O. Reg. 390/18: GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS: QUANTIFICATION, REPORTING AND VERIFICATION, Environmental Protection Act, R.S.O. 1990, c. E.19
Environmental Protection Act
GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS: QUANTIFICATION, REPORTING AND VERIFICATION
Historical version for the period July 4, 2019 to February 10, 2020.
Last amendment: 242/19.
Legislative History: 8/19, 77/19, 242/19.
This is the English version of a bilingual regulation.
CONTENTS
|
Interpretation |
|
|
Application |
|
|
Greenhouse gas |
|
|
Calculation of amount of greenhouse gas |
|
|
Duty to quantify, calculate |
|
|
Duty to report |
|
|
Continuing duty to report |
|
|
Electricity importation, duty to quantify |
|
|
Electricity importation, duty to report |
|
|
Electricity importation, continuing duty to report |
|
|
All activities, duties re 2018 reports, including verification |
|
|
Duty to verify, covered facilities |
|
|
Reporting, general |
|
|
Revised reports |
|
|
Accredited verification bodies, general duties |
|
|
Accredited verification bodies, duties re impartiality |
|
|
Verification statements |
|
|
Verification amount conclusion |
|
|
Production parameter verification conclusions |
|
|
Total annual emissions limit verification conclusion |
|
|
Verification reports |
|
|
Compromise to impartiality |
|
|
Requests for information |
|
|
Retention of records |
|
|
Change in information |
|
|
Giving or submitting records, form and manner |
|
|
Greenhouse gases and global warming potentials |
|
|
Specified ghg activities (subsection 1 (1)) |
|
|
Records to be retained (subsection 24 (1)) |
|
|
Biomass criteria (subsection 1 (1)) |
|
|
Contents of report |
|
Interpretation and Application
Interpretation
“accredited verification body” means a verification body that is accredited to ISO 14065 by a member of the International Accreditation Forum; (“organisme de vérification accrédité”)
“associated gas” means gas found in association with crude oil, either dissolved in crude oil or as a cap of free gas above the crude oil; (“gaz associé”)
“biogas” means a gas made from the anaerobic digestion of organic matter in wastewater or wastewater treatment systems; (“biogaz”)
“biomass” means organic matter, other than source separated organics and peat or peat derivatives, that meets the criteria set out in Schedule 4; (“biomasse”)
“CO2e” means, when used in reference to a quantity of greenhouse gas, the equivalent quantity of carbon dioxide, calculated in accordance with section 4; (“éq. CO2”)
“covered facility” has the same meaning as in Ontario Regulation 241/19 (Greenhouse Gas Emissions Performance Standards) made under the Act; (“installation assujettie”)
“Director” means the Director appointed under section 5 of the Act in respect of the section of this Regulation in which the reference appears; (“directeur”)
“distribution system” has the same meaning as in subsection 2 (1) of the Electricity Act, 1998; (“réseau de distribution”)
“electricity importation” means the importation of electricity into Ontario for consumption in Ontario; (“importation d’électricité”)
“facility” means all buildings, equipment, structures and stationary items, such as surfaces and storage piles that,
(a) are owned or operated by the same person, and
(b) are located,
(i) on a single site,
(ii) on two or more adjacent sites that function as a single integrated site, or
(iii) in the case of a pipeline transportation system, a transmission system or a distribution system, on two or more sites that are not adjacent; (“installation”)
“general stationary combustion equipment” includes any stationary combustion devices, including boilers, simple and combined cycle combustion turbines, engines, incinerators (including units that combust hazardous waste or gaseous waste) and process heaters but does not include,
(a) portable equipment,
(b) stationary emergency generators that have a nameplate generating capacity of less than 10 megawatts, and
(c) any auxiliary fossil fuel powered equipment, other than stationary emergency generators, that is intended for use only in emergency situations, including fire pumps and flares; (“équipement fixe de combustion général”)
“Guideline” means the guideline published by the Ministry and available from the Ministry, entitled “Guideline for Quantification, Reporting and Verification of Greenhouse Gas Emissions”, as amended from time to time; (“ligne directrice”)
“IESO” has the same meaning as in subsection 2 (1) of the Electricity Act, 1998; (“SIERE”)
“indirect useful thermal energy” means thermal energy that is generated at one facility and transferred to another facility; (“énergie thermique utile indirecte”)
“industrial activity” has the same meaning as in Ontario Regulation 241/19 (Greenhouse Gas Emissions Performance Standards) made under the Act; (“activité industrielle”)
“ISO 14064-3” means standard ISO 14064-3, published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and entitled “Greenhouse gases — Part 3: Specification with guidance for the validation and verification of greenhouse gas assertions”, as amended from time to time; (“ISO 14064-3”)
“ISO 14065” means standard ISO 14065, published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and entitled “Greenhouse gases — Requirements for greenhouse gas validation and verification bodies for use in accreditation or other forms of recognition”, as amended from time to time; (“ISO 14065”)
“NAICS” means the North American Industry Classification System maintained for Canada by Statistics Canada, as amended or revised from time to time; (“SCIAN”)
“Ontario Regulation 143/16” means Ontario Regulation 143/16 (Quantification, Reporting and Verification of Greenhouse Gas Emissions) made under the Climate Change Mitigation and Low-carbon Economy Act, 2016 as that Regulation read on July 31, 2018; (“Règlement de l’Ontario 143/16”)
“Ontario Regulation 452/09” means Ontario Regulation 452/09 (Greenhouse Gas Emissions Reporting) made under the Act as that Regulation read on July 31, 2018; (“Règlement de l’Ontario 452/09”)
“pipeline transportation system” means a facility consisting of a system of pipelines in Ontario, or a part of such a system, that transports natural gas and its associated installations, including storage installations but excluding straddle plants or other processing installations; (“réseau de transport par pipeline”)
“portable” means, when used in reference to a piece of equipment, equipment that is designed to be and can be moved from one location to another, subject to subsection (2); (“portable”)
“refinery fuel gas” means gas generated at a petroleum refinery process unit, including still gas and flexigas, or associated gas; (“gaz de combustion de raffinerie”)
“report” means a report required to be given to the Director under this Regulation or under Ontario Regulation 143/16; (“rapport”)
“reporting amount” means the reporting amount determined under section 6; (“quantité déclarée”)
“source separated organics” has the same meaning as in Ontario Regulation 160/99 (Definitions and Exemptions) made under the Electricity Act, 1998; (“matière organique séparée à la source”)
“specified GHG activity” means an activity set out in Column 1 of Schedule 2, as described in Column 2 of that Schedule; (“activité émettrice de GES précisée”)
“total annual emissions limit” has the same meaning as in Ontario Regulation 241/19 (Greenhouse Gas Emissions Performance Standards) made under the Act; (“limite des émissions annuelles totales”)
“transmission system” has the same meaning as in subsection 2 (1) of the Electricity Act, 1998; (“réseau de transport”)
“verification amount” means,
(a) in the case of a report in respect of 2018 or a previous year, the verification amount determined under section 8 as it read immediately before the day section 4 of Ontario Regulation 242/19 made under the Act came into force, and
(b) in the case of a report in respect of 2019 or a later year, the verification amount determined under section 12; (“quantité de vérification”)
“year” means a calendar year. (“année”) O. Reg. 390/18, s. 1 (1); O. Reg. 77/19, s. 1; O. Reg. 242/19, s. 1.
