Hazardous gases on agricultural operations
Learn about the dangerous gases found around farm operations and the safety precautions required to protect farm workers. This technical information is for Ontario farmers.
ISSN 1198-712X, Published November 2022
Introduction
This fact sheet focuses on dangerous gases found around farm operations and the safety precautions required to reduce exposure to them.
Hazardous gases on farms are found in silos, manure storages, anaerobic digesters, grain bins and improperly ventilated barns. Essentially, structures that provide a confined space in which gases can accumulate to dangerous levels or deprive the air of enough oxygen to sustain life. Plant material stored in a silo ferments, allowing the crop to be stored for a long time. However, the fermentation process uses up oxygen, produces carbon dioxide and, under certain conditions, nitrogen dioxide, as by-products. This results in an environment unsuitable for humans soon after the silo is filled, lasting for up to two weeks.
Manure that is stored for a long time undergoes anaerobic decomposition, which produces manure gases. Warm weather and poor ventilation can increase the concentration of these gases. Liquid manure tanks and anaerobic digesters can contain toxic levels of gases or can be devoid of oxygen. High hydrogen sulphide gas levels can also deteriorate exposed concrete above the liquid manure surface.
Hydrogen sulphide
Hydrogen sulphide (H2S) is the most dangerous of the manure gases. It is classified as a chemical asphyxiant because it immediately chemically interacts with the blood’s hemoglobin to prevent oxygen from being carried to the body’s vital organs and tissues. It is produced from the anaerobic decomposition of organic materials such as manure. Its characteristic rotten egg smell is easy to detect at low concentrations, but at higher concentrations, H2S paralyzes the sense of smell. In high concentrations, H2S causes instant paralysis and death.
Table 1 outlines the effect of H2S at various concentrations. H2S is heavier than air, therefore it tends to stay just above the surface of the manure. Ventilation systems and wind effects can cause the gas to move up into the barn space towards an exhaust fan or open window.
| H2S concentration | Effect on humans |
|---|---|
| 4 ppm | Easily detectable, moderate odour |
| 10 ppm | Eye irritation |
| 27 ppm | Unpleasant odour |
| 100 ppm | Coughing, eye irritation, loss of sense of smell after 2–15 min. exposure |
| 200–300 ppm | Eye inflammation and respiratory tract irritation after 1 hour |
| 500–700 ppm | Loss of consciousness and possible death in 30–60 min. |
| 800–1,000 ppm | Rapid unconsciousness, cessation of respiration and death |
| >1,000 ppm | Diaphragm paralysis on first breath, rapid asphyxiation |
Source: American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers, ASABE EP470.1 OCT2011 (R2016) Manure Storage Safety.
