Social media for small business
Focuses on using social media techniques to promote your business online. Part of Ontario’s e-Business Toolkit.
Disclaimer: This booklet is intended for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal, technical, business or other advice and should not be relied on as such. Please consult a lawyer or other professional advisor if you have any questions related to the topics discussed in the booklet. The Ontario Government does not endorse any commercial product, process or service referenced in this booklet, or its producer or provider. The Ontario Government also does not make any express or implied warranties, or assumes any legal liability for the accuracy, completeness, timeliness or usefulness of any information contained in this booklet, including web-links to other servers. All URLs mentioned in this document will link to an external website.
The rapid adoption of social media is becoming more apparent by the day and is changing the way we do business. It is no longer a matter of asking “should” you use social media to market your business, but “how” you should. This booklet will help you craft a social media strategy as part of your overall marketing mix.
Key concepts
Social media is a broad term used to describe all the different online technology tools that enable people to communicate easily via the Internet through sharing information and resources. Methods used include posts on blogs or forums, sharing of photos, audio clips, videos and links, creating profiles on social networking sites, and posting status updates—usually with a feedback mechanism. Although social media started out as a medium for friends and family to share information, smart marketers quickly caught on to how they could leverage it.
Key social media platforms and tools
There are many different types of social media. The following graphic highlights these various types and some corresponding examples that are popular now. However, this is a rapidly changing landscape and new social media sites are popping up all the time. Be on the lookout for new and emerging resources.
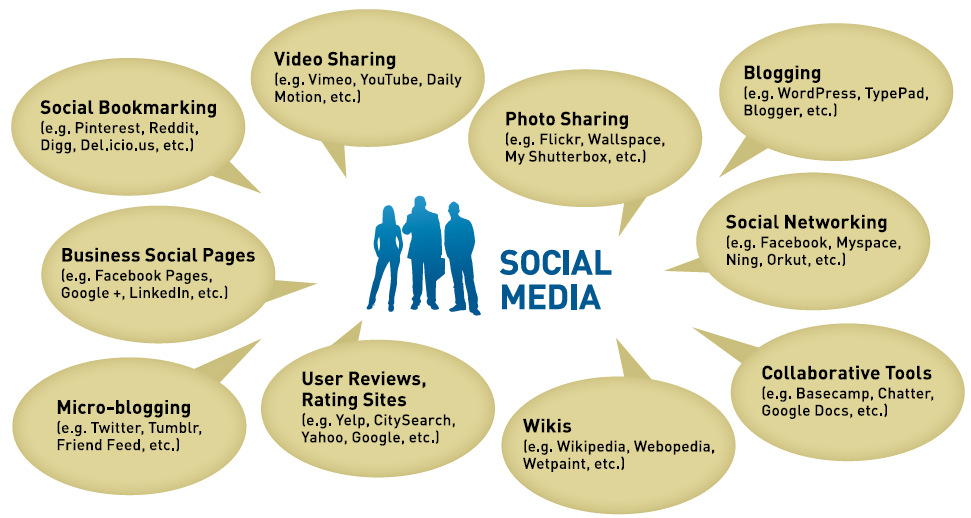
Figure 1 - Social Media
Depending on the industry you are in, certain types of social media may be more relevant than others. For example, those in the travel industry will find a site like Trip Advisor a useful social media tool. In addition, the use of social media may be more prevalent in some industries than others and will work differently for businesses in different fields. It is important to do your research to find out if and how your customers and prospects are engaging with social media.
Benefits of social media
From a marketing perspective, social media tactics can help you:
- Extend your marketing reach affordably.
- Increase brand awareness.
- Drive traffic to your website.
- Personalize customer service.
- Create excitement for events.
- Promote product/service launches.
- Build a community of customers who, by virtue of membership, endorse your products/services.
- Test market ideas.
- Open up new markets.
- Complement other marketing efforts such as paid marketing campaigns.
- Integrate a social element in your business by personalizing your company.
Getting started
1. Planning
If, like many small business owners, you find social media overwhelming, don’t try to do it all at once. Take small steps when you are starting out and bear in mind that it will take time, because it’s all about relationship building. Before using or expanding your use of social media, answer these questions:
Are you ready for social media marketing?
