Common trees
The list below highlights the most common tree species in Ontario that are tracked in forest resources inventories. For each tree species there are area and volume statistics for the managed forest zone, a brief description of the species and an interactive distribution map.
Tree species in Ontario – Quick facts
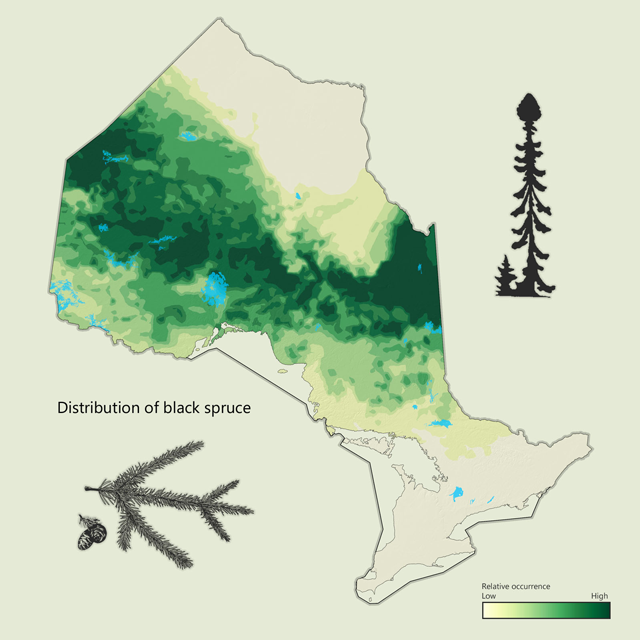
Black spruce is Ontario's most common tree
Poplar is Ontario's 2nd most common tree
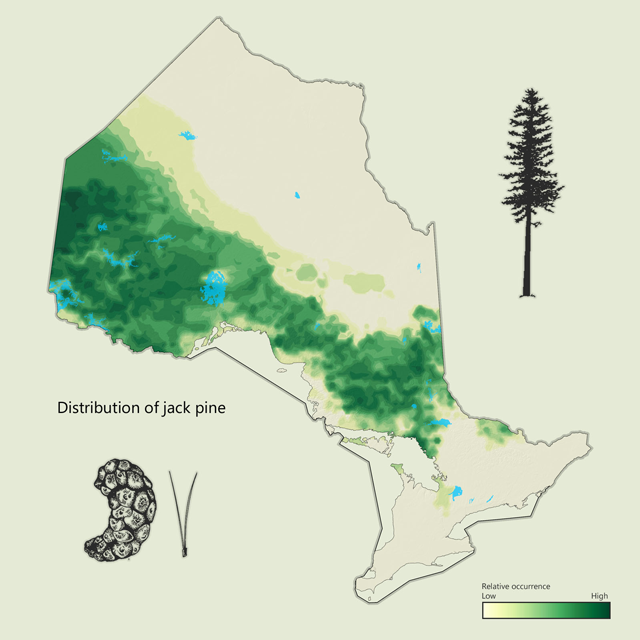
Jack pine is Ontario's 3rd most common tree
Sugar maple is Ontario's 5th most common tree
White pine is Ontario's official tree
Visual display
Tables and supporting data are available on the Ontario Data Catalogue. To support representation of complex data, a variety of tables, charts and maps are available in a visualization format.
Data visualization - Common tree species
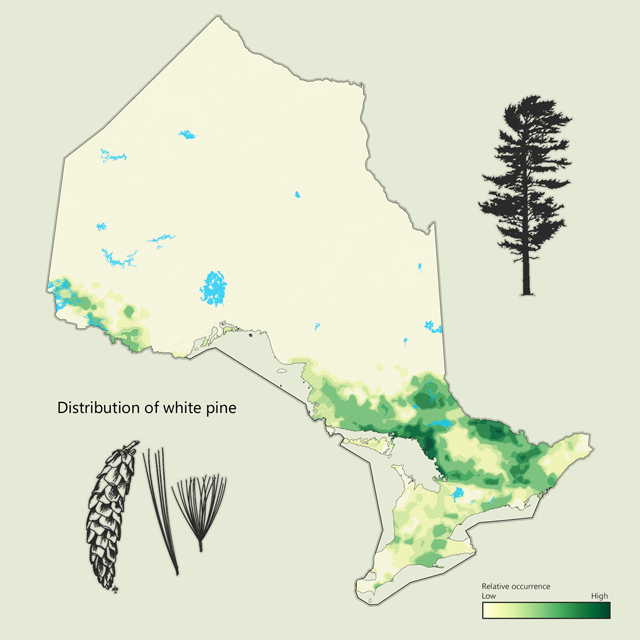
White pine - Pinus strobus
White pine is Ontario's provincial tree and is common throughout central and southern Ontario. It has long needles (six to twelve centimetres) that are soft to the touch and grow in bunches of five. White pine is traditionally used for trim, furniture and lumber, and has a light white, knotty wood.