The release of H2S is relatively low when manure remains undisturbed and the outside temperature is low. However, H2S levels can reach dangerous levels in seconds when a tank is agitated, especially if splashing or surface agitation takes place (Figure 1). Extra precautions are required when dealing with an under-floor manure storage (see Management Options – Manure Storages). Several deaths have occurred when workers have entered manure storages or the room above one in an attempt to save someone who had been overcome by H2S.
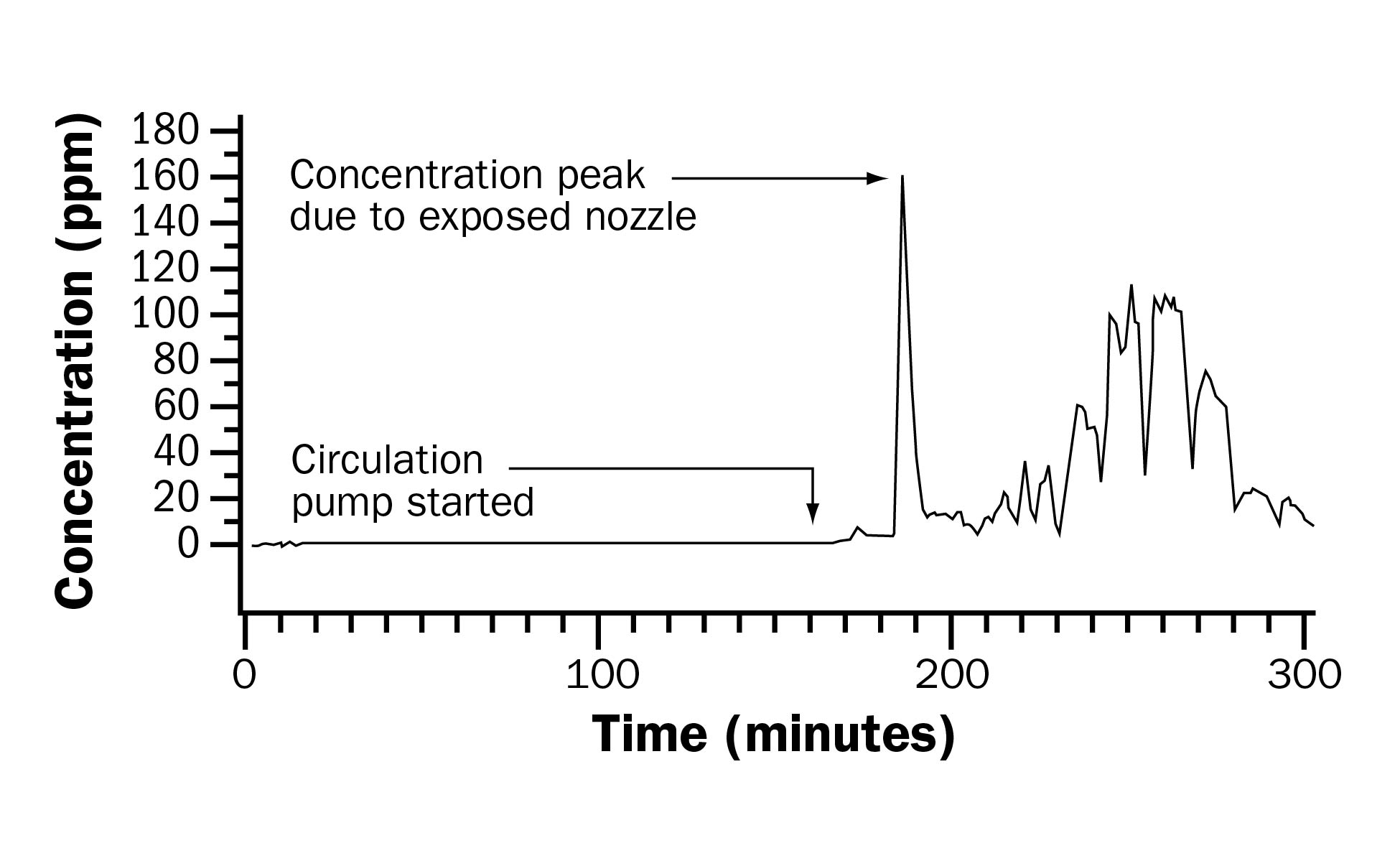
Source: Patni, N.K., and S.P. Clarke, ASAE, 2003.
H2S gas is a major concern for agricultural biogas systems. It can be present in many structures related to the production and consumption of biogas and can contain other hazardous gases. For management options of H2S in agricultural biogas systems, consult the OMAFRA fact sheet, Hydrogen sulphide in agricultural biogas systems.
Methane
Methane (CH4) is a colourless, odourless, non-toxic but combustible gas, generated by anaerobic digestion of organic material. If stored and managed properly, it can be used as a fuel source for internal combustion engines or cleaned and injected in the natural gas grid. It is lighter than air and therefore tends to rise from the manure storage. In well-ventilated livestock buildings, CH4 is unlikely to cause problems, however, in covered and in-barn storages, CH4 becomes trapped, and the concentration can reach dangerously explosive levels.
Agitating manure in a liquid storage results in a rapid increase in the release of manure gases and CH4. If allowed to accumulate in an enclosed space, CH4 gas causes explosions. Improperly designed plumbing pipes in staff rooms can also accumulate explosive levels of CH4. One solution is to equip floor drains with water traps to prevent migration of CH4 from the manure storage back into the staff room.
Clause 78, Part VIII, in O. Reg. 267/03, created under the Nutrient Management Act, 2002, requires that all new liquid manure storages provide some form of ventilation to prevent the accumulation and/or intensification of corrosive, noxious or explosive gases.
The American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers provides guidance for the management of hazardous gases with two published standards:
- Manure Storage Safety, ASABE EP470.1 OCT2011(R2016)
- Ventilating Manure Storages to Reduce Entry Risk, ANSI/ASABE S607 OCT2010 (R2019)
Both standards offer management options to minimize the risks — asphyxiation, poisoning and explosions — to humans and livestock exposed to manure gases when entering confined-space manure storages and to minimize the potential for drowning at manure storage sites.
A series of incidents in North America involving fires in hog barns caused by dangerous levels of CH4 have been a major concern lately. For more information on the causes and management practices of fires in hog barns, review the OMAFRA fact sheet, Methane gas in swine barns.
Ammonia
Ammonia (NH3), a colourless gas with a characteristically pungent odour, is produced by the decomposition of nitrogen compounds in animal manures. Classified as an irritant, this gas is lighter than air and can predispose livestock to various respiratory diseases if they are exposed to a significant level for an extended period of time.