- Does your target audience use social media and, if so, do you know where your prospects congregate online?
- Do you know what goals you are trying to achieve by engaging in social media?
- Can you allocate time and budget?
- Is there someone well suited to be your voice in social media?
- Do your employees require training?
- Do you need to hire or outsource a social media manager?
- Do you have clear key messages and branding to disseminate in the social media realm?
- Can these various online tools integrate with your offline marketing methods?
- Do you have a plan in place to guide your use of social media marketing?
2. Steps for creating a social media strategy
Having a solid social media strategy can really make a difference to the success of your marketing campaigns. Note that your plan will likely evolve and change accordingly as you learn what works for your business and what doesn’t.
- Conduct your research. Listen to the conversations and identify the industry thought leaders you want to follow so you will learn how to participate.
- Define your goals and metrics. What is it you want to achieve and how will you measure its effectiveness? For example, are you trying to drive real targeted traffic to your site? For your Facebook metrics, the number of “Likes” to your Facebook page and the amount of shared posts or status updates will tell you if you are successful. Or perhaps you are trying to build a community of followers who will promote your products or services. If so, good measures of success will be the number of your followers within the social platforms.
- Develop a strategic message and method. For each objective, you may need different methods and messaging to reach the target audience. For example, driving traffic to your site will require a campaign such as a contest or submitting a request form for a free white paper download. Or, if you’re trying to build a community, you’ll need to first build trust and credibility by being authentic in your dialogue and sharing valuable content.
- When evaluating the success of your efforts, first review the goals you established in Step 2. Do the metrics show success? You might need to adjust some elements of your online activities to stay on course. Be sure to keep track of metric trends over time and don’t be afraid to experiment.
3. Resources needed to implement
Contrary to popular belief, social media marketing is not free. The platforms may be free or inexpensive, but the following resources are needed to do social media marketing well:
- Budget. Getting started with social media marketing is a very simple and inexpensive process, requiring only an email address. Most, if not all, of the applications are free to use but there are hidden costs such as your time or hiring someone to run your social media strategy. Some additional costs may include professional versions of plugins (small applications) that expand the functionality of the core application. For example, these plugins could include the ability to sell online or control spam.
- Proper training and polices. Getting familiar with the workings of social media tools tends to be time consuming for most business owners and their employees. Proper training and social media policies should be put in place and key players assigned to manage your social activities. Even if you only select a few voices to represent the company, it is important that everyone from the top down is familiar with the policies, brand message and vision for the company.
- Self-editing website. Having a self-editing website or blog is paramount in order to frequently change the content you share on social media sites. Facebook and Twitter offer posts and micro-blogging tweets that can support your in-depth articles. These can be teasers that lead traffic back to your site to not only to read the full article or participate in viewing a video, for example, but to showcase the full offerings on the site.
Other hidden costs include the time to monitor your reputation online, to track results and to expand customer service.
4. Do-it-yourself option
Getting involved in social media is easy. The do-it-yourself (DIY) option is viable because social media tools are the most affordable and easy-to-implement technical offerings available online, and can be totally controlled by you. (See details in Nuts and Bolts Section below).
Tips for maximizing success when you start on your own
- Attend DIY workshops on online resources to find out how social media tools work and how they can be applied to your business.
- Consider your time involvement and whether you will incorporate a “social” business where everyone participates and has a role (for lead generation, customer service, peer-to-peer networking, etc.) or whether you will assign one person or a few select people to represent your company. The trend now is towards socializing the whole team.
- Offer social media training to your staff, and put a social media policy and schedule in place.
- Integrate ways to bring social media into all areas of your business—including customer service, sales, marketing and public relations.
- Ensure there is buy-in throughout your company.
5. Choosing a specialist to work with
Typically, small businesses do not hire a specialist initially, but eventually you may decide you need extra help if you lack the expertise and time in-house. Whether you are hiring a social media manager or outsourcing this work you will need to look for certain skills in order to represent your brand online powerfully.