| White pine metrics | Value |
|---|---|
| Total area containing species (ha) | 3,613,508 |
| Total area as lead species (ha) | 977,527 |
| Average proportion in Managed Forest Zone (MFZ) forest (%) | 2.3 |
| Gross total volume (cubic metres (m3)) | 210,618,739 |
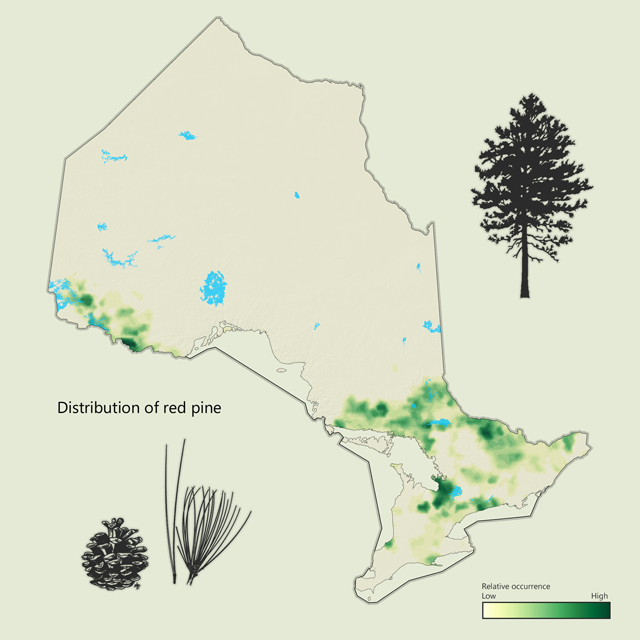
Red pine - Pinus resinosa
Red pine is a common tree throughout central and southern Ontario, as well as the northwest. It has long needles (10 to 16 centimetres) that are sharp, dark green and grow in pairs. Red pine has traditionally been used to make poles and lumber and has a strong pale red to reddish brown wood.
| Red pine metrics | Value |
|---|---|
| Total area containing species (ha) | 1,394,915 |
| Total area as lead species (ha) | 281,636 |
| Average proportion in MFZ forest (%) | 0.8 |
| Gross total volume (cubic metres) | 71,842,020 |
Jack pine - Pinus banksiana
Jack pine is a common tree found throughout Ontario but is more common on sandy or rocky sites in the north. It has short needles (two to four centimetres) that are sharp, slightly curved and grow in pairs. The cones are curved and will open after a forest fire. Jack pine is most commonly used for dimensional lumber but can be used to make pulp and paper.
| Jack pine metrics | Value |
|---|---|
| Total area containing species (ha) | 11,901,465 |
| Total area as lead species (ha) | 5,515,636 |
| Average proportion in MFZ forest (%) | 13.5 |
| Gross total volume (cubic metres) | 575,799,496 |
Black spruce - Picea mariana
Black spruce is the most common tree in Ontario and is primarily found in the Boreal forest. Although found on dry and sandy areas, it is often associated with wet or organic sites and can be a slow growing, long lived tree. Black spruce often occurs in large, relatively pure stands. Black spruce wood has long fibres, so it is used primarily for pulp and paper but is also used for dimensional lumber and other solid wood products.
