Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve Management Statement
This document provides policy direction for the protection, development and management of the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve and its resources.
Statement of Conservation Interest
March, 2003
Approval statement
I am pleased to approve this Statement of Conservation Interest for the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve.
The Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve, protecting mature white pine in association with poplar and birch growing on sand outwash plain and till ground moraine was regulated in December 2000. This 82-hectare conservation reserve is located in the Territorial District of Sudbury, in Northeastern Ontario and is composed entirely of Crown lands and waters.
Direction for establishing, planning and managing conservation reserves is defined under the Public Lands Act and current policy. The direction for this conservation reserve is in the form of a Statement of Conservation Interest, which defines the area that is being planned, the purpose for which the conservation reserve has been proposed, and it outlines the Ministry of Natural Resources' intent for the protected area. This Statement of Conservation Interest will provide guidance for the management of the conservation reserve and the basis for the ongoing monitoring of activities. More detailed direction is not anticipated at this time. Should significant developments be considered or complex issues arise that require additional studies, more defined management direction, special protection measures will be sought and a more detailed a Resource Management Plan will be prepared with full public consultation.
The public was informed and consulted prior to the regulation of the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Reserve under the Public Lands Act as well as during the preparation and review of this Statement of Conservation Interest.
The Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve will be managed under the jurisdiction of the Sudbury District Ministry of Natural Resources under the supervision of the Sudbury Area Supervisor as designated by the District Manager.
Submitted by:
Jennifer Moulton and Natalie Avoledo
Date: March, 2003
Recommended for approval by:
Cindy Blancher-Smith
District Manager
Date: March 28, 2003
Approved by:
Grant Ritchie for Rob Galloway
Regional Director
Date: August 28, 2003
1.0 Introduction
The Province of Ontario is home to a broad range of climate types, geography, and plant and animal species, all of which contribute to the variety and abundance of natural resources found here. The Ministry of Natural Resources is the lead conservation and resource management agency in the province and is therefore responsible for the management of these resources, in particular, forests, fisheries, wildlife, mineral aggregates and petroleum resources, Crown lands and waters, and provincial parks and protected areas (MNR 2000).
The Ministry of Natural Resources (MNR) is committed to the protection of natural and cultural heritage values and as such has developed strategies that will maintain the integrity and sustainability of the parks and protected areas system. Recently the Government of Ontario conducted a major land use planning exercise, which resulted in the release of the Ontario’s Living Legacy Land Use Strategy (MNR 1999). The Land Use Strategy (LUS) focuses on four specific objectives that were established to guide the planning process. These are: to complete Ontario’s system of parks and protected areas; to recognize the land use needs of the resource-based tourism industry; to provide forestry, mining, and other resource industries with greater land and resource use certainty; and to enhance hunting, angling and other Crown land recreation opportunities. A major part of the Ontario’s Living Legacy Land Use Strategy was the government’s initiative to establish 378 new protected areas. This commitment marks the largest expansion of provincial parks and conservation reserves in Ontario’s history.
The Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve (C195) was created as part of this expansion. As a result, the planning and management of this conservation reserve is consistent with the policies outlined in the Land Use Strategy. This conservation reserve is regulated under the Public Lands Act (PLA). Prior to its regulation, MNR met the Environmental Assessment Act requirements for the establishment and management of this conservation reserve.
Ontario’s network of natural heritage areas has been established to protect and conserve areas that represent the diversity of the natural regions of the province, including the species, habitats, special features and ecological systems which comprise that natural diversity. Protecting these natural heritage areas is key to the sustainable management of natural resources. It ensures that representative sites are retained in their natural state and can continue to contribute to Ontario’s natural environment (MNR 1997a).
In order to preserve these sensitive areas they require protection from incompatible uses to ensure their values will endure over time. Conservation reserves have been identified as a way of providing necessary protection from incompatible uses such as forestry and aggregate extraction, while still permitting many of the traditional uses that allow the people of Ontario to enjoy our special heritage. An approved Statement of Conservation Interest (SCI) or a Resource Management Plan (RMP) will guide the management and administration of each conservation reserve.