What to look for in a specialist:
- Experience with these tools as a user
- Strategic mindset and marketing smarts, with an understanding of how to effectively utilize the tools within the bigger marketing picture
- Good leadership skills, with the ability to work with people in your company
- Strong communication skills to create effective posts, tweets, interactive videos and campaigns to meet your objectives
- Project management skills to integrate the various tools both online and offline
6. Understanding best practices and pitfalls
Do’s
- Listen to the conversations related to your type of business and industry on social media sites such as LinkedIn, Twitter or Facebook. For example, if you have graphic design offerings, you should follow other graphic artists or marketing companies to see how they are conversing with their audience.
- Whether you receive positive or negative comments, always respond in a professional manner and learn from the writer’s input or comments.
- Participate—be authentic, transparent and consistent in all your communications.
- Have a content posting schedule in place.
- Create high quality content to share.
- Be consistent with your branding and messages on all social media platforms.
- Create comprehensive, keyword-rich profiles to share on social networking sites.
- Place calls to action within your posts—that is, include links back to your website so visitors can read something valuable like a good article.
Don’ts
- Refrain from blatant promotion and selling.
- Do not spam.
- Avoid being too personal or social rather than business-oriented.
- Don’t react emotionally online to negative comments about your brand or product or service.
Nuts & bolts
1. Becoming social online
There are many players and platforms to choose from in the rapidly evolving social media landscape. Each is unique and presents a different opportunity to engage with your target audience. Keep in mind though that companies come and go as they jostle for position and what is popular today may fall by the wayside tomorrow. You need to track emerging trends and be ready to adapt quickly.
Currently popular social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Pinterest, YouTube and LinkedIn all contribute to helping businesses with their branding, positioning, networking and collaboration efforts. Check them out to see what they offer and if your customers and prospects are there. Each has its particular use and effectiveness based on the type of audience and how that audience engages with them. For example, Twitter is a one-to-one customer and prospect engagement tool, excellent for real-time customer service, Facebook is a powerful community manager and LinkedIn is good for creating professional alliances and for recruiting employees.
So where do you start? The process itself is quite straightforward. To start along the path, all you need is an Internet connection. Start by setting up a profile on any of the various platforms. Your success will depend on your ability to develop new relationships by following and engaging with those you make connections with. Always try to share quality information, and be transparent, honest and authentic. Here are some tips to get you going.
- Sign up to the various social media platforms such as LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, Google Plus. When you create your company profile, briefly explain what you do and incorporate keyword phrases. Include a link back to your website or a specific landing page on your site.
- Research using keyword phrases to find the conversations in your subject areas, to listen carefully and to identify thought leaders to follow by signing up for RSS feeds.
- Once you feel ready to participate in conversations, start introducing yourself by sharing quality content and building relationships. Participate in Yahoo Answers, LinkedIn QA and discussions, comment on other people’s blogs and be a guest blogger.
- Write your own quality blog and share articles on ezine directories, incorporating “share” or “like” buttons on your blog.
- Share video content on YouTube, Vimeo or Viddler and share images on Flickr, 500px, SmugMug.
Social media and networking platforms
The tables below provide information about various social channels, including micro-blogging, social networking, business social networking, video sharing and photo sharing. Review the details provided to determine which channels would work best in order for you to achieve your goals.
Social networking
Social networking refers to websites that individuals use to socially engage through chatting, status updates and meetup. Within these virtual communities, users create home profile pages and share comments and links directly with other users. Examples include Facebook, Myspace, Ning, Orkut, CafeMom, Badoo.
| Description | To Do’s | Uses | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Best practices
- Build a strategy that is social by design.
- Create an authentic personalized brand voice.
- Make your page interactive.
- Nurture your relationships.
- Respond to feedback and continue to monitor what others are saying about you.
- Schedule your status updates through content schedulers like Hootsuite, ping.fm.
Business social networking
Business social networking provides business owners and employees an opportunity to brand themselves virtually and share content with other like-minded individuals. Examples include LinkedIn, Google Plus, Ning and Sprouter.
| Description | To Do’s | Uses | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Best practices
- Keep your profile as professional as possible, but with a personal touch.
- Be willing to share your contacts, participate in referrals and make sure your privacy settings allow people to find you.
- To drive traffic to your site, create specific and relevant to the conversation landing pages for your LinkedIn audience.
- Use privacy settings to manage what is public and what is not.
- Manage Notification settings to reduce spam.
- Draw attention by using formatted (bold, italics) text.