| Black spruce metrics | Value |
|---|---|
| Total area containing species (ha) | 27,321,946 |
| Total area as lead species (ha) | 14,848,443 |
| Average proportion in MFZ forest (%) | 35.6 |
| Gross total volume (cubic metres) | 1,476,576,968 |
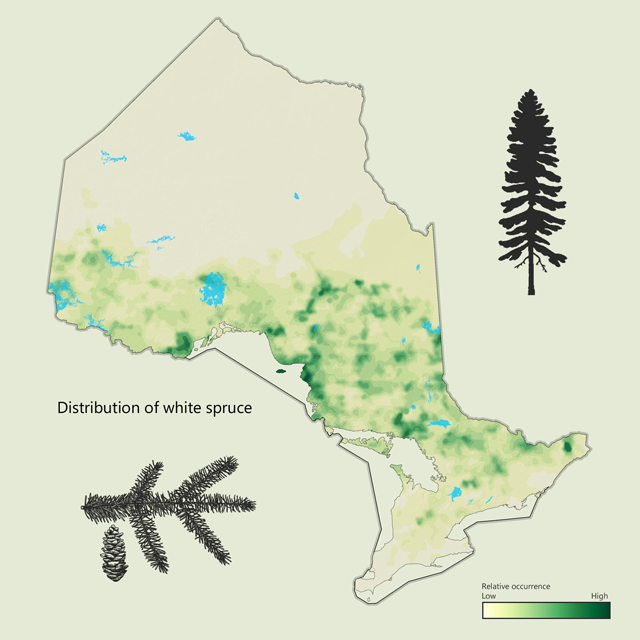
White spruce - Picea glauca
White spruce is found across Ontario but is most common in the Boreal forest, on dry to fresh upland sites. It has sharp short needles (two centimetres) that are bluish green to green in colour. The cones are small and light. White spruce is a favourite target for spruce budworm. White spruce is most commonly used as dimensional lumber but is also used in pulp and paper and is a popular Christmas tree.
| White spruce metrics | Value |
|---|---|
| Total area containing species (ha) | 6,467,851 |
| Total area as lead species (ha) | 443,860 |
| Average proportion in MFZ forest (%) | 2.7 |
| Gross total volume (cubic metres) | 133,252,447 |
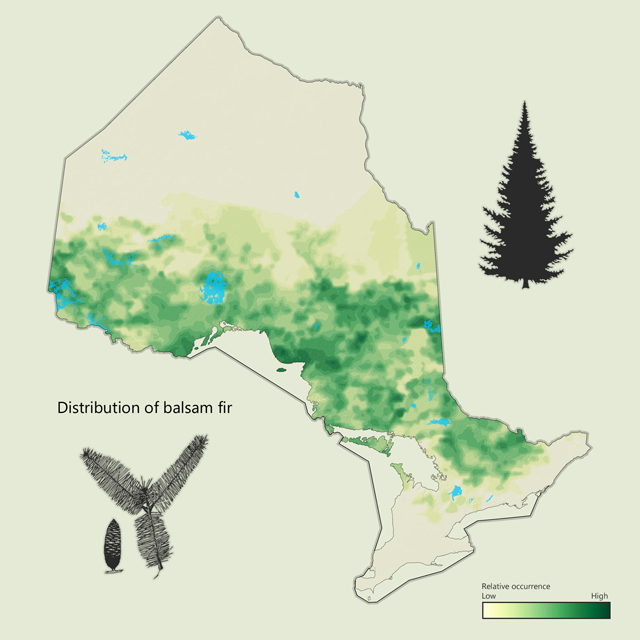
Balsam fir - Abies balsamea
Balsam fir is a common softwood species in Ontario. It has a tall narrow profile that tapers to a point at the top of the tree with sticky resin blisters on the trunk. It is often found growing under other species in clumps, as it is shade tolerant and is generally not as long lived as spruce. Balsam fir has traditionally been used for pulp, paper and lumber products.
| Balsam fir metrics | Value |
|---|---|
| Total area containing species (ha) | 11,309,035 |
| Total area as lead species (ha) | 1,071,974 |
| Average proportion in MFZ forest (%) | 5.3 |
| Gross total volume (cubic metres) | 240,639,259 |
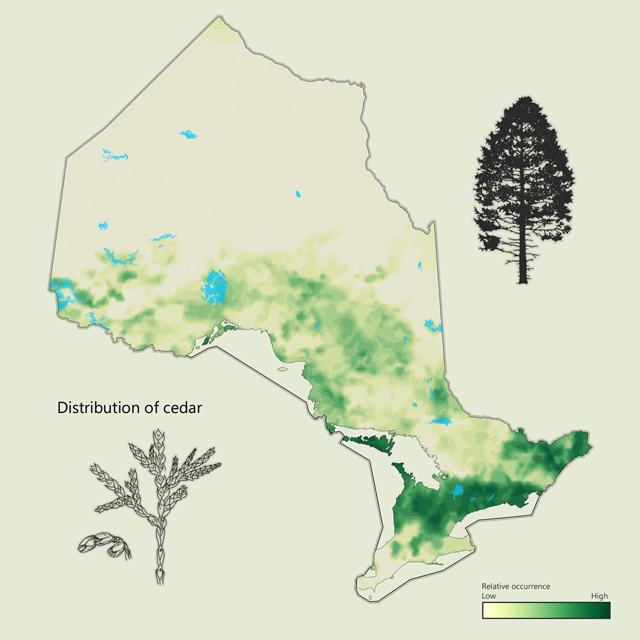
White cedar - Thuja occidentalis
Eastern white cedar is common throughout Ontario. It is a slow growing tree that prefers swampy areas but can be found on rocky upland sites. White-tailed deer eat the branches of cedar in the winter months. Cedar is often planted as an ornamental tree for hedges. Cedar wood is resistant to rot, and has many uses, including cedar shakes (shingles), fenceposts, lumber and boats.