NH3 irritates the eyes at levels in the range of 20–50 ppm, depending on the sensitivity of the person or animal. This gas is found mainly in swine, poultry and rabbit buildings, however, it can also be a problem in manure composting operations. As a guideline, if livestock or humans develop irritated eyes, improve the ventilation in the building.
Carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colourless, odourless and extremely dangerous gas. It Is classified as a chemical asphyxiant because it immediately chemically Interacts with the blood’s hemoglobin to prevent oxygen from being carried to the body’s vital organs and tissues. It Is the product of incomplete combustion by appliances or motor vehicles fueled by gaseous (propane, butane) or liquid (gasoline, diesel, fuel oil) or even solid fuels (wood or charcoal). This occurs when combustion appliances or engines are not functioning properly or are located in a low-oxygen environment. Generally, they do not pose a health hazard when maintained and used as per the operator specifications but may cause carbon monoxide poisoning when used in confined spaces or areas with low ventilation. Several types of appliances or motor vehicles can release CO and cause poisoning in a farm environment:
- heating appliances such as furnaces, fireplaces, stoves or portable heaters using gaseous, liquid or solid fuels
- combustion engines used in vehicles, such as tractors, trucks, snowmobiles, boats or all-terrain vehicles
- household appliances using natural gas or propane such as ranges, refrigerators or water heaters
- power tools such as lawnmowers and trimmers, chainsaws, pressure washers, welders, concrete saws or standby electrical generators
- outdoor appliances such as barbecues, oil lamps or heaters
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is colourless and odourless. It is the product of respiration of both plant material and animals and is found naturally in the atmosphere. Open-flame, non-vented space heaters also contribute carbon dioxide to the surrounding air space, as one of the products of combustion. CO2 is heavier than air and, like H2S, tends to accumulate just above the animal pen floor, surface of manure in a manure tank or silage surface in a silo. The main danger with CO2 is that it can create an oxygen deficiency, resulting in asphyxiation or suffocation. Properly ventilated livestock buildings do not generally contain dangerous levels of CO2; however, lethal concentrations can be found in sealed silos, liquid manure storages and grain storages.
As part of the ensiling process, living plant material quickly uses up available oxygen and dies. During this respiration process, oxygen is converted to water and CO2. CO2 displaces the oxygen in a sealed silo, making this environment unsuitable for humans without an external air supply.
Nitrogen dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) is a dangerous chemical asphyxiant produced as a result of chemical reactions that take place almost immediately after plant material is placed into a silo. Even short-term exposure can result in sudden death. NO2 has a characteristic bleach-like odour and may be visible as a reddish-brown haze. It is heavier than air, so it will tend to stay just above the silage surface. It may also flow down silo chutes and into feed rooms.
Weather conditions and cultural practices will affect the amount of nitrates in plant material, which in turn will set the stage for the production of NO2 in the silo. For example, a dry period during the growing season followed by abundant rainfall will encourage a corn crop to take up high levels of dissolved nitrates. If the corn is harvested before the nitrates can be converted to proteins, nitrous oxide (N2O) and nitric oxide (NO) are produced. Unstable NO combines with oxygen to form deadly NO2.
When inhaled, NO2 dissolves in the moisture on the internal lung surface to produce a strong acid called nitric acid. Nitric acid burns the lung tissues, which is followed by massive bleeding and death. Repeated exposure to lower concentrations of NO2 will cause chronic respiratory problems, including shortness of breath, coughing and fluid in the lungs.
Safe gas levels
The American Conference of Government Industrial Hygienists has established maximum safe gas concentrations, or threshold limit values, for an 8-hour work day and 40-hour work week for humans (Table 2). Although threshold limit values have not been established for animals, many researchers have suggested that animal responses are likely similar to humans.
| Gas | Threshold limit value |
|---|---|
| H2S | 10 ppm |
| NH3 | 25 ppm |
| CH4 | 1,000 ppm |
| CO | 25 ppm |
| CO2 | 5,000 ppm |
| NO2 | 3 ppm |
Source: ASABE EP470.1 Standard, OCT2011 (R2016).
Gas detection monitors
All of these hazardous gases can be measured with appropriate test equipment. Although much of the equipment is expensive and requires periodic re-calibration, there are some very reasonably priced gas detection tubes and handheld monitors commercially available from safety and scientific supply stores.