Micro-blogging sites
Micro-blogging is similar to blogging but with a limited number of characters available for each post. These posts can be easily shared and searched, and profile pages can be designed to fit your brand. Examples include Twitter, Tumblr, Friendfeed, Posterous and Cirip.ro.
| Description | To Do’s | Uses | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Best practices
- Short form links—some links tend to be very long addresses, so consider shortening them by going to either of the following sites—Bitly or goo.gl.
- Be authentic and transparent, truthful and personable.
- For effective re-tweeting, keep your messages to 100 characters in length, to allow for easy sharing.
- Monitor what people are saying about your brand and react professionally.
- Segment lists of followers to target marketing efforts.
- Don’t follow too many people at once.
Video sharing
Video sharing refers to social networking websites where users can upload and share videos. Examples include YouTube, Vimeo, Viddler, Sohu, Daily Motion, and Metacafe.
| Description | To Do’s | Uses | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Best practices
- Leverage reach of YouTube—make it accessible, link from all your social accounts, embed in your website.
- Set your settings to auto-play your video on your channel.
- Make your web address the first word in the video description.
- Title your videos with a keyword rich phrase to help target your video.
- Offer a text summary or consider captioning to make the video more accessible.
Photo sharing
Photo sharing sites give users the ability to upload and share photo images with others. Examples include Flickr, Pinterest, Wallpost, My Shutterspace and Picasa.
| Description | To Do’s | Uses | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Best practices
- Add keyword rich titles and descriptions to photos.
- Include relevant photo name, rather than number.jpg.
- Categorize photos to make search easier.
2. Social media aggregators
These are tools or platforms that enable users involved in social networking to catch up with their network activity all in one place. They will save you time if you are trying to monitor multiple social media sites and are also helpful for your content planning. Examples include:
- FriendFeed: A popular application that allows you to share content across Facebook, Flickr, Twitter and other social networks.
- HootSuite: A web-based social media aggregator for tracking and posting updates.
- Minggl: A browser add-on that lets you manage and interact with all your contacts from one place.
- Tweetdeck: An app that provides real-time social web access, allowing users to connect with Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn and MySpace.
3. URL shorteners
As a blog post typically uses the title as the URL it can be quite long. Services like Bitly or goo.glwill not only shorten your link but will also give you statistics on how many people actually clicked on the link.
4. Social bookmarking and content sharing
Social bookmarking is a method for you to organize, store, manage and search for bookmarks of resources online. Tagging is a significant feature of social bookmarking systems, enabling users to organize their bookmarks in flexible ways and develop shared vocabularies. It usually involves users assigning keyword descriptors to “tag” each bookmark or link they want to share, and then saving them to a public website. You are not actually sharing the “file”, just the “reference link” to it. This allows other people to search by those terms and find those pages. Most social bookmark sites organize their bookmarks with informal tags. You can get up-to-date bookmarks if you subscribe to the social bookmarking site feeds.
The best marketing strategy for a business is to place an icon of one of these bookmarking sites alongside an article, so site visitors can tag the article. The more times this web page is tagged, the higher the popularity ranking of the page. A high popularity ranking draws attention and drives traffic back to your site.
Here are some examples of popular social bookmarking and content sharing sites:
- Pinterest – a bulletin/pin board type of social media sharing based on themes. Useful for interior decorators, artists, crafters, etc.
- Reddit – a social news website where registered users submit news or articles and other users vote on whether they like them. The most popular ones display at the top of the list.
- Technorati – an Internet search engine that searches blogs. Technorati tags are added to your blog postings; the more viewers click on them, the more authoritative your blog content is deemed.
- Digg – a social news website which allows submission of stories and voting privileges, also known as “digging” and “burying”.
- StumbleUpon – a “discovery” search engine allowing users to discover and rate web pages, photos, videos, using peer-sourcing and social networking principles.
- Delicious – a social bookmarking web service for storing, sharing, and discovering web bookmarks. Web users save what they like using the Delicious bookmarklet in their browser bar to add websites to “themed stacks” for easy sharing.
5. Blogging
The difference between a blog and a website is that a blog is frequently updated with commentaries, news, articles with images, videos and text, and therefore is an excellent way to share information and expertise with your target audience and engage people. In addition, readers of your blog can leave comments and, by replying, you will start a dialogue.