| White cedar metrics | Value |
|---|---|
| Total area containing species (ha) | 4,049,482 |
| Total area as lead species (ha) | 744,385 |
| Average proportion in MFZ Forest (%) | 2.4 |
| Gross total volume (cubic metres) | 130,782,955 |
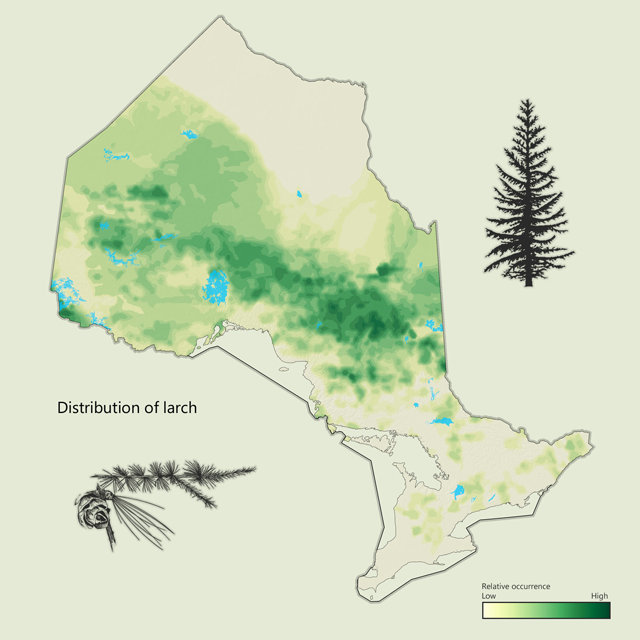
Larch (tamarack) - Larix laricina
Larch, or tamarack, is found throughout Ontario, but is more common in the north. This coniferous tree has needles that turn yellow in autumn and drop off. Although larch grows on many sites, it prefers swamps or wet organic soils, and is usually associated with black spruce. Larch wood is tough yet flexible, and has been used for lumber, pulp, poles and snowshoes.
| Larch metrics | Value |
|---|---|
| Total area containing species (ha) | 6,222,935 |
| Total area as lead species (ha) | 487,548 |
| Average proportion in MFZ forest (%) | 3.4 |
| Gross total volume (cubic metres) | 145,743,974 |
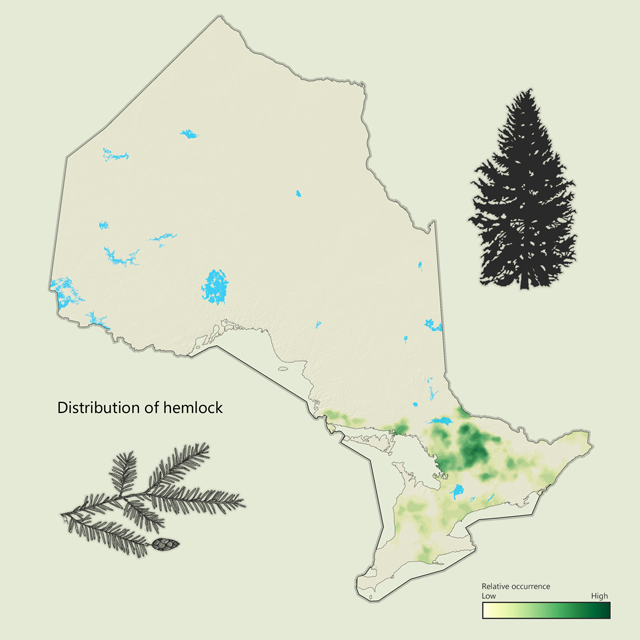
Hemlock - Tsuga canadensis
Hemlock is a long living tree found across the Great Lakes-St. Lawrence and Deciduous forest regions. It is commonly associated with yellow birch, and maple, and is very shade tolerant. It is usually found on cool moist soils near water, and is an excellent wildlife tree, providing cover from snow. White-tailed deer often yard in the winter under stands of hemlock. Hemlock has been used for lumber and railway ties and is often planted as an ornamental tree.