(2) For the purposes of this Regulation, a piece of equipment is not portable if any of the following circumstances apply:
1. It is attached to a foundation.
2. It is at the same location at a facility for more than 12 consecutive months.
3. It has been located at a seasonal facility for two or more years and is used on a regular basis during at least three months of the year.
4. It is moved from one location to another in an attempt to circumvent the requirements of this Regulation.
(3) For the purposes of the definition of “facility”, two sites are adjacent if the boundary of one site touches or, were it not for an intervening highway, road allowance, railway line, railway allowance or utility corridor, would touch the boundary of the other site.
(4) Where this Regulation incorporates by reference a provision of ISO 14064-3 or ISO 14065, the definitions set out in the standard are incorporated by reference for the purposes of interpreting the provision, except if the term has been defined in this Regulation, in which case the definition in this Regulation applies for the purposes of interpreting the provision.
Application
2. (1) This Regulation applies in respect of activities engaged in by persons on or after January 1, 2017.
(2) The requirements in this Regulation relating to a greenhouse gas apply only in respect of a greenhouse gas listed in Column 1 of Schedule 1.
(3) This Regulation does not apply to the IESO.
Greenhouse gas
3. For the purposes of clause (g) of the definition of “greenhouse gas” in subsection 1 (1) of the Act, nitrogen trifluoride is prescribed as a greenhouse gas.
Calculation of amount of greenhouse gas
4. (1) The amount of greenhouse gas in tonnes of CO2e shall be calculated for the purposes of this Regulation by applying the following formula:
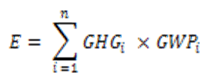
where,
E = the amount of greenhouse gas, expressed in tonnes of CO2e,
GHGi = the total amount of greenhouse gas i, expressed in tonnes,
GWPi = the applicable global warming potential for greenhouse gas i, as determined in accordance with subsection (2),
n = the number of greenhouse gases, and
i = the greenhouse gas.
O. Reg. 77/19, s. 2.
(2) For the purposes of applying the formula set out in subsection (1), the applicable global warming potential for a greenhouse gas is,
(a) in the case of a calculation in respect of 2018, the number set out in Column 5 of Schedule 1 opposite the greenhouse gas; and
(b) in the case of a calculation in respect of 2019 or a subsequent year, the number set out in Column 6 of Schedule 1 opposite the greenhouse gas. O. Reg. 77/19, s. 2.
Duty to quantify, calculate
5. (1) This section applies to a person who is the owner or operator of a facility at which a specified GHG activity is engaged in during a year.
(2) The person is required to quantify the amount of greenhouse gas emitted during all specified GHG activities at the facility during a year.
(3), (4) Revoked: O. Reg. 77/19, s. 3 (1).
(5) The person shall, subject to subsection (6), use the standard quantification methods set out in the Guideline to quantify the amount in respect of each specified GHG activity. O. Reg. 390/18, s. 5 (5); O. Reg. 77/19, s. 3 (2).
(6) The person may use methods other than the standard quantification methods in quantifying a maximum of the lesser of 20,000 tonnes and 3 per cent of the final quantification required under subsection (2).
(7) The following rules apply where the standard quantification methods in respect of an activity include a choice of calculation methodologies:
1. The person shall select one of the calculation methodologies and use it for all subsequent quantifications in respect of the activity unless the Director consents in writing to the use of another methodology.
2. If the Director consents to the use of another methodology, the person shall use the methodology consented to for all subsequent quantifications in respect of the activity unless the Director consents in writing to the use of another methodology. O. Reg. 390/18, s. 5 (7); O. Reg. 77/19, s. 3 (3-5).
(8) All amounts of greenhouse gas quantified or calculated shall be expressed as tonnes of CO2e.
(9) If the reporting amount or the verification amount is a number that is not a whole number when expressed in tonnes, the number shall be rounded up to the nearest tonne.
(10) For the purposes of this section, if there is a change during a year in the owner or operator of a facility, the owner or operator at the end of the year is deemed to have been the owner or operator for the entire year.
(11) For greater certainty, quantifications and calculations carried out in accordance with Ontario Regulation 143/16 before the day Ontario Regulation 389/18 made under the Climate Change Mitigation and Low-carbon Economy Act, 2016 came into force are deemed to have been carried out in accordance with this section.
Duty to report
6. (1) This section applies to a person who is required under section 5 to quantify the amount of greenhouse gas emitted during all specified GHG activities at a facility during a year.
(2) The person is required to give a report to the Director with respect to the specified GHG activities engaged in at the facility for the year if the reporting amount in respect of the facility for the year, determined in accordance with the following formula, is 10,000 tonnes of CO2e or more:
R = (A – B – C)
where,
R = the reporting amount,
A = the amount of greenhouse gas emitted during all specified GHG activities engaged in at the facility, quantified in accordance with section 5,
B = the portion of A that is carbon dioxide emitted from the combustion of biomass, and
C = the amount of greenhouse gas emitted during the generation of indirect useful thermal energy at another facility in respect of which a calculation is required under the Guideline.
O. Reg. 390/18, s. 6 (2); O. Reg. 77/19, s. 4.
(3) A report with respect to activities engaged in during a year shall be given to the Director on or before June 1 in the following year.
(4) A person who was required under Ontario Regulation 143/16 to give a report with respect to specified GHG activities engaged in during 2017 to the Director shall, if the report was not given to the Director before the day this section comes into force, give the report to the Director as soon as possible.
(5) For greater certainty, a report with respect to 2017 that was given in accordance with Ontario Regulation 143/16 before the day Ontario Regulation 389/18 made under the Climate Change Mitigation and Low-carbon Economy Act, 2016 came into force is deemed to be a report given in accordance with this section.
(6) The report shall contain all applicable information set out in Schedule 5.
Continuing duty to report
7. (1) A person who is required to give the Director a report with respect to specified GHG activities engaged in at a facility for a year shall give the Director a report with respect to the specified GHG activities engaged in at the facility for each subsequent year.
(2) A person who was required under subsections 6 (2) to (4) of Ontario Regulation 143/16 to give the Director a report with respect to the activities for 2017 and for each subsequent year is required to give the Director those reports in accordance with those provisions as if they had not been revoked, subject to subsection (3).
(3) For the purpose of applying subsections 6 (2) to (4) of Ontario Regulation 143/16, those provisions are not subject to section 7, 8, 8.1 or 9 of that Regulation.
(4) Subject to subsections (5) and (5.1), the requirement in subsections (1) and (2) to give reports with respect to specified GHG activities engaged in at a facility for subsequent years ceases to apply in a year to a person if,
(a) the person has complied with this Regulation or Ontario Regulation 143/16 for the three consecutive years preceding the year; and
(b) the reporting amount in respect of the facility has been less than 10,000 tonnes of CO2e for each of those years. O. Reg. 390/18, s. 7 (4); O. Reg. 242/19, s. 3 (1).