The layout of blogs is typically different from a website layout, offering widgets, like a calendar, or plugins, like sidebar testimonials, to expand its functionality.
There are many blog application programs available for you to choose from: ones that are hosted by a blogging program such as wordpress.com, blogger.com, typepad.com or tumblr.com; or ones that you can set up within your existing website hosting service.
Below are some quick tips on using your blog to promote your business:
Tips for using your own blog to promote your business
- Create a professional looking blog.
- Keep your blog posts positive and to the point.
- Create useful content for your target audience. Write about your area of business expertise. Provide updates about your business, and your products and services.
- Provide links on your blog to the sales section of your website.
- Make content available in an RSS feed to permit syndication of your blog material, making the material available to other websites.
- Think carefully before posting your entry. Is it respectful? Professional?
- Follow sound customer service principles.
- If you have your own blog you can write about upcoming business events and sales.
- Link to other relevant websites and blogs.
- Claim your blog at Technorati. This can help ensure that you are indexed in blog search engines.
- Track your progress. Review your web traffic and where your web traffic is coming from (i.e. referring domains).
For more details on blogging, see the Blogs for Small Business booklet.
6. Creating content
Like most business owners, you may feel challenged when it comes to what to write about to engage your target audience. Maybe you are accustomed to creating content for one-way dissemination of information, but have not considered writing content to develop conversations and build relationships. There are actually endless topics to write about; it is just a matter of being creative and listening to your followers and fans—who may or may not be your existing clients.
Find content ideas by: looking at your competitors’ blogs to see what they are writing about; reading blogs in directories or ezines on your subject matter; and following like-minded individuals on social networking sites like Twitter, Facebook and LinkedIn. It is also a good idea to set up a Google Alert on your subject area.
Here are some sites you can visit to get content ideas.
How to get content ideas
- Competitor Sites
- Compete
- Open Site Explorer
- Blog Directories
- Google.com (click on “Blogs”)
- Article Ezines
- Ezine Articles
- SubmitYourArticle.com
- Twitter Search
- Twitter Search Advanced
- TweetDeck
- Twellow
- Facebook Groups
- Facebook Search
- Facebook (click on “Groups”)
- Google Alerts
Guidelines for creating content
- Use tools. If you are just starting out, you can access the above tools to first identify the keywords that your audience would use to search for your offerings. Once you have identified five main keywords, investigate various blog directories, or type “http://keyword:blog” in the search bar, or go to Google search, type in the keyword, then select blogs in the filter. This will give you a feel for what people are writing about in your industry. You can also set up Google Alerts, which will email you whenever something is being written about a particular topic.
- Develop a content schedule. Choose 10–12 key topic areas for developing content once a month, and then expand on them. Remember to develop conversations around what people are asking or commenting on.
- Develop segment-specific content. When setting up your lists, circles or groups, develop content that is specific to people’s interests.
- Repackage content. You can repurpose material in a variety of ways for the social media world. For example, write and post a 300–400 word article on your blog, then extract from that 10 tips to post on Twitter over a given period of time, one-by-one. From that same article, you could also do a frequently asked question/answer discussion on LinkedIn. You could also create a video from the article, perhaps even incorporating a customer’s testimonial.
Proven writing tips for social media
- Use keywords. Incorporate your keyword phrases within your titles, body copy of your posts, status updates, tweets and group discussions. Make sure to add tags to your blog posts and YouTube videos. These are like keywords that people use to find you.
- Have clear titles. Keep titles simple and short, and incorporate numbers when appropriate – for example, “7 Tips to Social Media Success”.
- Be short and to the point. Most of the social media tools have limited character length. Focus on one idea.
- Avoid sales lingo. Social media is not the place for blatant pitching or selling of your products and services. It can be used to help support the pre and post sales experience, but should not be used as a sales channel.
7. Syndication of web content
RSS (Really Simple Syndication) syndicates your web content to other sites and builds inbound links, making RSS one of the most effective SEO strategies today. You or your developer can create a special file such as an RSS file along with a link to it, which creates a “web feed”. Most blog, calendar and news content developed in a blog or content management system can be syndicated to be shared with others. Note: each RSS feed requires a Title, Description and Link.
Once you have syndicated your blog or web pages, it is important to market the fact.