The management direction for this conservation reserve is a Statement of Conservation Interest. As a stewardship document, the SCI is the minimum level of management direction established for this conservation reserve. SCIs define the area that is being planned, the purpose for which the conservation reserve has been proposed, and it outlines the Ministry of Natural Resources' intent for the protected area. This SCI will govern the lands and waters within the regulated boundary of the conservation reserve. However, to ensure MNR protection objectives are being fully met within the conservation reserve, the surrounding landscape and related activities must consider the site’s objectives and heritage values. In addition, it is the intent of this SCI to create public awareness that will promote responsible stewardship of protected areas and surrounding lands. With management partners such as Ontario Parks, industry, local governments, etc. the MNR District Offices will be able to pursue and advance sound environmental, economic and social strategies and policies related to the protection of conservation reserves and provincial parks.
The purpose of this SCI is to identify and describe the values of the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve and outline the Ministry’s management intent. The management direction will protect the site’s natural heritage values for the benefit of all Ontario residents and demonstrate its compatibility within the larger sustainable landscape. This direction will comply with land use intent as stated by the Ontario’s Living Legacy Lands Use Strategy (MNR 1999).
The Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve, protects mature white pine in association with poplar and birch growing on the sand outwash and till ground moraine in Site District 4E-3. Regulated in December 2000, this 82- hectare conservation reserve is located in the Territorial District of Sudbury, in Northeastern Ontario and is composed entirely of Crown lands and waters. The guidelines for the management of this conservation reserve are found in this document.
2.0 Goals and objectives
2.1 Goal of the Statement of Conservation Interest
The goal of a conservation reserve, as stated in Policy PL 3.03.05, is to protect the natural heritage values on public lands while permitting compatible land use activities. The goal of this Statement of Conservation Interest is to provide the framework and direction to guide management decisions in order to ensure the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve will meet this goal through both short and long-term objectives.
2.2 Objectives
2.2.1 Short Term Objectives
Objective 1: To define the purpose for which the conservation reserve has been identified and to outline the Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources' management intent for the protected area.
Strategies:
- By identifying the state of the resource with respect to the natural heritage values being protected
- By identifying current land use activities that are occurring on the land base
Objective 2: To determine the best management strategy to protect the integrity of the values in the site.
Strategies:
- By determining the land use compatibility of current and potential land uses
- By developing specific guidelines and prescriptions to manage existing and potential land uses
Objective 3: To create public awareness of the values within this conservation reserve and promote responsible stewardship of the protected area.
Strategies:
- By creating fact sheets and pamphlets describing this conservation reserve and the resource(s) or values that it contains and protects
- By seeking partnerships with local stakeholders to ensure the values of the site are properly protected
This Statement of Conservation Interest meets the planning requirements for conservation reserves as determined in Procedure PL 3.03.05 which states that management plans must be written within three years of the regulation date (OMNR 1997b).
2.2.2 Long Term Objectives
Objective 1: To determine the long term management goals of the conservation reserve.
Strategies:
- By identifying the research needs, client services, and marketing strategies necessary to determine the position of this conservation reserve among the system of parks and protected areas in Ontario
Objective 2: To determine the representative targets of the site.
Strategies:
- By identifying the scientific values in relation to provincial benchmarks
- By identifying any monitoring or research necessary to identify and maintain the integrity of these characteristics beyond this plan
Objective 3: To provide direction for the evaluation of new uses or economic ventures proposed.