The most economical approach is to monitor gases with reactor tubes in which the gas changes the colour of a reactant and gives a good estimate of its concentration. These reactor tubes can be used with a calibrated pump to draw a measured sample of gas through the tube and obtain the result within a few minutes. However, to take an air sample, the person operating the pump must be present in the confined space, exposing himself to the potentially hazardous atmosphere.
These tubes are also available as passive dositubes that react slowly when exposed to the environment containing the gas of interest and yield an average gas concentration over time. Depending on the gas, the required exposure time would vary from several hours to as much as 2 days.
Commercial handheld monitors available from safety and scientific supply stores can also measure hazardous gases (Figure 2). Handheld detectors monitor environmental gases constantly, are compact in size and sound an alarm when a dangerous gas level is detected. They can be equipped with a sampling hose and pump used to monitor the atmosphere of a confined space outside harm’s way. When purchasing a gas monitor, note whether the unit can be calibrated at the farm or has to be serviced. Certain units will stop working if the calibration has expired.
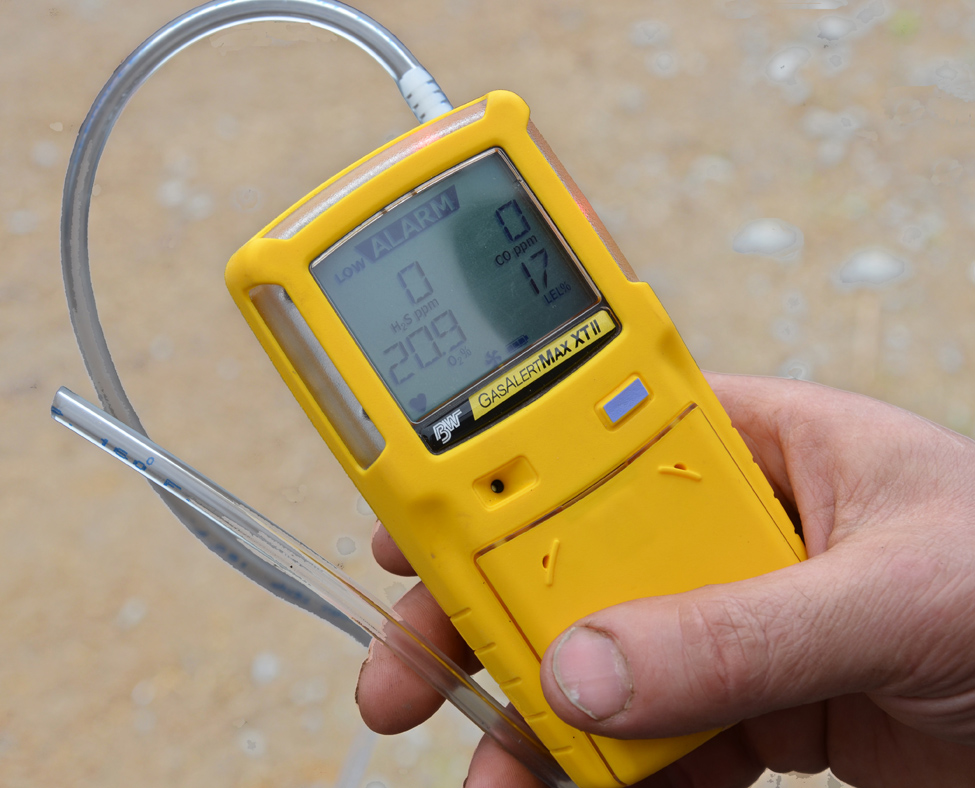

Operating the calibrating equipment requires minimal training. The monitors cost from $350–$600 for one gas; multi-gas monitors equipped with a pump may cost up to $1,500. An alternative to purchasing the equipment is to rent the unit (for a week or two) and the appropriate personal protective equipment from a specialized safety supply store. Specialized stores provide training services with rental equipment or are in contact with local training providers. The key is to plan ahead if the farming operation requires personal protective equipment.
Management options
Manure storages
- Ensure covered manure storages are ventilated to prevent the accumulation of all hazardous gases.
- Always maintain at least 0.3 m (1 ft) of freeboard between the manure surface and the bottom of the slats to prevent animals from routinely breathing H2S and CO2.
- Post a “Danger, Deadly Gases” warning sign in a visible location near each pump-out station.
- Do not agitate the liquid manure in storage unless absolutely necessary. If agitation is necessary, keep the agitator below the liquid surface and do not direct the stream of agitated manure towards a post or wall. Research has shown that gas levels will increase to lethal levels in seconds when splashing or surface agitation takes place (Figure 1). Remove all livestock, if possible, before agitating and emptying. Monitor gas levels in the barn.