- Let your website visitors know you have RSS feeds. Put the orange RSS icon on all pages that have a feed and place a prominent link on the home page so that your visitors know that you have feeds and offer syndicated content.
- Promote your RSS feeds through email and encourage your readers to learn more about RSS Readers or about receiving feeds directly into their email account.
- Ensure you have a visible RSS icon in side bar of your syndicated blog posts so that your audience can subscribe.
8. Impact of mobile devices (including QR Codes)
People are increasingly using their mobile devices to micro-blog through their Twitter and Facebook accounts, as well as activating various mobile apps for entertainment, productivity and commerce. Mobile usage by the Generation X-ers and Boomers is rising, with many participating in instant commenting, restaurant and spa reviews and other similar services and even using mobile devices to gather like-minded individuals to help support their causes.
What are QR Codes? How can they be incorporated in your marketing mix?
QR (Quick Response) Codes are two-dimensional bar codes typically found on print materials, but increasingly on other things such as mugs, posters, store-front windows and even architectural structures. QR Codes offer immediate access to what is relevant. When people scan a QR Code with their mobile device, they link to digital content that is found either on your blog, website or other online medium. It can also activate a phone call or text message. The ability of QR Codes to connect people to each other and to multimedia digital content is very useful for businesses and consumers alike. There is no limit to how you can use QR Codes for your business, including sharing content, building community (e.g. Likify), promoting special offers and helping improve your overall search engine optimization.
Example of QR Code usage
Google Places – When you register your local business with Google Places you receive a decal for your place of business that includes a QR Code to your company website. Be sure that the QR Code links to the most relevant information potential customers are interested in such as hours of operation and current specials and offers. (Source: Social Media Examiner).
9. Going local – couponing
Group buying sites such as Groupon and Living Social leverage group discounting, which enables local businesses to offer big savings to consumers. These sites are very popular and successful for both consumers and businesses. Many offer short-term daily deals that discount products and services by more than 50% and typically sell-out of such offerings within just a few hours. Some of the group sites promote sharing discounts with friends and provide a free product or service if the buyer signs up three friends. They also allow the buyer to purchase gift certificates. All coupons have expiry dates.
The types of businesses that can best leverage these sites include retail, spas, health care, restaurants and travel services. To participate as a vendor, you can sign up at any of the participating sites. A chart of group buying sites can be found at ToMuse.com.
10. Recruiting and job hunting
Social media tools like LinkedIn have revolutionized the recruiting and job hunting environment. Not only can businesses use them to post job vacancies, but much of the pre-interview work can be done easily by researching candidates’ social footprints. LinkedIn isn’t the only social network that helps in the job search process—Facebook, Twitter, YouTube and Google+ have all been used by people to land jobs in innovative ways.
Measuring your social media efforts
Increasingly, businesses want to know if their investment (time and money) in social media is doing more than raising awareness. Is it driving profitable revenue growth? Revisit the goals you set out in your social media plan to establish some benchmarks and to gauge your performance compared to your other marketing efforts. When evaluating the metrics, look to the overall return on investment (ROI) you stated in your objectives as the indicator of success or failure. Sometimes, due to overlap of various marketing efforts, you may not be able to clearly determine what contributes to the success or failure of your plan.
Your social media activities can’t be measured just in terms of activity—like the number of visitors. Focus instead on the quality of relationships you have built rather than the quantity. The level of engagement of your target audience with your business is a more meaningful measure of how well you are doing.
Here are three levels of engagement to monitor—the higher the level, the greater the engagement and likelihood of action.
| Level | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Level 1 |
|
| Level 2 |
|
| Level 3 |
|
If you want to benchmark against others in your industry, here are some performance indicators you can use to measure against your competitors or peers:
| Distribution – visibility | Interaction – engagement | Influence – branding value |
|---|---|---|
Questions to ask – What social media channels are you using, how can people reach you, are you visible?
|
Questions to ask – How likely are followers going to engage, spread your message and interact with your brand?
|
Questions to ask – How do attitudes change due to the social media activities? This is the branding value that should convert into sales.
|
*Source: Priit Kallas, 48 Social Media KPIs (Key Performance Indicators)
Competitive research resources
- Hootsuite
- Wildfire App
- HowSociable
It is important to integrate all these metrics with the comments, conversations and sentiments you are hearing in the social media world. Then think about what you can do with all this information you collect. Here are some things to consider:
- Are there new marketing and PR opportunities that surface?