| Hemlock metrics | Value |
|---|---|
| Total area containing species (ha) | 979,942 |
| Total area as lead species (ha) | 157,070 |
| Average proportion in MFZ forest (%) | 0.5 |
| Gross total volume (cubic metres) | 35,523,069 |
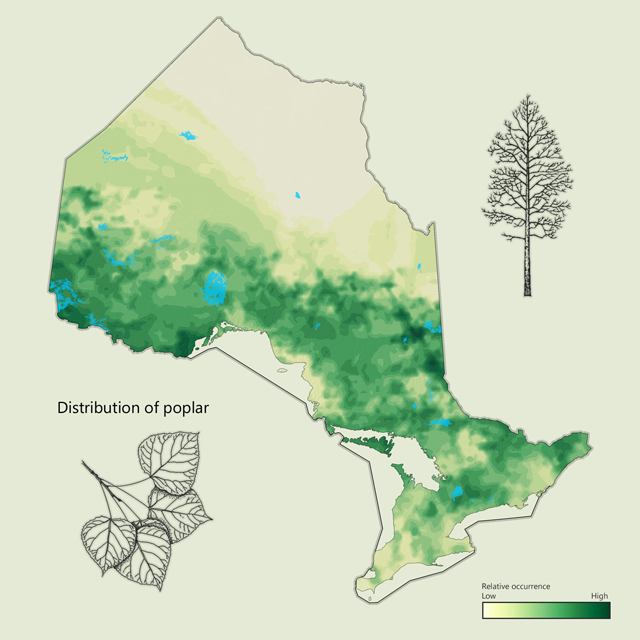
Poplar (aspen) - Populus spp.
Poplar or trembling aspen is a common tree throughout Ontario. An early successional species, it is often the first tree to grow on a newly disturbed site. Native poplar in Ontario also includes large-toothed aspen and balsam poplar. Poplar has a very light, soft wood, and is commonly used in composite board products, as well as pulp and paper.
| Poplar metrics | Value |
|---|---|
| Total area containing species (ha) | 16,592,859 |
| Total area as lead species (ha) | 5,798,466 |
| Average proportion in MFZ forest (%) | 13.9 |
| Gross total volume (cubic metres) | 965,657,778 |
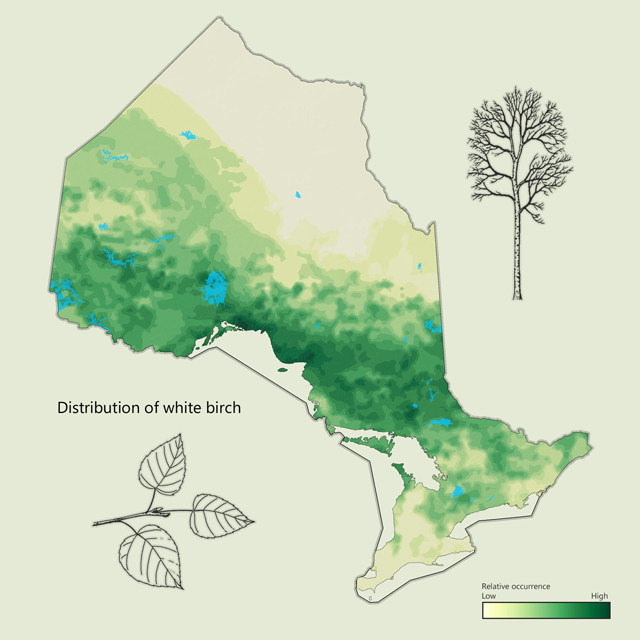
White birch - Betula papyrifera
White birch is a common tree found throughout Ontario. The smooth white paper-like bark is immediately recognizable, and the tree is sometimes referred to as "paper" birch. Often found in homogenous stands, white birch is an important source of food for many birds and animals which consume the leaves, buds and seeds. White birch is often used as firewood but is also used for veneer, pulp and paper and specialty products like hockey sticks.