- If the barn has under-floor (pit) ventilation and the porosity of the slatted floor is such that an air velocity through the slats of at least 0.10 m/s (20 ft/min.) can be obtained, use the pit ventilation system. Ensure that any openings such as pump-out ports are sealed off. For the pump-out port, this might require the use of a piece of plywood or flexible skirt to fit around the tractor-driven pump. This will maximize the amount of air being drawn from the room down through the slats. If gas detection equipment is available, monitor gas levels in the barn.
- If the barn does not have under-floor ventilation, or if conditions are such that an air velocity down through the slats of at least 0.10 m/s (20 ft/min.) cannot be obtained, provide maximum room ventilation. Be aware that there exists a greater risk when there is no under-floor ventilation. Do not enter the barn during or immediately following pumping or agitation. If gas detection equipment is available, monitor gas levels in the barn.
- It is highly recommended that a H2S gas monitor with an alarm is used to monitor gas levels in the barn, whenever this type of storage is agitated or emptied (Figure 2). In addition, consider taking H2S awareness training, available from consultants in Ontario.
- When flushing gutters, provide maximum ventilation. Do not enter the barn during or immediately following flushing. If gas detection equipment is available, monitor gas levels in the barn.
- Ideally, locate all pump-out openings outside the building to eliminate the danger of working in a confined area. Surround them with a safety railing.
- Do not attempt to rescue an animal if it collapses during pumping or agitation. Turn off the pump, provide maximum ventilation and wait a reasonable time before entering the barn. If gas detection equipment is available, ensure a safe concentration level prior to entering.
- Avoid any source of ignition, such as smoking, in the barn or near a manure storage facility. Avoid operating welding equipment in confined spaces without testing and monitoring the atmosphere and providing constant ventilation.
- Covered manure storages, even when empty, should only be entered by trained personnel equipped with suitable self-contained breathing apparatus. Never assume that gas levels are safe.
- If a rescue becomes necessary, call your local fire department. Do not attempt a rescue on your own.
- If you suspect that you have been exposed to high levels of manure gas, consult your physician or the anti-poison centre immediately.
- Inspect the safety fence periodically to ensure there are no openings and that warning signs are still in place.
- Ensure that modifications to the ventilation system or any reconfiguration of the livestock building do not affect the venting of hazardous gases in under-barn manure storages. Consult an agricultural engineer when making structural or ventilation modifications where an under-barn manure storage is present.
Liquid manure tankers
- Never assume a tanker is safe to enter, even when empty. H2S, which is heavier than air, will collect at the bottom of the tanker and remain there, even though there is an opening at the top. In August 2000, three men lost their lives during an attempted repair of a manure tanker and the subsequent rescue effort. Never enter a liquid manure tanker unless you are equipped with suitable self-contained breathing apparatus.
- When working around liquid manure storages and tankers, farm workers can protect themselves by wearing a pocket-sized H2S monitor that will sound an alarm when dangerous gas levels are reached.
- Newer liquid tankers are equipped with safety hatches to prevent unauthorized entry. However, a large number of older units in use across Ontario do not have a safety hatch. Retrofit these tankers with a safety hatch on the top opening to prevent unauthorized entry. These safety hatches can be purchased from a number of farm equipment dealers or can be custom made. Figure 3 shows an example safety hatch.
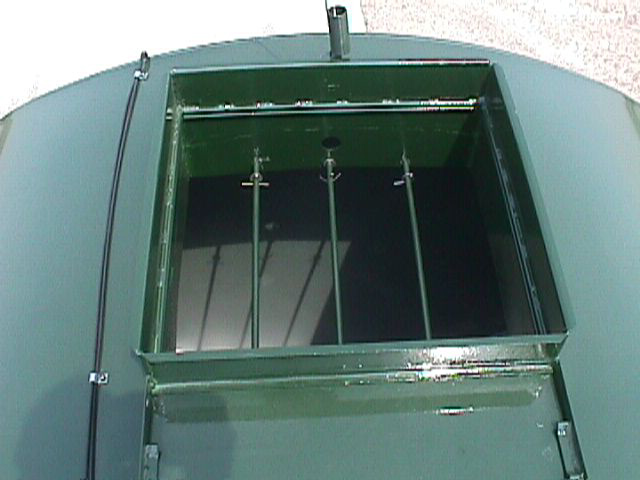

Silos
- Post a “Danger, Deadly Gases” warning sign in a visible location near the silo.
- Do not allow children or visitors near the silo for three weeks after filling.
- Provide sufficient feed room ventilation to exhaust any silo gas that might have spilled down from the silo.