- Can you identify customer service issues or unmet needs?
- Do you see any themes pointing to the need for content changes on your web site or in your social media efforts?
- Is there a need to revisit your social media channels and make any changes, based on where you are getting the best results?
Bringing all of this together will help you deepen your understanding of your customers and give you a better handle on measurements that matter. Remember that measurement is an ongoing process. You have to keep listening to the conversations in social media over time, responding and adjusting your efforts.
Where is social media heading?
Watch for these trends:
- Businesses will demand more social management and measurement tools (e.g. Social CRM like Sales Force Social CRM, Nimble, Pivotol and Hootsuite allow real-time tracking and connection to your database).
- Better measurement tools will constantly be introduced to meet the demands of business owners for more accountability in their social media efforts and for a return on investment (ROI).
- Businesses will need to consider how to integrate social into the whole culture of the business from top to bottom. Regardless of its size, all members of the business should be on board and understand and follow a common policy when working in the social arena.
- Video and mobile will continue to forge ahead in the social sphere, creating new ways to engage and communicate with customers and prospects.
- Social is now being integrated beyond websites or mobile devices. Look for increased uses in your car, home and entertainment devices (e.g. 3D television) that let you share what you are watching.
- Niche social sites are emerging, providing deep community engagement to learn and share with groups that have the same interests. For example, Pinterest has become a popular social photo sharing website fashioned around the age-old concept of the pinboard.
- Shopping via social will continue to grow. Peer review and word of mouth will become a more powerful buying incentive than traditional marketing and advertising channels. Businesses will have to find ways to shift this trend to their advantage.
- Social will continue to change rapidly with new platforms and players coming on board (and disappearing just as quickly). Businesses will need to stay on top of emerging trends and be ready to adapt.
- Social search results will command as much attention as all other search results. If you don’t have a social presence, you have less chance of achieving a high search engine ranking. (See the Increasing Traffic to Your Website through SEO booklet).
Related topics covered in other booklets
- Creating a dynamic web presence
- E-commerce: purchasing and selling online
- Integrating mobile with your marketing strategy
- Increasing traffic to your website through search engine optimization techniques
- Blogs for small business
Best practices for engaging in social media
- Listen and participate in social media conversations to understand the rules and market landscape.
- Develop a plan for what you want to achieve with your social media efforts.
- Create compelling, high-quality content that resonates with your audience.
- Contribute, collaborate, inform, educate but do not sell.
- Network with industry influencers who will share good content and promote you in the process.
- Optimize your social media efforts by tracking results and fine-tuning your strategy accordingly.
- When responding to a negative comment, don’t argue or become personal. Always reply in a professional manner and learn from the writer’s input or comments.
- Always address issues as they arise within the social media. Don’t stay silent as this will cause more challenges.
- Don’t sell! Be informative, transparent and authentic. Share quality content.
Glossary of terms
- @username
- When posting a tweet to a subscribed Twitter user, this format will address that particular user and is still visible to all others who follow that particular user.
- Blogging
- A personal journal published on the Internet consisting of posts typically 300-500 words in length. Can incorporate video, audio or other multimedia and typically is displayed chronologically and categorized for easy search.
- Call to action
- A catch phrase to express the process of getting a web viewer to fulfill an action within the web page - for example, filling in a form, clicking on a button or paying for a transaction.
- Circles
- Terminology referring to the Google+ social networking tool. Circles are groupings of people that you share your thoughts, links and photos with. You can have different circles of like-minded individuals.
- CRM
- Customer relationship management (CRM) is a business strategy directed to understand, anticipate and respond to the needs of existing and potential clients in order to grow the relationship value.
- Direct message (DM)
- In the Twitter program this is a way for users to send private messages to each other.
- Ezine directory
- A searchable database of various electronic newsletter articles or electronic magazine articles categorized by theme or niche topic area. Articles submitted to these directories increase your traffic exposure, build awareness and credibility.
- A social network that connects people with friends, family and business associates.
