Charging electric vehicles
Learn how and where to charge your electric vehicle (EV).
Types of EV Chargers
Electric Vehicles (EVs) can charge at different speeds depending on the charger type and the capacity of the battery. There are four main types of chargers:
Level 1 Charging
- Slowest charging option (120 Volts/15 Amps), adds about 5–8 km of range per hour
- Uses a regular cord and wall outlet (like the one you use for a lamp)
- Best for overnight charging or for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) with smaller batteries
Level 2 Charging
- Faster than Level 1 chargers (240 Volts/30 Amps), adds about 35 km of range per hour
- The most common type of charger, it uses a special outlet, like the one for a stove or dryer
- These chargers can be installed in homes and commercial facilities by licensed electricians
- Commonly installed in residential garages, workplaces, and public parking facilities
Level 3 (Direct Current (DC) Fast Charging)
- Very fast: (400-1000 Volts/ up to 400Amps) can add about 250 km of range per hour
- Can charge a battery up to 80% in 20–45 minutes
- Ideal for highway travel and quick top-ups during long trips
- Found at highway rest stops, commercial and public charging stations
- Not suitable for home use due to high power needs and cost
Megawatt Charging System (MCS)
- Ultra-fast charging technology (up to 1,250 volts and 3,000 amps) for medium- and heavy-duty EVs such as trucks, buses, and long-haul freight transport.
- large commercial EVs can recharge their substantial battery packs in under 30 minutes
- Still being developed and not widely available yet
Other Charging Technologies
New ways to charge EVs are being developed:
- Battery Swapping: Allows a dead battery to be swapped out for a fully charged one in minutes. Useful for fleets and transit systems.
- Wireless Charging: Charges without plugging in. There are two main types:
- static wireless charging, where the vehicle is parked over a charging pad (e.g., in a garage or at a bus stop)
- dynamic wireless charging, which enables charging while the vehicle is in motion over specially equipped roads.
- Mobile Charging: Portable chargers or trucks that bring power to your EV. Useful for emergencies, events or in areas locations lacking fixed infrastructure.
- Overhead Catenary Systems: Electric wires above the road power vehicles including buses, trams and freight trucks while they move or at designated stops. Commonly used in urban transit networks and rail systems.
EV charger locations
You can charge your EV at home or at publicly available charging stations. In Ontario, there are over 4,000 stations with more than 11,500 charging ports.
Ontario has also installed 32 Level 2 chargers at carpool lots including:
| Municipality | Highway | Crossroad |
|---|---|---|
| Innisfil | Hwy 400 | Innisfil Beach Road |
| Milton | Hwy 401 | Guelph Line (Main Street North) |
| Beamsville | QEW | Ontario Street |
| Arnprior | Hwy 417 | Ottawa Road 29 |
| Cavan | Hwy 115 | Peterborough Road 10 |
| Gananoque | Hwy 401 | Highway 401 & Highway 2 |
| Cambridge | Hwy 401 | Hwy 401 & Townline Road |
| Windsor | Herb Gray Parkway | Howard Avenue Diversion |
Installing a Home or Business Charger
Follow these steps to install an EV charging station at your home or business:
- Get a permit from the Electrical Safety Authority (ESA) before starting the installation.
- Installation must be done by a licensed electrical contractor in compliance with the Ontario Electrical Safety Code.
- Confirm that all equipment is certified for use in Canada by a nationally recognized certification agency such as Canadian Standards Association, Underwriters Laboratories Inc., Intertek Testing Services or displays other certification marks approved by ESA.
Visit the Electrical Safety Authority website for more details about EV charging station installation.
Support for Public Charging Stations
Ontario’s EV ChargeON program helps communities in Ontario by providing funding for the installation of public electric vehicle (EV) chargers.
Supporting Charging Innovation
In 2024, the Ontario Vehicle Innovation Network, Ontario’s flagship initiative for the automotive and mobility sector, launched the Advanced Charging and Vehicle-to-Grid Stream under its Research and Development Partnership Fund.
Through this stream, Ontario small-and-medium enterprises are provided up to $1 million to develop new charging technologies and solutions that are critical to electrification and the transition to EVs.
EV Charging Parking Signs
Signs for EV charging spots include:
- a no parking symbol
- an EV charger symbol
- the text “EXCEPT WHILE CHARGING”
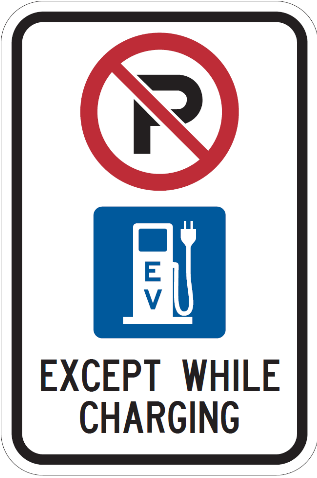

Business owners or operators with EV charging stations may choose to install a sign at parking spaces with chargers. Signs can be purchased from companies who manufacture them according to Regulation 615: Signs.
For more information:
- Reserved Parking for Electric Vehicle Charging Act, 2019
- Section 27. 1(1) of Regulation 615 for sign specifications
Reserved parking for electric vehicle charging spaces
Only electric vehicles plugged into a charging station are permitted to park in spaces with a designated EV parking sign.
Tickets can be issued for:
- parking a non-electric vehicle in a designated EV charging space
- parking an EV in a designated EV charging space that is not plugged in
Ticketed vehicle owners may be subject to a fine of $125 under section 30.2 of the Highway Traffic Act.