(5) Subsection (4) ceases to apply to a person if, for any year following its application, the reporting amount in respect of the facility is 10,000 tonnes of CO2e or more.
(5.1) Subsection (4) does not apply in respect of a person who is the owner or operator of a covered facility. O. Reg. 242/19, s. 3 (2).
(6) The requirements in subsections (1) and (2) cease to apply to a person if the specified GHG activities permanently cease to be engaged in at the facility and the person,
(a) provides notice to the Director that the activities have ceased permanently;
(b) gives the Director a report in respect of the final year in which the activities were engaged in at the facility; and
(c) complies with the applicable requirement in subsection (7). O. Reg. 77/19, s. 5.
(7) For the purposes of clause (6) (c),
(a) if the permanent cessation of activities occurred in 2018 and the person was required to have a report for the facility verified in 2018, the person shall have the report mentioned in clause (6) (b) verified by an accredited verification body in accordance with this Regulation and shall submit to the Director a verification statement prepared in accordance with section 18 and a verification report prepared in accordance with section 21; or
(b) if the permanent cessation of activities occurred in 2019 or a subsequent year and the person was required to have a report for the facility verified in the year prior to the year in which the permanent cessation occurred, the person shall have the report mentioned in clause (6) (b) verified by an accredited verification body in accordance with this Regulation and shall submit to the Director a verification statement prepared in accordance with section 18 and a verification report prepared in accordance with section 21. O. Reg. 77/19, s. 5.
(8) A report for a subsequent year under this section shall be given on or before June 1 in the year following the year for which the report is prepared.
(9) The report shall contain all applicable information set out in Schedule 5 with respect to the subsequent year.
Electricity importation, duty to quantify
8. (1) A person who engages in electricity importation during 2019 or any subsequent year and who is a market participant within the meaning of subsection 2 (1) of the Electricity Act, 1998 shall quantify the total electricity, expressed in megawatt hours, imported by the person during the year. O. Reg. 242/19, s. 4.
(2) The person shall use the standard quantification method or methods set out in the Guideline to quantify the amount of electricity imported. O. Reg. 242/19, s. 4.
(3) The following rules apply where the standard quantification methods in respect of electricity importation include a choice of calculation methodologies:
1. The person shall select one of the calculation methodologies and use it for all subsequent quantifications, unless the Director consents in writing to the use of another methodology.
2. If the Director consents to the use of another methodology, the person shall use the methodology consented to for all subsequent quantifications, unless the Director consents in writing to the use of another methodology. O. Reg. 242/19, s. 4.
(4) If the amount of electricity imported is a number that is not a whole number when expressed in megawatt hours, the number shall be rounded up to the nearest megawatt hour. O. Reg. 242/19, s. 4.
Electricity importation, duty to report
9. (1) If the total electricity imported for a year is greater than zero megawatt hours, as quantified by a person under section 8, the person shall give the Director a report with respect to the electricity importation during the year, containing all applicable information set out in Schedule 5. O. Reg. 242/19, s. 4.
(2) A report with respect to electricity importation engaged in during a year shall be given to the Director on or before June 1 in the following year. O. Reg. 242/19, s. 4.
Electricity importation, continuing duty to report
10. (1) A person who is required to give the Director a report with respect to electricity importation for a year under section 9 shall give the Director a report with respect to the activity for each subsequent year. O. Reg. 242/19, s. 4.
(2) Subject to subsection (3), the requirement in subsection (1) to give reports for subsequent years ceases to apply in a year to a person in respect of electricity importation if the person has complied with the applicable requirements of this Regulation or Ontario Regulation 143/16, as the case may be, for the three consecutive years preceding the year and the total electricity imported by the person has been zero megawatt hours for each of those years. O. Reg. 242/19, s. 4.
(3) Subsection (2) ceases to apply to a person if, for any year following its application, the total electricity imported by the person has been more than zero megawatt hours. O. Reg. 242/19, s. 4.
(4) The requirement in subsection (1) to give reports for subsequent years ceases to apply to a person if the person,
(a) permanently ceases to engage in the activity and provides notice to the Director that the activity has ceased permanently; and
(b) gives the Director a report in respect of the final year in which the activity was engaged in. O. Reg. 242/19, s. 4.
(5) The report shall contain all applicable information set out in Schedule 5. O. Reg. 242/19, s. 4.
(6) A report with respect to electricity importation engaged in during a year shall be given to the Director on or before June 1 in the following year. O. Reg. 242/19, s. 4.
All activities, duties re 2018 reports, including verification
11. The following provisions, as they read immediately before the day section 4 of Ontario Regulation 242/19 made under the Act came into force, continue to apply in respect of reports respecting 2018, as if these provisions had not been revoked:
1. Sections 8, 9, 10 and 11.
2. Subsection 16 (4).
3. Paragraph 3 of subsection 17 (2).
4. Paragraph 2 of subsection 19 (2).
5. Subparagraph 10 ii of Schedule 5 to the Regulation. O. Reg. 242/19, s. 4.
Duty to verify, covered facilities
12. (1) The owner or operator of a covered facility shall determine the verification amount in respect of the facility for each year in which the facility is registered, in accordance with the following formula:
V = (A – B − C) − (D − E)
where,
V = the verification amount,
A = the amount of greenhouse gas emitted during all specified GHG activities engaged in at the facility, quantified in accordance with section 5,
B = the portion of A that is carbon dioxide emitted from the combustion of biomass,
C = the amount of greenhouse gas emitted during the generation of indirect useful thermal energy at another facility in respect of which a calculation is required under the Guideline,
D = the portion of A that is emitted,
(a) from coal storage,
(b) during the operation of equipment related to the transmission, storage and transportation of natural gas,
(c) as fugitive HFC emissions during the operation of cooling units at electricity generators, and
(d) as fugitive emissions during the operation of geothermal electricity generating facilities, and
E = the portion of D that is carbon dioxide emitted from the combustion of biomass.
O. Reg. 242/19, s. 4.
(2) The owner or operator shall,
(a) have the report verified by an accredited verification body in accordance with this Regulation; and
(b) submit a verification statement prepared in accordance with section 18 and a verification report prepared in accordance with section 21 to the Director on or before September 1 in the year in which the report to be verified is required to be submitted to the Director. O. Reg. 242/19, s. 4.
(3) This section ceases to apply in respect of the owner or operator of a facility if the facility ceases to be a covered facility. O. Reg. 242/19, s. 4.
13. Revoked: O. Reg. 77/19, s. 8.
Reporting, general
14. (1) This section applies in respect of reports given to the Director under this Regulation.
(2) A report with respect to specified GHG activities engaged in at a facility must be with respect to all specified GHG activities engaged in at the facility.
(3) If a person is required to give the Director a report with respect to specified GHG activities engaged in at more than one facility, a separate report must be given with respect to each facility.
(4) If a person is required to give the Director a report with respect to electricity importation, the report shall not be combined with a report with respect to a specified GHG activity engaged in at a facility. O. Reg. 77/19, s. 9.
(5) Revoked: O. Reg. 77/19, s. 9.
(6) A person who is required to give the Director a report shall comply with all applicable sampling, analysis, measurement and recordkeeping requirements set out in the Guideline.
