and
(c) the use of the rescue equipment required in accordance with the relevant plan. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
304. (1) The employer shall ensure that the rescue equipment identified in the relevant plan is,
(a) readily available to effect a rescue in the confined space;
(b) appropriate for entry into the confined space; and
(c) inspected as often as is necessary to ensure it is in good working order, by a person with adequate knowledge, training and experience who is appointed by the employer. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(2) The inspection under clause (1) (c) shall be recorded in writing by the person, and the record of the inspection may be incorporated into the entry permit under section 302. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(3) The employer shall establish methods of communication that are appropriate for the hazards identified in the relevant assessment, and shall make them readily available for workers to communicate with the attendant described in section 307. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
305. The employer shall ensure that each worker who enters a confined space is provided with adequate personal protective equipment, clothing and devices, in accordance with the relevant plan. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
306. The employer shall, in accordance with the relevant plan, ensure that each worker entering a confined space is adequately protected,
(a) against the release of hazardous substances into the confined space,
(i) by blanking or disconnecting piping, or
(ii) if compliance with subclause (i) is not practical in the circumstances for technical reasons, by other adequate means;
(b) against contact with electrical energy inside the confined space that could endanger the worker,
(i) by disconnecting, de-energizing, locking out and tagging the source of electrical energy, or
(ii) if compliance with subclause (i) is not practical in the circumstances for technical reasons, by other adequate means;
(c) against contact with moving parts of equipment inside the confined space that could endanger the worker,
(i) by disconnecting the equipment from its power source, de-energizing the equipment, locking it out and tagging it, or
(ii) if compliance with subclause (i) is not practical in the circumstances for technical reasons, immobilizing the equipment by blocking or other adequate means; and
(d) against drowning, engulfment, entrapment, suffocation and other hazards from free-flowing material, by adequate means. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
307. (1) Whenever a worker is to enter a confined space, the employer shall ensure that an attendant,
(a) is assigned;
(b) is stationed outside and near,
(i) the entrance to the confined space, or
(ii) if there are two or more entrances, the one that will best allow the attendant to perform his or her duties under subsection (2);
(c) is in constant communication with all workers inside the confined space, using the means of communication described in the relevant plan; and
(d) is provided with a device for summoning an adequate rescue response. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(2) The attendant shall not enter the confined space at any time and shall, in accordance with the relevant plan,
(a) monitor the safety of the worker inside;
(b) provide assistance to him or her; and
(c) summon an adequate rescue response if required. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
308. An adequate means for entering and exiting shall be provided for all workers who enter a confined space, in accordance with the relevant plan. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
309. If there is a possibility of unauthorized entry into a confined space, the employer shall ensure that each entrance to the confined space,
(a) is adequately secured against unauthorized entry; or
(b) has been provided with adequate barricades, adequate warning signs regarding unauthorized entry, or both. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
310. (1) The employer shall appoint a person with adequate knowledge, training and experience to perform adequate tests as often as necessary before and while a worker is in a confined space to ensure that acceptable atmospheric levels are maintained in the confined space in accordance with the relevant plan. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(2) If the confined space has been both unoccupied and unattended, tests shall be performed before a worker enters or re-enters. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(3) The person performing the tests shall use calibrated instruments that are in good working order and are appropriate for the hazards identified in the relevant assessment. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(4) The employer shall ensure that the results of every sample of a test are recorded, subject to subsection (5). O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(5) If the tests are performed using continuous monitoring, the employer shall ensure that test results are recorded at adequate intervals. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(6) The tests shall be performed in a manner that does not endanger the health or safety of the person performing them. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(7) In this section,
“sample” means an individual reading of the composition of the atmosphere in the confined space;
“test” means a collection of samples. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
311. (1) This section applies only in respect of atmospheric hazards described in clause (a) of the definition of “atmospheric hazards” in section 294. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(2) The employer shall ensure that this section is complied with, by ventilation, purging, rendering the atmosphere inert or other adequate means, in accordance with the relevant plan. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(3) The employer shall ensure that no worker enters or remains in a confined space that contains or is likely to contain an airborne combustible dust or mist whose atmospheric concentration may create a hazard of explosion. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(4) The employer shall ensure that no worker enters or remains in a confined space that contains or is likely to contain an explosive or flammable gas or vapour, unless one of the following applies:
1. The worker is performing only inspection work that does not produce a source of ignition. In the case of an explosive or flammable gas or vapour, the atmospheric concentration is less than 25 per cent of its lower explosive limit, as determined by a combustible gas instrument.