Strategies:
- A Test of Compatibility shall be undertaken to evaluate the impact of suggested use(s), either positive or negative, on the protected values and administrative needs of the conservation reserve
3.0 Management planning
3.1 Planning context
3.1.1 Planning area
The planning area for this site will consist of the regulated boundary for the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve as defined in section 4.1.3 Administrative Description. This land base will form the area directly influenced by the Statement of Conservation Interest. However, in order to ensure that the protection objectives are being fully met within the conservation reserve, the surrounding landscape and related activities must carefully consider the site’s values. Any strategies noted within this plan related to the site’s boundary or beyond will need to be presented for consideration within a larger planning context.
3.1.2 Management planning context
The need to complete the parks and protected areas system has long been recognized as an important component of ecological sustainability. This was reaffirmed in 1997 when the Lands for Life planning process was announced. Previous gap analysis studies were used to determine where candidate areas would be proposed in order to protect additional representative features. The Kawawia Lake Old Growth stand was chosen as one of the candidate life science features and subsequently appeared in the Ontario’s Living Legacy Land Use Strategy as C195. The site was then regulated as Schedule 52, in Ontario Regulation 686/00 made under the Public Lands Act, December 20, 2000 and filed December 21, 2000 amending Ontario Regulation 805/94 (Conservation Reserves).
By regulation, under the Public Lands Act, this conservation reserve cannot be used for commercial forest harvest or hydroelectric power development. Direction is provided in the Ontario’s Living Legacy Land Use Strategy (MNR 1999). Currently no mining tenure exists within the site and the site has been withdrawn under the Mining Act. Most recreational and non-commercial activities that have traditionally been enjoyed within the conservation reserve can continue provided that they pose little threat to the natural heritage values. Similarly, most non-industrial resource uses such as fur harvesting are permitted if they are compatible with the values of the reserve (MNR 1999). This SCI and future management will continue to try and resolve conflicts regarding incompatibility between uses and to ensure that identified values are adequately protected.
This Statement of Conservation Interest will only address known issues or current proposals with respect to permitted uses or potential economic opportunities brought forward to the District Manager during this planning stage. However, in terms of approving future permitted uses and/or development(s), there are established mechanisms in place to address such proposals. Any future proposals will be reviewed using the Procedural Guideline B – Land Uses – Test of Compatibility Procedure PL 3.03.05 (MNR 1997b) or other standard MNR environmental screening processes (see Appendix A).
3.2 Planning process
Management of a conservation reserve includes, as a minimum, the regulation, provision of public information, stewardship, and security. It also includes authorization and setting conditions on permitted uses and ongoing monitoring of compliance with the approved management document. Management of conservation reserves is the responsibility of the Ministry of Natural Resources at the district level, and will be done in accordance with Policy PL 3.03.05 (MNR 1997a) and an approved management document.
Once a conservation reserve has been established through the land use planning process it will be regulated under Section 4 of the Public Lands Act as an amendment to Ontario Regulation 805/94. Following the regulation it must be determined what level of management planning is required to fulfill the protection targets. There are two policy documents involved: a Statement of Conservation Interest as the minimal requirement for providing planning direction, and a Resource Management Plan (RMP) which would deal with more complex issues where several conflicting demands are placed on the resources. The guidelines for the preparation of these documents is outlined in Procedural Guideline A –Resource Management Planning (Conservation Reserves Procedure PL 3.03.05) (MNR 1997b). The appropriate document must be completed within three years of the regulation date.
In most cases management direction for conservation reserves will take the form of a SCI. A SCI is the minimum level of planning direction required for a conservation reserve. This form of management direction is generally used when the conservation reserve is seen to have few or no issues associated with it and any issues that do exist are local in nature and can be easily addressed through this process. If major issues arise and/or it is recognized that new decisions will need to be made beyond what is directed in the Land Use Strategy (MNR 1999) a RMP is warranted.