- Facebook “likes”
- Instead of writing a comment for a message or a status update, a Facebook user can click the “Like” button as a quick way to show approval and share the message.
- Facebook timeline
- The new Facebook format for personal profiles. It is essentially a digital scrapbook of a user’s life, displaying their profile in an actual timeline format. This way friends and fans can see exactly the point in time when something occurred.
- Facebook wall
- Typically on the homepage of one’s Facebook account when logging in, there is a wall of posts, including images, text, video and links that have been posted by friends of that account.
- Google+
- This is Google’s social networking site, similar to Facebook, but it uses Circles, hangouts, streams and many other features.
- Google Alerts
- A method to track whether someone is talking about a particular subject and keyword phrase. This is good way to measure if someone is “Talking about you.”
- Guest blogging
- Blogging on other people’s blogs through invitation, posting articles, video, podcasts, etc.
- Hangouts
- Collect people together who happen to be online; they can come from different circles and they just want to hangout. Similar to if you were in your local cafe and bump into a few friends and then join them to “hangout”.
- Hashtags (#)
- Add them in-line with your twitter post to aggregate other like-minded or already grouped posts together to be able to follow more easily. Example: #DigitalConference12 – All those attending this conference can follow the conversations pertaining to the activities and impressions of the event.
- Hootsuite
- Application that allows you to manage multiple Twitter profiles, pre-schedule tweets and view metrics.
- A business-oriented social networking site that is mainly used for professional networking.
- Micro-blogging
- Broadcasting short length character messages such as tweets restricted to 140 characters.
- Plugins
- A set of software components that add specific capabilities to a larger software application and are frequently found in blog applications like WordPress.
- Quick Response Codes (QR Codes)
- 2-D bar graphs that when scanned by a cell phone can link to information on the Internet. Typically seen on business cards, promotional print materials, on products, shop windows, etc. Also widely used for marketing campaigns like contests, event, registration, etc.
- Social news website with content that is user generated and is voted on by users. The most interesting content displays at the top of the news list.
- Re-tweets (RT)
- On the social networking service, Twitter. The message is reposted or forwarded to your followers.
- RSS Feed
- A, series of web feed formats used to publish frequently updated works, like blog entries, news headlines, audio, etc. in a standardized format. RSS feeds benefit publishers by letting them syndicate content automatically.
- Social media monitoring
- The process of monitoring and responding to mentions related to a business that occurs in social media.
- Spam
- The use of electronic messaging to send unsolicited mail messages typically in bulk to unsuspecting individual email addresses. Spam has now extended beyond email and can be sent through online forms, directories, blog comments, etc. Someone who sends spam is known as a spammer.
- Spam control
- Software scripts or plugins help to reduce the amount of spam that comes in from input-forms (e.g. contact us form or request for proposal form, etc.) from your site. Blacklisting/Whitelisting (safeguarding email addresses that are valid and blocking those that are not) and allocating specific words to watch out for are methods for spam control
- Stream
- The stream centralizes all the conversation you are having with the people in your circles. You might see text, video, etc. The content that you share within your circle will appear on this stream.
- StumbleUpon
- A platform similar to Digg, Delicious and Reddit. When you rate a website that you like using StumbleUpon, you automatically share it with like-minded people around the globe
- Tweets
- The name of the 140-character message post sent via Twitter.
- A platform where users share 140-character-long messages publicly. Users can “follow” others by subscribing to each others’ messages. Additionally, users can use the @username command to direct a message towards another Twitter user or Direct Message DM.
- Vanity URL
- In some of the social media platforms, business pages can be developed and a specific web address or vanity URL can be set up. See specific details in the Help sections of each of the platforms to understand the procedure. Having a vanity URL is helpful in keeping with your overall branding.
- Viral marketing
- Refers to marketing techniques that use pre-existing social networks to produce increases in brand awareness or to achieve other marketing objectives through self-replicating processes.
- Widget
- An element of a graphical user interface that displays an information arrangement changeable by the user, such as a window or text box.
- WordPress
- Popular blogging platform to publish posts but can also be used as a content management system for a website.
This publication is part of an e-Business Toolkit which includes a series of booklets on advanced e-business topics and an introductory handbook How You Can Profit from E-Business. The entire Toolkit is available at ontario.ca/ebusiness.