(7) If the Guideline specifies that certain emissions are to be reported as emitted from a particular specified GHG activity, the emissions shall be reported as specified in the Guideline.
Revised reports
15. (1) A person who gives a report with respect to specified GHG activities to the Director shall revise the report and give the revised report to the Director if the person has become aware of an error, omission or misstatement in the report within seven years after the date the report was given to the Director and the person has made one of the following determinations:
1. The per cent discrepancy in the verification amount is 5 per cent or more, as determined in accordance with subsection (3).
2. It is probable that the per cent discrepancy in the verification amount is 5 per cent or more, based on the individual or aggregate effect of one or more errors, omissions or misstatements identified.
3. The per cent discrepancy in any production parameter reported in respect of an activity is 0.1 per cent or more, as determined in accordance with subsection (4).
4. If the report is in respect of a covered facility and is given to the Director on or after the day notice is published in the Canada Gazette of an order of the Governor General in Council under section 189 of the Greenhouse Gas Pollution Pricing Act (Canada) deleting Ontario from the list of provinces and areas set out in Part 2 of Schedule 1 to that Act, the per cent discrepancy in the total annual emissions limit reported in respect of the facility is 0.1 per cent or more, as determined in accordance with subsection (4.1) of this section. O. Reg. 390/18, s. 15 (1); O. Reg. 242/19, s. 5 (1-4).
(2) Revoked: O. Reg. 242/19, s. 5 (5).
(3) The per cent discrepancy in a verification amount shall be determined by applying the following formula:
PD = (SOU / TRE × 100)
where,
PD = per cent discrepancy,
SOU = the net result of summing overstatements and understatements resulting from errors, omissions and misstatements, expressed in tonnes of CO2e, and
TRE = the amount.
O. Reg. 390/18, s. 15 (3); O. Reg. 242/19, s. 5 (6).
(4) The per cent discrepancy for each production parameter reported in respect of an activity shall be determined by applying the following formula:
PD = (QPDv − QPDi) / QPDi × 100
where,
PD = per cent discrepancy for the production parameter,
QPDv = actual quantity of the production parameter, and
QPDi = quantity of the production parameter as set out in the report.
(4.1) For the purposes of paragraph 4 of subsection (1), the per cent discrepancy in the total annual emissions limit reported in respect of the facility that is the subject of the report shall be determined by applying the following formula:
PD = (QAELv − QAELi) / QAELi × 100
where,
PD = per cent discrepancy for the total annual emissions limit for the facility,
QAELv = actual total annual emissions limit for the facility, and
QAELi = total annual emissions limit for the facility as set out in the report.
O. Reg. 242/19, s. 5 (7).
(5) The person may revise a report and give the revised report to the Director within seven years after the date the report was given to the Director if,
(a) the per cent discrepancy in the verification amount is less than 5 per cent;
(b) the per cent discrepancy in the production parameter under subsection (4) is less than 0.1 per cent; or
(c) in the case of a report given to the Director on or after the day mentioned in paragraph 4 of subsection (1), the per cent discrepancy in the total annual emissions limit under subsection (4.1) is less than 0.1 per cent. O. Reg. 390/18, s. 15 (5); O. Reg. 242/19, s. 5 (8, 9).
(6) Subject to subsection (7), the revised report must be given to the Director as soon as possible.
(7) If the revised report is required to be verified under subsection (8), the person shall give the revised report to the Director within 90 days after the day the person became aware of the error, omission or misstatement.
(8) A person who gives the Director a revised report shall have the revised report verified by an accredited verification body in accordance with this Regulation and submit to the Director a new verification statement prepared in accordance with section 18 and a new verification report prepared in accordance with section 21 if either of the following circumstances applies:
1. The revised report would have been required to be verified if it had been the original report given to the Director.
2. The revised report would not have been required to be verified if it had been the original report given to the Director, but the original report was required to be verified.
(9) A verification statement and verification report required under subsection (8) shall be submitted to the Director within 120 days after the day the person became aware of the error, omission or misstatement that led the person to prepare the revised report.
(10) Revoked: O. Reg. 77/19, s. 10 (2).
Accredited verification bodies, general duties
16. (1) In verifying reports under this Regulation, an accredited verification body shall comply with,
(a) clause 6.3 of ISO 14065, as it relates to verification teams; and
(b) clauses 4.2 to 4.10 of ISO 14064-3, as they relate to verification, except for clauses 4.3.1 and 4.3.5.
(2) In verifying reports under this Regulation, an accredited verification body shall ensure that,
(a) any person selected to form part of a verification team meets the requirements for a verifier set out in clause 4.1 of ISO 14064-3;
(b) no person selected to form part of a verification team subcontracts the conduct of verifications to another person;
(c) each verification is reviewed by a peer reviewer in accordance with clause 8.5 of ISO 14065, as it relates to verification activities; and
(d) before a verification statement including a positive, qualified positive or adverse verification conclusion is prepared, the determination that forms the basis of the conclusion is reviewed by the peer reviewer. O. Reg. 390/18, s. 16 (2); O. Reg. 242/19, s. 6 (1).
(3) For the purposes of clause 4.6 of ISO 14064-3, if the report is with respect to a specified GHG activity engaged in at a facility, the accredited verification body shall visit the facility if,
(a) the report is the first report with respect to the facility;
(b) no accredited verification body has visited the facility for the purposes of conducting a verification of the two most recent reports with respect to the facility;
(c) the most recent verification of a report with respect to the facility resulted in an adverse verification statement or an adverse verification conclusion being submitted to the Director;
(d) the verification is the first by the accredited verification body in respect of a report prepared with respect to the facility; or
(e) the accredited verification body is of the opinion that a visit to the facility is necessary for the purposes of determining whether the report contains a material discrepancy. O. Reg. 390/18, s. 16 (3); O. Reg. 242/19, s. 6 (2).
(4) Revoked: O. Reg. 242/19, s. 6 (3).
(5) For the purposes of determining under clause (3) (b) whether a visit has occurred in respect of the two most recent reports, a visit in respect of a report under section 10 or 13 as those provisions read immediately before the day section 8 of Ontario Regulation 77/19 made under the Act came into force shall not be included in the determination. O. Reg. 390/18, s. 16 (5); O. Reg. 77/19, s. 11 (2); O. Reg. 242/19, s. 6 (4, 5).
(6) For the purposes of subsection (3), references to a report include a report under this Regulation, Ontario Regulation 143/16 or Ontario Regulation 452/09. O. Reg. 390/18, s. 16 (6); O. Reg. 242/19, s. 6 (6).
(7) For the purposes of verifying a report, an accredited verification body is not required to verify amounts identified as B and D in section 12 that are set out in the report. O. Reg. 390/18, s. 16 (7); O. Reg. 242/19, s. 6 (7).
Accredited verification bodies, duties re impartiality
17. (1) An accredited verification body shall comply with clause 5.4 of ISO 14065.
(2) An accredited verification body shall not conduct a verification of a report if any of the following circumstances apply:
1. The accredited verification body has a potential conflict of interest that is a threat to the body’s impartiality or there is another threat to the body’s impartiality and the threat cannot be effectively managed with a mitigation plan that the Director has consented to in writing.