- Check with your local fire department to see if pressure-demand remote breathing apparatus is part of their emergency equipment. Self-contained breathing apparatus (such as scuba) equipment is not suitable because of the air tank. It is sometimes too big for climbing the silo chute or the outside ladder-cage or too small to contain enough reserve air to rescue someone.
- During filling, adjust the distributor as needed to level the silage. Do not level the material by hand.
- If it is necessary to enter the silo when filling is complete, do so immediately following the last load, on the same day. Remember to leave the blower running while inside.
- Oxygen-limiting silos are a special case and should never be entered. If it becomes absolutely necessary to enter such a silo, it is essential that an external air supply is worn and back-up emergency safety measures are in place. Consult publication I33 Alert: Atmospheric Hazards Associated with Oxygen-Limited Structures (Silos) on Farms for suggested precautions.
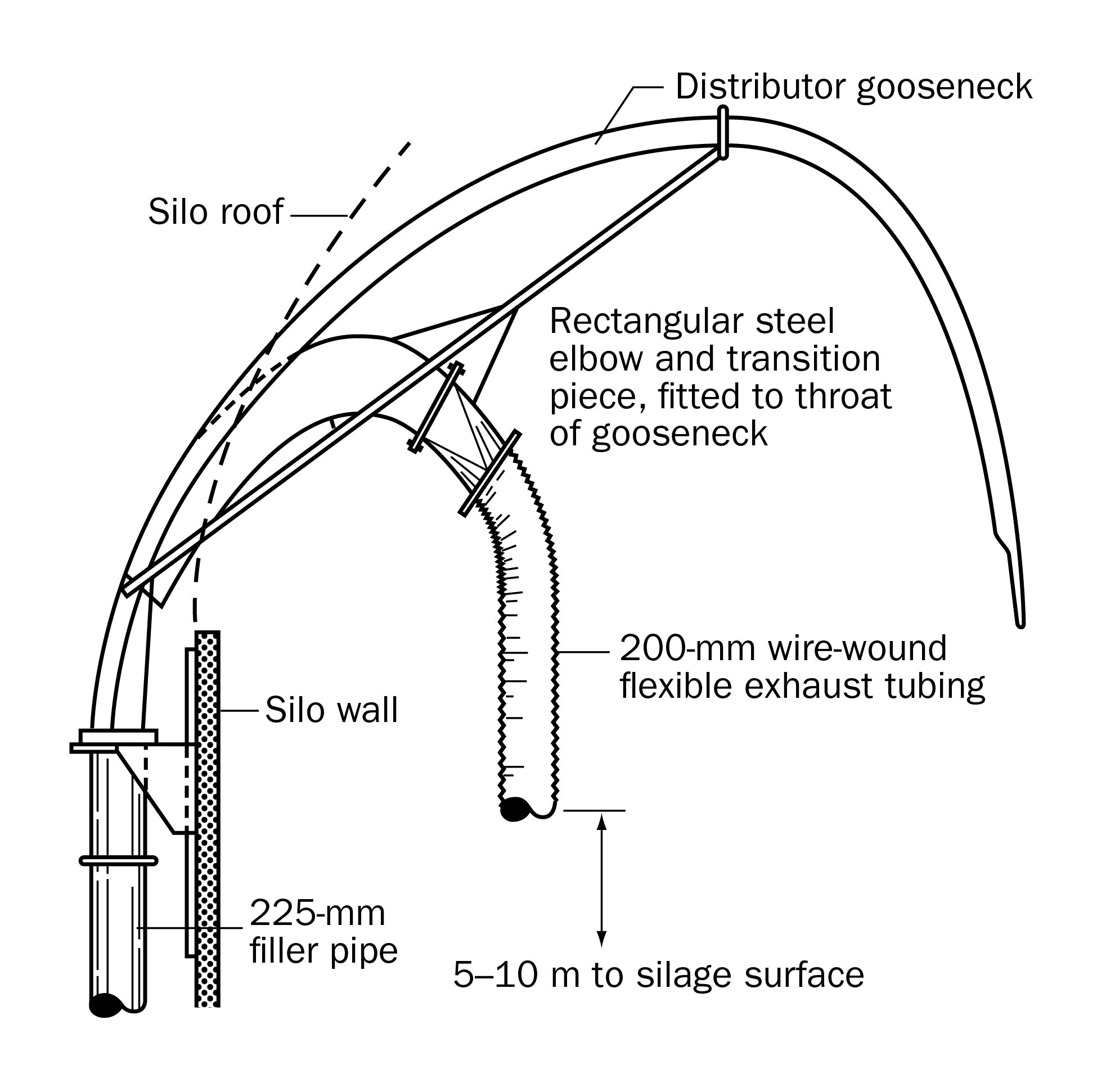
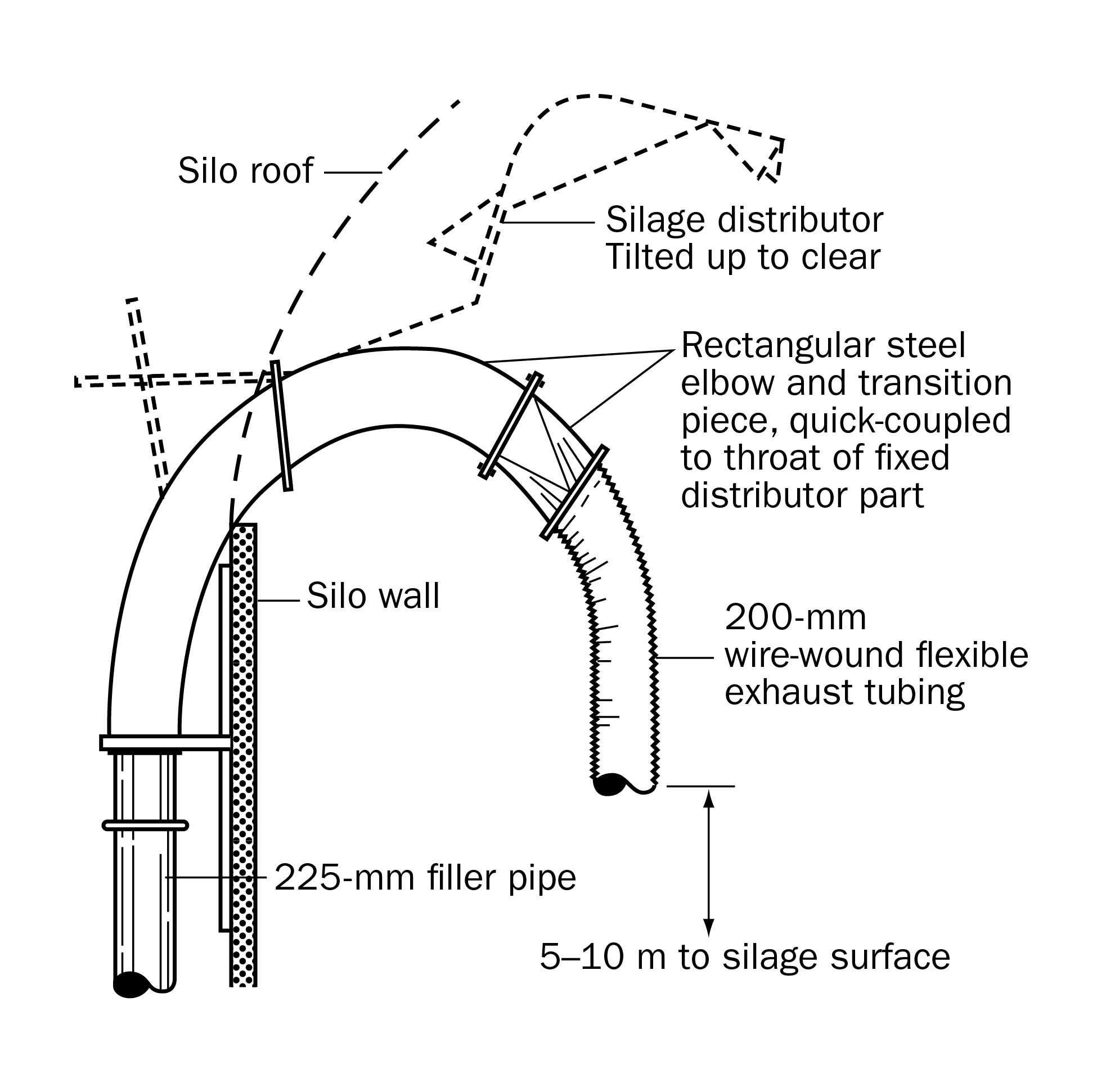
- A top unloader can ventilate a silo effectively. However, if it becomes necessary to service a defective unloader, assume that gases are present. To expel gases before entering, run the forage blower with the chute doors closed and the roof vent open. If the head space is greater than 5 m (15 ft), attach a tube adapter to the blower pipe (Figures 4 and 5). For a 7.2-m (24-ft) diameter silo with 5–10 m (15–30 ft) of head space, let the blower run for 30 min. For larger diameter silos or silos with a deeper head space, increase the ventilation time. Leave the forage blower running while in the silo.