| White birch metrics | Value |
|---|---|
| Total area containing species (ha) | 17,097,828 |
| Total area as lead species (ha) | 3,163,344 |
| Average proportion in MFZ forest (%) | 10.4 |
| Gross total volume (cubic metres) | 420,002,832 |
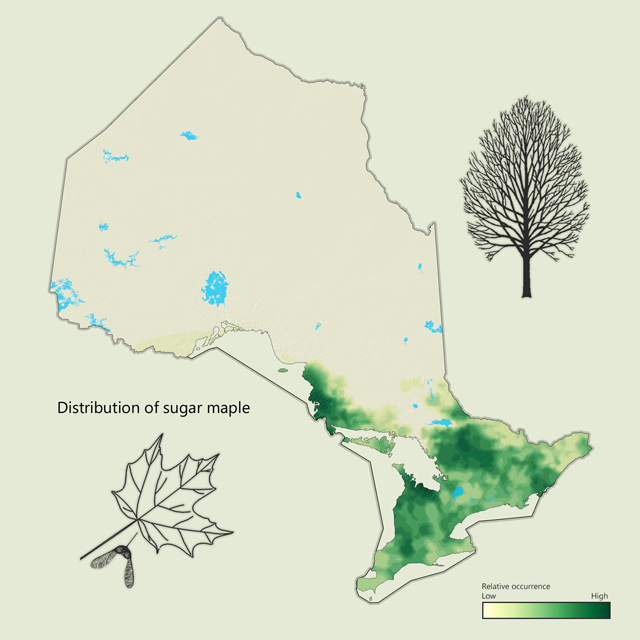
Sugar maple - Acer saccharum
Sugar maple is a common tree in the Great Lakes - St. Lawrence and Deciduous forest regions. The leaf of the sugar maple is found on the Canadian flag. It is also well known for supplying the sap used to produce maple syrup. With a hard-white wood, sugar maple is often used for furniture or flooring, but is also popular as firewood.
| Sugar maple metrics | Value |
|---|---|
| Total area containing species (ha) | 3,429,963 |
| Total area as lead species (ha) | 1,862,280 |
| Average proportion in MFZ forest (%) | 3.3 |
| Gross total volume (cubic metres) | 213,921,048 |
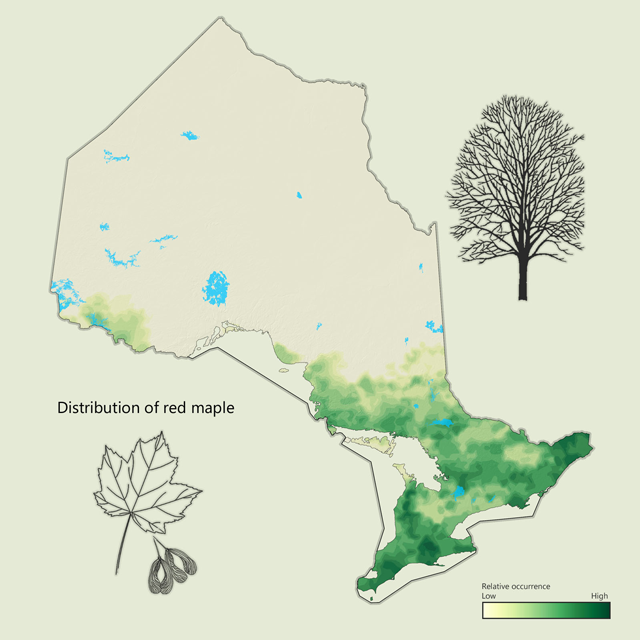
Red maple - Acer rubrum
Red or soft maple is less common than sugar maple and is found in the Great Lakes - St. Lawrence and Deciduous forest regions. It is often found on wetter sites than sugar maple and is known for its brilliant red leaves in autumn. Red maple is often planted as an ornamental tree and is an important source of food for wildlife. Summaries also include some silver maple under this species.