2. The accredited verification body has provided greenhouse gas consultancy services to the owner or operator of the facility within the previous three years and the resulting threat to the body’s impartiality cannot be effectively managed with a mitigation plan that the Director has consented to in writing.
3. The accredited verification body has verified six consecutive reports prepared with respect to the facility, unless at least three years have passed since the last verification. O. Reg. 390/18, s. 17 (2); O. Reg. 77/19, s. 12 (1); O. Reg. 242/19, s. 7 (1).
(3) For the purposes of paragraph 2 of subsection (2), an accredited verification body provides greenhouse gas consultancy services if it provides any of the following services:
1. Greenhouse gas quantification.
2. Greenhouse gas data monitoring or recording.
3. Greenhouse gas information system or internal auditing services.
4. Training that supports greenhouse gas emissions reporting under this Regulation or any other greenhouse gas reporting program. O. Reg. 390/18, s. 17 (3); O. Reg. 242/19, s. 7 (2).
(4) If an accredited verification body ceases to verify reports under this Regulation with respect to a facility after having verified such reports for two or more consecutive years, the accredited verification body shall not verify a report under this Regulation with respect to the facility until at least three years have passed. O. Reg. 242/19, s. 7 (3).
(5) For the purposes of determining under paragraph 3 of subsection (2) and under subsection (4) a number of reports that have been verified or a number of years in which reports have been verified, the verification of a report under section 10 or 13 as those provisions read immediately before the day section 8 of Ontario Regulation 77/19 made under the Act came into force shall not be included in the determination. O. Reg. 390/18, s. 17 (5); O. Reg. 77/19, s. 12 (2); O. Reg. 242/19, s. 7 (4, 5).
(6) For the purposes of subsection (4), references to a report include a report prepared under Ontario Regulation 143/16 or Ontario Regulation 452/09.
(7) Before completing a verification of a report under this Regulation, an accredited verification body shall assess the potential for any compromised impartiality in conducting the verification and provide to the Director a written assessment report that,
(a) identifies any potential compromised impartiality; and
(b) if any potential compromised impartiality is identified under clause (a), proposes a mitigation plan in respect of it.
(8) After verification of a report has begun, the accredited verification body shall, if any potential compromise of its impartiality arises, immediately undertake the assessment mentioned in subsection (7) and submit a written assessment report in accordance with that subsection to the Director.
Verification statements
18. (1) When verifying a report under this Regulation, an accredited verification body shall determine, in accordance with sections 19 and 20, whether there is a reasonable level of assurance that the report contains no material discrepancy and whether the report was prepared in accordance with this Regulation and, in the case of a report given to the Director on or after the day mentioned in paragraph 4 of subsection 15 (1), whether the total annual emissions limit for the facility was determined in accordance with Ontario Regulation 241/19 (Greenhouse Gas Emissions Performance Standards) made under the Act. O. Reg. 390/18, s. 18 (1); O. Reg. 242/19, s. 8.
(2) The accredited verification body shall submit a verification statement in respect of a report to the person who gave the report to the Director and shall ensure that the verification statement meets the requirements set out in clause 4.9 of ISO 14064-3.
(3) Revoked: O. Reg. 77/19, s. 13.
Verification amount conclusion
19. (1) The accredited verification body shall include in the verification statement and report a verification amount conclusion described in Column 1 of the following Table if the determination set out opposite the conclusion in Column 2 of the Table has been made:
TABLE
Types of Verification Amount Conclusions
|
Item |
Column 1 |
Column 2 |
|
1. |
Positive. |
Both of the following circumstances apply: |
|
2. |
Qualified positive. |
Both of the following circumstances apply: |
|
3. |
Adverse. |
One or both of the following circumstances apply: 2. The report was not prepared substantially in accordance with this Regulation. |
O. Reg. 390/18, s. 19 (1); O. Reg. 77/19, s. 14 (1-3); O. Reg. 242/19, s. 9 (1-4).
(2) A material discrepancy in emissions exists if the per cent discrepancy in the verification amount, as determined under subsection (3), is 5 per cent or more. O. Reg. 242/19, s. 9 (5).
(3) The per cent discrepancy in a verification amount shall be determined by applying the following formula:
PD = (SOU / TRE × 100)
where,
PD = per cent discrepancy,
SOU = the net result of summing overstatements and understatements resulting from errors, omissions and misstatements, expressed in tonnes of CO2e, and
TRE = the amount.
O. Reg. 390/18, s. 19 (3); O. Reg. 242/19, s. 9 (6).
(4) A material discrepancy in emissions exists if the individual or aggregate effect of one or more errors, omissions or misstatements identified in the course of verification makes it probable that there is a discrepancy of 5 per cent or more in the verification amount. O. Reg. 390/18, s. 19 (4); O. Reg. 242/19, s. 9 (7).
Production parameter verification conclusions
20. (1) The accredited verification body shall include in the verification statement and report a production parameter verification conclusion as described in Column 1 of the following Table for each production parameter listed in the Guideline for the activities addressed by the report, if the determination set out opposite the type in Column 2 of the Table has been made in respect of the production parameter:
TABLE
TYPES OF Production parameter verification conclusions
|
Item |
Column 1 |
Column 2 |
|
1. |
Positive. |
Both of the following circumstances apply: |
|
2. |
Qualified positive. |
Both of the following circumstances apply: |
|
3. |
Adverse. |
One or both of the following circumstances apply: |
O. Reg. 390/18, s. 20 (1); O. Reg. 77/19, s. 15 (1-4); O. Reg. 242/19, s. 10.
(2) A material discrepancy in a production parameter exists if the per cent discrepancy for the production parameter reported in respect of an activity is 0.1 per cent or more, based on the following formula:
PD = (QPDv − QPDi) / QPDi × 100
where,
PD = per cent discrepancy for the production parameter,
QPDv = quantity of the production parameter determined and verified by the accredited verification body, and
QPDi = quantity of the production parameter as set out in the report.
(3) Revoked: O. Reg. 77/19, s. 15 (5).
Total annual emissions limit verification conclusion
20.1 (1) This section applies in respect of the verification of a report given to the Director on or after the day mentioned in paragraph 4 of subsection 15 (1). O. Reg. 242/19, s. 11.
(2) The accredited verification body shall include in the verification statement and report a total annual emissions limit verification conclusion for the facility that is the subject of the report as described in Column 1 of the following Table, if the determination set out opposite the type in Column 2 of the Table has been made in respect of the total annual emissions limit for the facility:
TABLE
TYPES OF total annual emissions limit verification conclusions
|
Item |
Column 1 |
Column 2 |
|
1. |
Positive. |
Both of the following circumstances apply: |
|
2. |
Qualified positive. |
Both of the following circumstances apply: |
|
3. |
Adverse. |
One or both of the following circumstances apply: |
O. Reg. 242/19, s. 11.
(3) A material discrepancy in the total annual emissions limit for the facility exists if the per cent discrepancy for the total annual emissions limit for the facility is 0.1 per cent or more, based on the following formula:
PD = (QAELv − QAELi) / QAELi × 100
where,
PD = per cent discrepancy for the total annual emissions limit for the facility,
QAELv = actual total annual emissions limit for the facility, and
QAELi = total annual emissions limit for the facility as set out in the report.