2. The worker is performing only cold work. In the case of an explosive or flammable gas or vapour, the atmospheric concentration is less than 10 per cent of its lower explosive limit, as determined by a combustible gas instrument.
3. The worker is performing hot work. All the following conditions are satisfied:
i. In the case of an explosive or flammable gas or vapour, the atmospheric concentration is less than 5 per cent of its lower explosive limit, as determined by a combustible gas instrument.
ii. The atmosphere in the confined space does not contain, and is not likely to contain while a worker is inside, an oxygen content greater than 23 per cent.
iii. The atmosphere in the confined space is monitored continuously.
iv. The entry permit includes adequate provisions for hot work and corresponding control measures.
v. An adequate alarm system and exit procedure are provided to ensure that workers have adequate warning and are able to exit the confined space safely if either or both of the following occur:
A. In the case of an explosive or flammable gas or vapour, the atmospheric concentration exceeds 5 per cent of its lower explosive limit.
B. The oxygen content of the atmosphere exceeds 23 per cent by volume. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(5) Subsections (3) and (4) do not apply if,
(a) the atmosphere in the confined space,
(i) has been rendered inert by adding an inert gas, and
(ii) is monitored continuously to ensure that it remains inert; and
(b) a worker entering the confined space uses,
(i) adequate respiratory protective equipment,
(ii) adequate equipment to allow persons outside the confined space to locate and rescue the worker if necessary, and
(iii) such other equipment as is necessary to ensure the worker’s safety. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(6) The equipment mentioned in subclauses (5) (b) (i), (ii) and (iii) shall be inspected by a person with adequate knowledge, training and experience, appointed by the employer, and shall be in good working order before the worker enters the confined space. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
312. (1) This section applies only in respect of atmospheric hazards described in clause (b) or (c) of the definition of “atmospheric hazards” in section 294. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(2) If atmospheric hazards exist or are likely to exist in a confined space, the confined space shall be purged, ventilated or both, before any worker enters it, to ensure that acceptable atmospheric levels are maintained in the confined space while any worker is inside. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(3) If mechanical ventilation is required to maintain acceptable atmospheric levels, an adequate warning system and exit procedure shall also be provided to ensure that workers have adequate warning of ventilation failure and are able to exit the confined space safely. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(4) If compliance with subsection (2) is not practical in the circumstances for technical reasons,
(a) compliance with subsection (3) is not required; and
(b) a worker entering the confined space shall use,
(i) adequate respiratory protective equipment,
(ii) adequate equipment to allow persons outside the confined space to locate and rescue the worker if necessary, and
(iii) such other equipment as is necessary to ensure the worker’s safety. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(5) The equipment mentioned in subclauses (4) (b) (i), (ii) and (iii) shall be inspected by a person with adequate knowledge, training and experience, appointed by the employer, and shall be in good working order before the worker enters the confined space. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
313. (1) The employer shall retain every assessment, plan, co-ordination document under section 296, record of training under subsection 300 (5) or 301 (2), entry permit under section 302, record of an inspection under subsection 304 (2) and record of a test under section 310, including records of each sample, for the longer of the following periods:
1. One year after the document is created.
2. The period that is necessary to ensure that at least the two most recent records of each kind that relate to a particular confined space are retained. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
(2) If section 296 applies, the documents described in subsection (1) shall be retained by the employer responsible for creating them. O. Reg. 630/05, s. 3.
See: O. Reg. 630/05, ss. 3, 5.
Note: On September 30, 2006, the Regulation is amended by adding the following Table:
|
Number of Regulation in Revised Regulations of Ontario, 1990 |
Title |
|
833 |
Control of Exposure to Biological or Chemical Agents |
|
835 |
Designated Substance —Acrylonitrile |
|
836 |
Designated Substance — Arsenic |
|
837 |
Designated Substance — Asbestos |
|
839 |
Designated Substance — Benzene |
|
840 |
Designated Substance — Coke Oven Emissions |
|
841 |
Designated Substance — Ethylene Oxide |
|
842 |
Designated Substance —Isocyanates |
|
843 |
Designated Substance — Lead |
|
844 |
Designated Substance — Mercury |
|
845 |
Designated Substance — Silica |
|
846 |
Designated Substance — Vinyl Chloride |
O. Reg. 630/05, s. 4.
See: O. Reg. 630/05, ss. 4, 5.