| Red maple metrics | Value |
|---|---|
| Total area containing species (ha) | 5,054,126 |
| Total area as lead species (ha) | 493,498 |
| Average proportion in MFZ forest (%) | 2.2 |
| Gross total volume (cubic metres) | 118,109,667 |
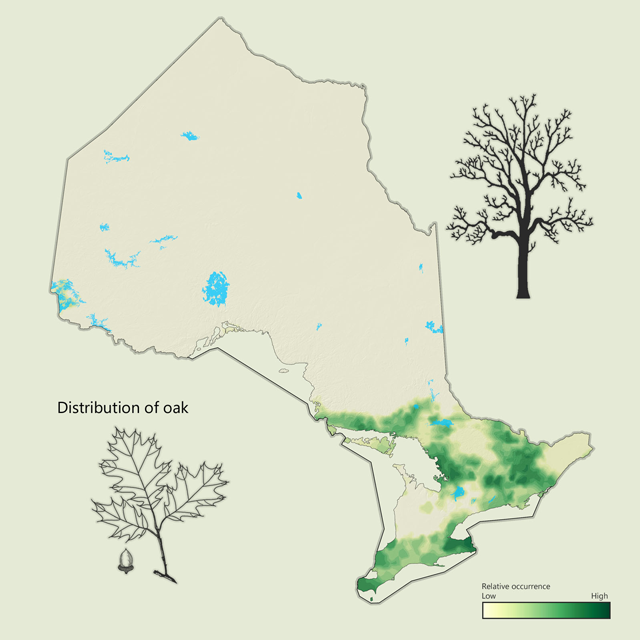
Oaks - Quercus spp.
Oak is a common hardwood species in central and southern Ontario. It is known for its large crown and distinctive leaves. Native oaks in Ontario include red, white and black oak, red being the most common. The acorns of oak trees are an important food source for animals such as deer, turkeys, squirrels and woodpeckers. Oak is a highly valued wood, often used for trim, flooring or furniture, and has a very hard reddish-brown wood.
| Oak metrics | Value |
|---|---|
| Total area containing species (ha) | 1,564,013 |
| Total area as lead species (ha) | 380,333 |
| Average proportion in MFZ forest (%) | 1.0 |
| Gross total volume (cubic metres) | 55,825,999 |
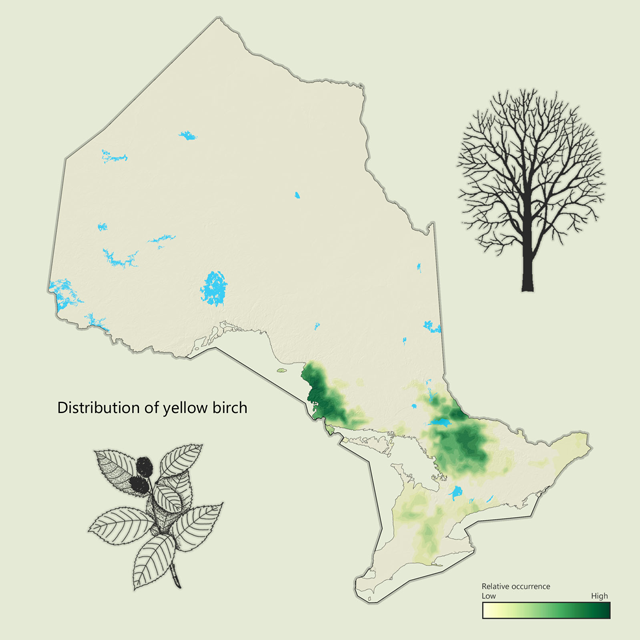
Yellow birch - Betula alleghaniensis
Yellow birch is a common hardwood across the Great Lakes - St. Lawrence forest, preferring cool moist upland sites. The silvery gray to yellowish bark gives the tree its name. Catkins and seeds are eaten by wildlife. Yellow birch is commonly used in furniture, cabinet making, plywood and doors.