- If someone collapses inside a silo, begin ventilating with the forage blower immediately, as explained above, and contact your local fire department. A fresh air supply is critical for both the victim and rescuers. Never attempt to rescue someone yourself. This has been attempted many times and, without the proper equipment and training, has resulted in many incidents of multiple fatalities.
Carbon monoxide
- For all fixed or mobile heating appliances and power tools, read the operation manual and follow routine inspection and maintenance as indicated. Hire contractors to fix the heating appliances on the farm and send the power tools to your local small engine repair shop for maintenance, inspection and repairs (tune-ups).
- Visually inspect and maintain all chimneys and vents of heating appliances for obstruction, debris, signs of rodents, snow or condensation build-up.
- When remotely starting engines, vehicles, or tractors, do so in properly ventilated open areas or use mechanical ventilation equipment as per the Ontario Building Code Section 6.2.2 Ventilation, O. Reg. 332/12. Leaving a crack at the bottom of a garage door by slightly lifting it is a prohibited practice.
- Supply sufficient fresh-air when temporarily using gasoline or diesel-powered tools such as concrete cutters, standby generators, welders or pressure washing equipment in a garage, basement, shed, barn or liquid manure pump-out pit.
- Retrofit your unvented propane infrared heaters used in livestock barns with sufficient combustion air supply openings as per the Gaseous Fuels Code Adoption Document under O. Reg. 212/01 (Gaseous Fuels). The use of supplementary fossil fuel heater, such as a propane heater, inside a livestock building is a prohibited practice.
Agricultural biogas systems
Consult the OMAFRA fact sheet, Hydrogen sulphide in agricultural biogas systems, for detailed management options for the various structures that store organic materials or produce and are in contact with biogas.
Farm labour concerns and hazardous gases
Since 2006, the Ontario Occupational Health and Safety Act, 1990 applies, with some limitations and conditions, to all farming operations that have paid workers, under O. Reg. 414/05, Farming Operations. It does not apply to a farming operation operated by a self-employed person who does not have paid workers.
Hazard alert, I33 Alert: Atmospheric Hazards Associated with Oxygen-Limited Structures (Silos) on Farms was published following a fatality in Eastern Ontario involving an unplanned entry in an oxygen-limited atmosphere. The worker was overcome immediately after entering a silo by the hazardous atmosphere. The hazard alert lists relevant legislative requirements for employers and employees and suggested precautions for entry in oxygen-limiting structures, such as training, supervision, work procedures, signage, atmospheric monitoring, PPE (personal protective equipment) and mechanical ventilation. In general, the employer shall take every precaution reasonable for the protection of a worker.
For a more complete overview of legislative requirements and suggested practices, consult the Guide to the Occupational Health and Safety Act for Farming Operations, published by the Ontario Ministry of Labour, (Ministry of Labour, Health and Safety Contact Centre:
Conclusion
Never assume that the environment inside a silo or manure storage is safe. Do not enter a liquid manure tank or recently filled silo, under any circumstances, without a pressure-demand remote breathing apparatus. These confined spaces often contain lethal concentrations of hazardous gases. Always have a lifeline attached, with a responsible, trained and competent safety person in view of your work. Follow the management suggestions outlined in this fact sheet and the legislative requirements of the Occupational Health and Safety Act, 1990. Post clearly visible warning signs to warn others to stay away.
This fact sheet provides basic awareness information on hazardous gases found on agricultural operations. This document does not intend to provide assurance of compliance with occupational health and safety regulations in Ontario. To receive local assistance for compliance with the Occupational Health and Safety Act, call Workplace Safety Prevention Services, toll-free at
References
Ontario Ministry of Labour. 2009. Occupational Health and Safety Guidelines for Farming Operations in Ontario, “Section 7: Hazardous Atmospheres and Confined Spaces.” ISBN: 1-4249-0804-3.
Ontario Ministry of Labour. 2011. Confined Spaces Guideline. ISBN: 978-1-4435-6842-5.
Patni, N.K., and S.P. Clarke. 2003. Gaseous Emissions in Swine Barns and During Slurry Mixing in Sub-Floor Pits. ASAE Meeting Paper Number 034081. American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers, St. Joseph, MI, U.S.
This fact sheet was revised by Terrence Sauvé, farmstead optimization and safety, engineering specialist, OMAFRA, Michel Gagné, chemist and industrial hygienist, Commission des normes, de l’équité, de la santé et de la sécurité du travail (retired).
Disclaimer
The information in this document is provided for informational purposes only and should not be relied upon to determine legal obligations. To determine your legal obligations, consult the relevant law. If legal advice is required, consult a lawyer. In the event of a conflict between the information in this fact sheet and any applicable law, the law prevails.