O. Reg. 242/19, s. 11.
Verification reports
21. (1) If an accredited verification body verifies a report, it shall prepare a verification report that sets out, at a minimum, the following:
1. The verification statement.
2. The verified verification amount, proposed verification amount conclusion, verified production parameter and proposed production parameter verification conclusion.
3. The verified total annual emissions limit and the proposed total annual emissions limit verification conclusion, if the report is given to the Director on or after the day mentioned in paragraph 4 of subsection 15 (1).
4. A description of the objectives and scope of the verification and the criteria applied in conducting the verification.
5. A description of the data and information supporting the verification report.
6. Details of the independent quantifications and checking of the data and information supporting the verification report.
7. A record of any error, omission, misstatement or non-compliance identified during the verification.
8. A record of any corrections made to the report as a result of the identification of anything mentioned in paragraph 7.
9. An assessment of the data management systems.
10. A summary of conclusions.
11. The peer reviewer’s approval of the verification report and the proposed verification statement.
12. Revoked: O. Reg. 242/19, s. 12.
13. Revoked: O. Reg. 77/19, s. 16 (2).
O. Reg. 390/18, s. 21 (1); O. Reg. 77/19, s. 16; O. Reg. 242/19, s. 12.
(2) An accredited verification body shall provide a copy of a verification report prepared under subsection (1) to the person whose report was verified on or before the date that the verification statement is submitted to the person.
Compromise to impartiality
22. (1) If the Director determines, after receiving a written assessment report under section 17, that there is a compromise to an accredited verification body’s impartiality, the Director shall do one of the following by providing written notice to the accredited verification body:
1. Consent to the proposed mitigation plan, if any.
2. Require the accredited verification body to cease conducting the verification and refuse to consent to any proposed mitigation plan.
(2) The accredited verification body shall comply with the requirement of a notice under paragraph 2 of subsection (1).
Requests for information
23. (1) The Director may ask a person to provide the following information:
1. Information, including calculations and quantifications carried out in accordance with the Guideline, demonstrating that the person was not required to give reports to the Director and prepared based on information that is in the custody or control of the person and to which the person has or may reasonably obtain access.
2. Copies of any submissions that the person was required to make under section 46 of the Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999 (Canada).
3. Copies of any submissions made under the Greenhouse Gas Emissions Information Production Order (SOR/2018-214), made under the Greenhouse Gas Pollution Pricing Act (Canada), pursuant to subsections 197 (2) and (3) of that Act.
4. Any historical information used by the person to fill in missing data, or required by the Director to assess the filling in of missing data for emissions and production parameters.
5. Any records used by the person to determine production parameters, the total annual emission limit and compliance obligations under Ontario Regulation 241/19 (Greenhouse Gas Emissions Performance Standards) made under the Act.
6. Any information other than information set out in paragraphs 4 and 5 that, in the opinion of the Director, is necessary for the purposes of the Director assessing the accuracy of the person’s report under this Regulation, including information in respect of production, energy use, material use or process parameters.
7. Copies of any records the person is required to retain under this Regulation. O. Reg. 390/18, s. 23 (1); O. Reg. 242/19, s. 13.
(2) A person who receives a request under this section shall provide the information to the Director by the date specified in the request.
Retention of records
24. (1) A person who is required to give a report to the Director under this Regulation shall, in addition to complying with clause 4.10 of ISO 14064-3, keep the records set out in Schedule 3 of this Regulation in a paper or electronic format for at least seven years after the year to which the information relates.
(2) An accredited verification body shall keep each of the following records in a paper or electronic format for a period of at least seven years after they have been created or submitted:
1. Documents and records generated during a verification.
2. Verification statements.
3. Verification reports.
4. All documents upon which the conclusions in a verification statement or a verification report were based.
Change in information
25. (1) If, during a year with respect to which a report is required to be given to the Director with respect to specified GHG activities engaged in at a facility, there is a change in the owner or operator of the relevant facility, the new owner or operator shall notify the Director in writing of the change within 30 days after the change. O. Reg. 390/18, s. 25; O. Reg. 77/19, s. 17.
(2) Subsection (1) does not apply if the new owner or operator has provided notice of the change to the Director under Ontario Regulation 241/19 (Greenhouse Gas Emissions Performance Standards) made under the Act. O. Reg. 242/19, s. 14.
Giving or submitting records, form and manner
26. (1) In this Regulation, if a record is required to be given or submitted, other than a record required to be given or submitted by the Director, the record shall be submitted in a form provided by or approved by the Director and in a manner approved by the Director.
(2) The Director may require that a record that is given to the Director under this Regulation be given in an electronic format specified by the Director.
27. Omitted (revokes other Regulations).
28. Omitted (provides for coming into force of provisions of this Regulation).
Schedule 1
GreenhousE Gases and GLOBAL WARMING POTENTIALS
|
Item |
Column 1 Common Name of Greenhouse Gas |
Column 2 Chemical Formula |
Column 3 Chemical Name |
Column 4 Chemical Abstract Service Registry No. |
Column 5 Global Warming Potential, 2018 |
Column 6 |
|
1. |
Carbon dioxide |
CO2 |
Carbon dioxide |
124-38-9 |
1 |
1 |
|
2. |
Methane |
CH4 |
Methane |
74-82-8 |
21 |
25 |
|
3. |
Nitrous oxide |
N2O |
Nitrous oxide |
10024-97-2 |
310 |
298 |
|
4. |
Sulfur hexafluoride |
SF6 |
Sulfur hexafluoride |
2551-62-4 |
23,900 |
22,800 |
|
5. |
Nitrogen trifluoride |
NF3 |
Nitrogen trifluoride |
7783-54-2 |
17,200 |
17,200 |
|
6. |
HFC-23 |
CHF3 |
Trifluoromethane |
75-46-7 |
11,700 |
14,800 |
|
7. |
HFC-32 |
CH2F2 |
Difluoromethane |
75-10-5 |
650 |
675 |
|
8. |
HFC-41 |
CH3F |
Fluoromethane |
593-53-3 |
150 |
92 |
|
9. |
HFC-43-10mee |
C5H2F10 |
1,1,1,2,3,4,4,5,5,5- Decafluoropentane |
138495-42-8 |
1,300 |
1,640 |
|
10. |
HFC-125 |
C2HF5 |
Pentafluoroethane |
354-33-6 |
2,800 |
3,500 |
|
11. |
HFC-134 |
C2H2F4 |
1,1,2,2-Tetrafluoroethane |
359-35-3 |
1,000 |
1,100 |
|
12. |
HFC-134a |
C2H2F4 |
1,1,1,2-Tetrafluoroethane |
811-97-2 |
1,300 |
1,430 |
|
13. |
HFC-143 |
C2H3F3 |