1. (1) Every first aid room referred to in section 281.1 of this Regulation shall be equipped with,
(a) a current edition of a standard St. John Ambulance First Aid Manual;
(b) medical instruments, including dressing scissors, dressing forceps, safety pins, a graduated medicine glass, tongue depressors and cotton-tipped applicators;
(c) denatured ethyl alcohol; and
(d) dressings, including individually-wrapped adhesive dressings, individually-wrapped sterile gauze pads of various sizes, gauze bandages of various sizes, adhesive plaster, absorbent cotton, triangular bandages, splints of various sizes and splint padding.
(2) Every first aid room shall be furnished with,
(a) hot and cold running water;
(b) three wash basins (preferably stainless steel);
(c) one instrument sterilizer;
(d) one cabinet for surgical dressings;
(e) one enamel foot bath;
(f) one sanitary disposal receptacle with a lid;
(g) one couch in a cubicle separate from or curtained off from the rest of the first aid room;
(h) one stretcher; and
(i) two blankets.
2. (1) Every first aid room shall have one first aid box that contains at least the items listed in this section for use by a medical attendant at the site of an accident.
(2) A first aid box shall contain,
(a) a current edition of a standard St. John Ambulance First Aid Manual; and
(b) dressings, including twenty-four individually-wrapped adhesive dressings, twelve 3" square gauze pads, four rolls of 2" gauze bandage, four rolls of 4" gauze bandage, four individually-wrapped sterile surgical pads suitable for pressure dressing, six triangular bandages and one roll-up splint.
O. Reg. 583/91, s. 9.
Form 1
(Subsection 182 (1)) diesel powered equipment notice
Occupational Health and Safety Act
Insert regs\graphics\1990\854\854001au.tif
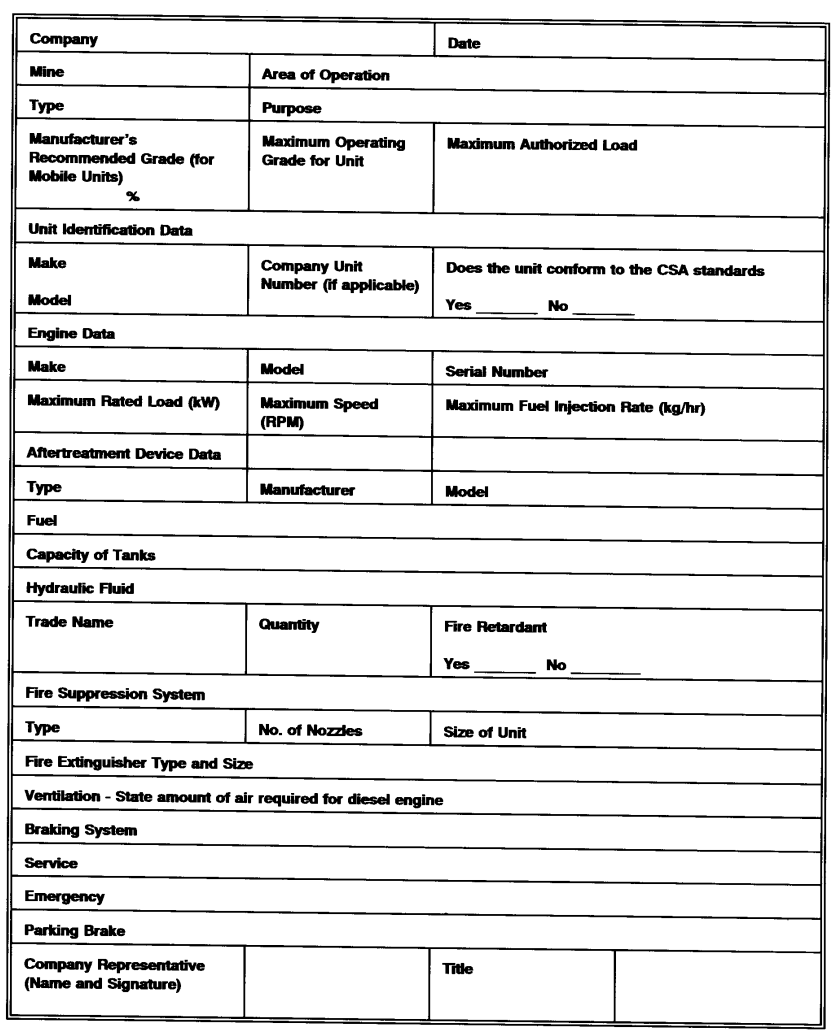
O. Reg. 779/94, s. 12.