| Yellow birch metrics | Value |
|---|---|
| Total area containing species (ha) | 2,198,339 |
| Total area as lead species (ha) | 216,472 |
| Average proportion in MFZ forest (%) | 1.0 |
| Gross total volume (cubic metres) | 67,337,387 |
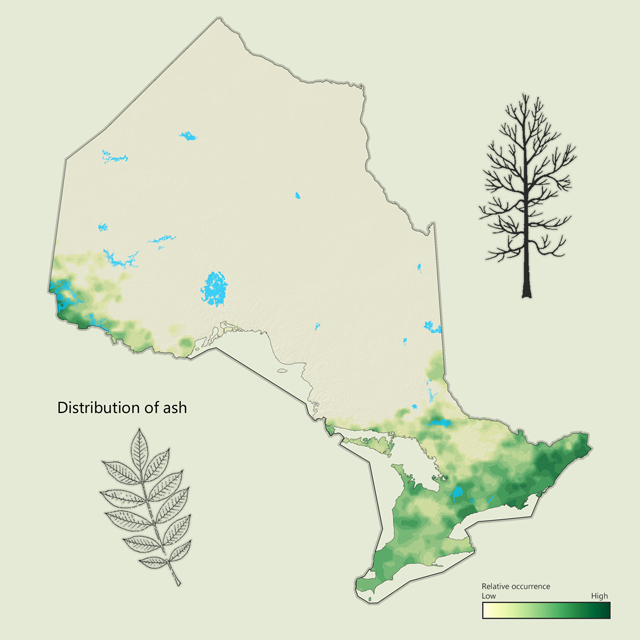
Ash - Fraxinus spp.
Both black and white ash are common trees across Ontario. Black ash is often associated with wet sites in central and northern Ontario. White ash is more common in the south on drier sites. Ash in Ontario has been impacted dramatically by emerald ash borer over the past few years, especially in the southwest. Ash has a very hard and strong wood and has been used for tool handles, baseball bats and furniture, but is used as pulp and is excellent firewood.
| Ash metrics | Value |
|---|---|
| Total area containing species (ha) | 1,211,055 |
| Total area as lead species (ha) | 141,155 |
| Average proportion in MFZ forest (%) | 0.6 |
| Gross total volume (cubic metres) | 29,059,902 |
Other species tracked in inventories
Species tracked within Ontario's forest resources inventory are heavily dependent on what can be interpreted or tracked by the digital imagery used to compile an inventory. Some species are very difficult to differentiate from other similar species in digital imagery, and some are found in such small quantities they rarely make up a significant stand component.
| Other species | Leading species | As stand component |
|---|---|---|
| Basswood | 3,671 | 445,659 |
| Beech | 3,778 | 624,612 |
| Butternut | 22 | 930 |
| Cherry | 847 | 106,926 |
| Elm | 741 | 63,427 |
| Hickory | 2,008 | 42,002 |
| Ironwood | 1,927 | 121,933 |
| Scots pine | 3,845 | 15,867 |
Historical leading species area
Traditionally referred to as “working group”, leading species has been a common form of tracking forest cover type since forest inventories were first developed. The areas represented in this summary reflect the designated management unit area circa 2016 and does not include the large parks reflected in the managed forest zone as those inventories were not available in past reports.
| Lead species | 1986 | 1996 | 2006 | 2016 | 2021 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White pine | 772,910.5 | 639,540.3 | 880,882.1 | 860,958.7 | 977,527.1 |
| Red pine | 193,037.1 | 177,438.1 | 183,307.5 | 191,049.0 | 281,636.0 |
| Jack pine | 5,027,534.1 | 4,837,252.2 | 5,210,856.6 | 5,609,906.4 | 5,515,668.9 |
| Spruce | 13,972,738.1 | 15,310,874.2 | 14,816,525.9 | 14,622,040.5 | 15,291,740.3 |
| Balsam fir | 1,835,067.1 | 2,053,373.7 | 1,032,381.1 | 1,021,332.5 | 1,071,973.9 |
| Hemlock | 151,815.3 | 121,437.8 | 167,710.6 | 173,907.9 | 157,069.9 |
| Other conifers | 1,338,530.8 | 991,136.8 | 1,110,508.6 | 1,127,778.2 | 1,236,562.3 |
| Poplar | 6,168,985.6 | 5,613,205.4 | 6,612,674.8 | 6,489,545.7 | 5,798,258.1 |
| White birch | 3,167,731.7 | 3,168,357.3 | 3,469,123.4 | 3,514,604.6 | 3,163,403.6 |
| Sugar maple | 2,760,327.1 | 2,678,869.4 | 2,088,905.9 | 1,986,550.3 | 1,862,231.5 |
| Yellow birch | 170,978.4 | 182,469.6 | 171,417.6 | 180,767.1 | 216,472.5 |
| Other hardwoods | 943,157.5 | 795,305.2 | 857,363.5 | 823,216.5 | 1,028,327.8 |
| Total: | 36,502,813.3 | 36,569,259.9 | 36,601,657.8 | 36,601,657.4 | 36,600,871.8 |