1,1,2-Trifluoroethane |
430-66-0 |
300 |
353 |
|
14. |
HFC-143a |
C2H3F3 |
1,1,1-Trifluoroethane |
420-46-2 |
3,800 |
4,470 |
|
15. |
HFC-152 |
C2H4F2 |
1,2-Difluoroethane |
624-72-6 |
43 |
53 |
|
16. |
HFC-152a |
C2H4F2 |
1,1-Difluoroethane |
75-37-6 |
140 |
124 |
|
17. |
HFC-161 |
C2H5F |
Fluoroethane |
353-36-6 |
12 |
12 |
|
18. |
HFC-227ea |
C3HF7 |
1,1,1,2,3,3,3- Heptafluoropropane |
431-89-0 |
2,900 |
3,220 |
|
19. |
HFC-236cb |
C3H2F6 |
1,1,1,2,2,3-Hexafluoropropane |
677-565 |
1,300 |
1,340 |
|
20. |
HFC-236ea |
C3H2F6 |
1,1,1,2,3,3-Hexafluoropropane |
431-63-0 |
1,200 |
1,370 |
|
21. |
HFC-236fa |
C3H2F6 |
1,1,1,3,3,3-Hexafluoropropane |
690-39-1 |
6,300 |
9,810 |
|
22. |
HFC-245ca |
C3H3F5 |
1,1,2,2,3-Pentafluoropropane |
679-86-7 |
560 |
693 |
|
23. |
HFC-245fa |
C3H3F5 |
1,1,1,3,3-Pentafluoropropane |
460-73-1 |
950 |
1,030 |
|
24. |
HFC-365mfc |
C4H5F5 |
1,1,1,3,3-Pentafluorobutane |
406-58-6 |
890 |
794 |
|
25. |
Perfluoromethane |
CF4 |
Tetrafluoromethane |
75-73-0 |
6,500 |
7,390 |
|
26. |
Perfluoroethane |
C2F6 |
Hexafluoroethane |
76-16-4 |
9,200 |
12,200 |
|
27. |
Perfluoropropane |
C3F8 |
Octafluoropropane |
76-19-7 |
7,000 |
8,830 |
|
28. |
Perfluorobutane |
C4F10 |
Decafluorobutane |
355-25-9 |
7,000 |
8,860 |
|
29. |
Perfluorocyclobutane |
c-C4F8 |
Octafluorocyclobutane |
115-25-3 |
8,700 |
10,300 |
|
30. |
Perfluoropentane |
C5F12 |
Dodecafluoropentane |
678-26-2 |
7,500 |
9,160 |
|
31. |
Perfluorohexane |
C6F14 |
Tetradecafluorohexane |
355-42-0 |
7,400 |
9,300 |
|
32. |
Perfluorodecalin |
C10F18 |
Octadecafluorodecalin |
306-94-5 |
N/A |
7,500 |
|
33. |
Perfluorocyclopropane |
c-C3F6 |
Hexafluorocyclopropane |
931-91-9 |
N/A |
17,340 |
O. Reg. 77/19, s. 18.
SCHEDULE 2
specified GHG activities (Subsection 1 (1))
|
Item |
Column 1 |
Column 2 |
|
1. |
Adipic acid production. |
The production of adipic acid using oxidation. |
|
2. |
Ammonia production. |
The production of ammonia through the reaction of nitrogen with hydrogen that has been produced by one of the following: |
|
3. |
Carbonate use. |
The use of one or more carbonates in a production process, excluding the following: |
|
4. |
Cement production. |
The production of Portland, masonry, pozzolanic or any other hydraulic cement. |
|
5. |
Coal storage. |
The storage of coal at a facility that combusts coal. |
|
6. |
Copper and nickel production. |
The production of one or both of copper and nickel through smelting, refining and solvent extraction-electrowinning, using one or more of the following processes: |
|
7. |
Electricity generation. |
The operation of any combustion device, including a cogeneration (combined heat and power) device, that combusts solid, liquid or gaseous fuel for the purpose of producing electricity, excluding the following: |
|
8. |
Ferroalloy production. |
The production of ferrochromium, ferromanganese, ferromolybdenum, ferronickel, ferrosilicon, ferrotitanium, ferrotungsten, ferrovanadium, silicomanganese or silicon metal using pyrometallurgical techniques. |
|
9. |
General stationary combustion. |
The combustion of solid, liquid, or gaseous fuel or combustible material using general stationary combustion equipment for one or more of the following purposes: |
|
10. |
Glass production. |
The production of flat glass, container glass, pressed and blown glass or wool fiberglass using one or more glass melting furnaces to melt a mixture of raw materials, excluding production in an experimental furnace or a research and development process unit. |
|
11. |
HCFC-22 production and HFC-23 destruction. |
The production of HCFC-22 from chloroform and hydrogen fluoride and any process in which HFC-23 is destroyed. |
|
12. |
Hydrogen production. |
The production of hydrogen gas using steam hydrocarbon reforming, partial oxidation of hydrocarbons or other transformation of hydrocarbon feedstock. |
|
13. |
Indirect useful thermal energy use. |
The use of thermal energy at one facility that was generated at another facility. |
|
14. |
Iron and steel production. |
The production of iron or steel, which may include the processing of taconite iron ore and the production of metallurgical coke. |
|
15. |
Lead production. |
One of the following: |
|
16. |
Lime production. |
The production of a lime product using calcination of limestone or other highly calcareous materials, including dolomite, aragonite, chalk, coral, marble or shell, but excluding production at a kraft pulp mill, soda pulp mill, sulfite pulp mill or a facility that only processes sludge containing calcium carbonate from water softening processes. |
|
17. |
Magnesium production. |
The production of magnesium metal or products containing magnesium through one of the following: |
|
17.1 |
Mobile equipment operation. |
The operation of machinery, including vehicles without public road licences, for the purpose of transporting or moving substances, materials, equipment or products that are used at a facility. |
|
18. |
Nitric acid production. |
The production of nitric acid that is 30 to 70 per cent in strength using the catalytic oxidation of ammonia. |
|
19. |
Operation of equipment for a transmission system or a distribution system (electricity). |
The operation of equipment for the purposes of a transmission system or a distribution system. |
|
20. |
Operation of equipment related to the transmission, storage and transportation of natural gas. |
The operation of equipment related to any of the following: |
|
21. |
Petrochemical production. |
The production of petrochemicals, including acrylonitrile, carbon black, propylene, ethylene, ethylene dichloride, ethylene oxide and methanol, from feedstocks derived from petroleum or from petroleum and liquefied natural gas, excluding the following: |
|
22. |
Petroleum refining. |
The production of any product through the distillation of crude oil or the redistillation, cracking, rearrangement or reforming of unfinished petroleum derivatives. |
|
23. |
Phosphoric acid production. |
The production of phosphoric acid from phosphate rock and acid. |
|
24. |
Primary aluminum production. |
The production of aluminum using the Hall-Héroult process, electrolysis in prebake and Søderberg cells or anode baking in prebake cells, excluding production using experimental cells or research and development process units. |
|
25. |
Pulp and paper production. |
The production of market pulp or pulp and paper at a facility that has chemical recovery, semi-chemical recovery and lime kilns. |
|
26. |
Refinery fuel gas use. |
The use of any combustion device that combusts refinery fuel gas separately or in combination with any type of gas or uses refinery fuel gas as a chemical feedstock. |
|
27. |
Soda ash production. |
The production of soda ash using a production line to carry out calcining of trona or sodium sesquicarbonate or to directly produce carbon dioxide through the use of a liquid alkaline feedstock process. |
|
28. |
Zinc production. |
The primary production of zinc using electro-thermic distillation, pyrometallurgical processing or electrolytic processing or the secondary production of zinc. |
O. Reg. 390/18, Sched. 2; O. Reg. 242/19, s. 15.
SCHEDULE 3
Records to be retained (Subsection 24 (1))
1. A report the person has given to the Director under this Regulation, Ontario Regulation 143/16 or Ontario Regulation 452/09.
2. A verification report prepared in respect of a report mentioned in paragraph 1.
3. A list of all units, processes, activities and operations that were taken into account in quantifying or estimating greenhouse gas emissions, production parameters, material usage or process data.
4. All records and documents used to quantify or estimate greenhouse gas emissions data, production parameters, fuel usage, material usage or process data from each activity.
5. If the person engages in electricity importation, NERC E-tags, power contracts, IESO settlement data and all other information needed to confirm the transactions.
6. Documentation of the process for collecting greenhouse gas data, production parameters, material usage or process data.
7. A record showing any greenhouse gas emissions, production parameters, material usage or process data quantifications and the quantification methods used.
8. A record showing all emission factors used for quantifications, including documentation for any site specific factors developed under the applicable standard quantification method.
9. All input data used for greenhouse gas estimates.
10. Documentation of biomass fractions for specific fuels.
11. All data submitted to the Director under this Regulation, Ontario Regulation 143/16 or Ontario Regulation 452/09.
12. All quantifications made to fill in missing data.
13. Names and documentation of key personnel involved in quantifying and reporting on greenhouse gas data, production parameters, material usage or process data.
14. A log relating to each year, documenting all procedural changes made in data collection and calculations and changes to instrumentation for estimations and quantifications of greenhouse gas, production parameters, material usage or process data.
15. If a measurement-based quantification method is used,
i. a list of all emission points monitored,
ii. collected monitoring data,
iii. quality assurance and quality control information,
iv. a detailed technical description of the continuous emissions monitoring system, including documentation of any findings and approvals by the Province,
v. raw and aggregated data from the continuous emissions monitoring system,
vi. a log book showing all system down-times, calibrations, servicing and maintenance of the continuous emissions monitoring system, and
vii. documentation of any changes in the continuous emissions monitoring system over time.
16. Any other information that is required for verification of a report mentioned in paragraph 1.
17. If the facility is a covered facility, all records and documents used to quantify or calculate the total annual emissions limit and the annual activity emissions limits that were used as inputs.
18. If the facility is a covered facility, a record showing the calculation of the total annual emissions limit and of the annual activity emissions limits that were used as inputs, and the methods used.
O. Reg. 390/18, Sched. 3; O. Reg. 242/19, s. 16.
SCHEDULE 4
BIOMASS CRITERIA (Subsection 1 (1))
1. It must be organic matter that is available on a renewable basis.
2. It must be organic matter that is derived from a plant, animal or micro-organism or must be a product made of such organic matter.
3. It must meet one of the following criteria:
i. It is grown or harvested for the purpose of being used to generate electricity, heat or other useful energy.
ii. It is waste from harvesting or processing agricultural products or waste from processing forestry products, including spent pulping liquor.
iii. It is agricultural waste within the meaning of Regulation 347 of the Revised Regulations of Ontario, 1990 (General — Waste Management) made under the Act.
iv. It is organic waste material from a greenhouse, nursery, garden centre or flower shop.
v. It is pulp and paper biosolids, within the meaning of Ontario Regulation 267/03 (General) made under the Nutrient Management Act, 2002.
vi. It is waste from food processing, distribution and preparation operations, such as food packing, food preserving, wine making, cheese making, restaurants and grocery stores, including organic waste from the treatment of wastewater from facilities where food or feed is processed or prepared.
vii. It is sewage biosolids within the meaning of Ontario Regulation 267/03 made under the Nutrient Management Act, 2002.
viii. It is hauled sewage.
ix. It is waste from the operation of a sewage works subject to the Ontario Water Resources Act.
x. It is woodwaste within the meaning of Regulation 347 of the Revised Regulations of Ontario, 1990 made under the Act.
xi. It is a forest resource made available under a forest management plan approved under the Crown Forest Sustainability Act, 1994 or a managed forest plan approved under the Managed Forest Tax Incentive Program.
xii. It is landfill gas.
xiii. It is biodiesel.
xiv. It is biofuel.
xv. It is biogas.
xvi. It is biologically derived organic matter found in municipal and industrial waste, both within the meaning of Regulation 347 of the Revised Regulations of Ontario, 1990 made under the Act.
xvii. It is fuel whose heat generating capacity is derived entirely from one or more items described in subparagraphs i to xvi.
1. The name and address of the person required to give the report to the Director and the address of any facility in respect of which the report is prepared.
2. The business number assigned to the person by the Canada Revenue Agency.
3. The GHG ID number assigned by the Ministry to the person or facility, as the case may be.
4. The period of time to which the report relates.
5. The date on which the report is given to the Director.
6. Production parameters, material usage and process data required to be included in the report under the Guideline.
6.1 If the report is given to the Director on or after the day mentioned in paragraph 4 of subsection 15 (1) and the facility is a covered facility, the total annual emissions limit for the facility.
7. The total carbon dioxide emissions from the combustion of biomass during the activities with respect to which the report is prepared.
8. Such other information as may be specified in the Guideline relating to quantifications and calculations performed under this Regulation.
8.1 If the report is given to the Director on or after the day mentioned in paragraph 4 of subsection 15 (1) and the facility is a covered facility, the calculation of the total annual emissions limit and of each annual activity emissions limit that was used as an input.
9. If the report is with respect to specified GHG activities engaged in at a facility, the following information:
i. The primary NAICS code and any secondary and tertiary NAICS codes associated with each specified GHG activity.
i.1 If the facility is a covered facility, a list of the industrial activities engaged in at the facility.
ii. The reporting amount.
iii. The verification amount.
iv. The amount of greenhouse gas emitted during each specified GHG activity during the year, expressed in tonnes of CO2e.
v. The amount of each greenhouse gas, expressed in tonnes, emitted during each specified GHG activity.
vi. The estimated amount of carbon dioxide that is captured at the facility from the specified GHG activities and an explanation of how the estimated total was determined, including an explanation of how the carbon dioxide may have been used, transferred from or stored at the facility.
10. If the report is with respect to electricity importation, the following information:
i. The primary NAICS code and any secondary and tertiary NAICS codes associated with the activity.
ii. The total amount of electricity imported.
11. Revoked: O. Reg. 77/19, s. 19 (2).
12. A statement signed and dated by an individual who is authorized by the person mentioned in paragraph 1 to sign on behalf of the person, certifying that,
i. the individual has examined the report to ensure that it is complete and accurate, and
ii. the report has been prepared in accordance with this Regulation and the statements and information contained in the report are true and accurate to the best of the individual’s knowledge.
O. Reg. 390/18, Sched. 5; O. Reg. 77/19, s. 19; O. Reg. 242/19, s. 17.
Schedule 6 Revoked: O. Reg. 77/19, s. 20.