For current planning purposes, the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve will be managed under the auspices of a Statement of Conservation Interest. Interested parties from both the private and public sectors were consulted during the Ontario’s Living Legacy (OLL) planning process from candidate conservation reserve to regulation. Following the regulation of the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve in December 2000, a Terms of Reference was written to direct the completion of the management planning for this site and four other conservation reserves that were regulated at the same time. The First Nations and the public were notified that the management planning for the five conservation reserves was beginning. This notification occurred via mail-out to the First Nations and stakeholders and an advertisement appeared in two local newspapers during the week of October 8th, 2001. The Ministry of Natural Resources is exempt from providing notification of this planning process on the Electronic Bulletin Registry, under Section 30 of the Environmental Bill of Rights (EBR).
A draft version of this SCI was sent for review to members of the public and First Nations and MNR staff both at the district and regional office levels during July 2002. Comments provided to MNR were considered in this final document. Upon approval of this SCI, public notification will occur via mail-out to interested stakeholders and a notice will appear in the same two local newspapers.
Public consultation will be solicited during a review of any future land use proposals that would require new decisions to be made. In addition, any future proposal and/or any new, significant management direction considered will be published on the Environmental Bill of Rights Registry.
The implementation of the policy will be the mandate of the MNR at the district level; however, association with various partners may be sought to assist in the delivery. This SCI is a working document; therefore it may be necessary to make revisions to it from time to time (see section 6.4 Implementation and Plan Review).
4.0 Background information
4.1 Location and Site Description
4.1.1 Location
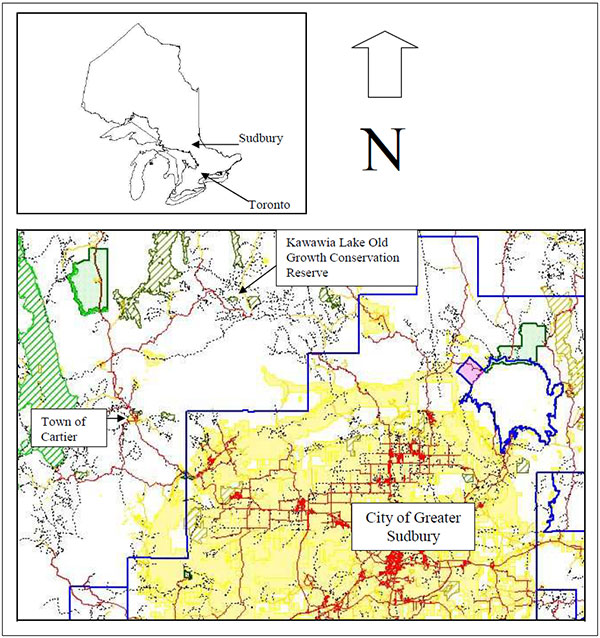
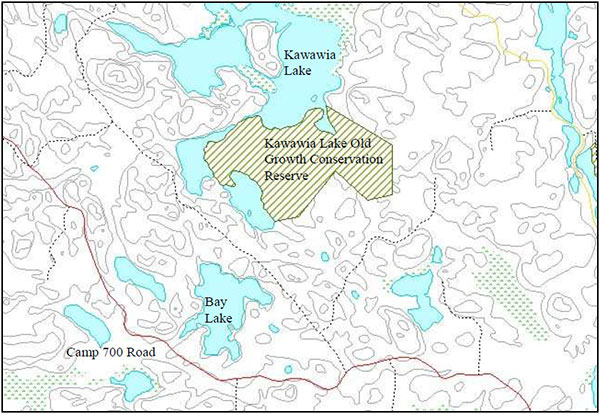
The Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve is approximately 90 kilometres northwest of the City of Greater Sudbury (Map 1) and is located within the Sudbury MNR District, in the Northeast Region MNR area. The site is located in the geographic Township of Leinster in the Territorial District of Sudbury, and is approximately 30 kilometres northeast of the Town of Cartier, accessible to 4x4s, ATVs or by walking from extensions off of the Camp700 Road. Kawawia Lake forms the northern and western boundaries of the conservation reserve (Map 2). Table 1 describes the location and provides administrative details of the site.
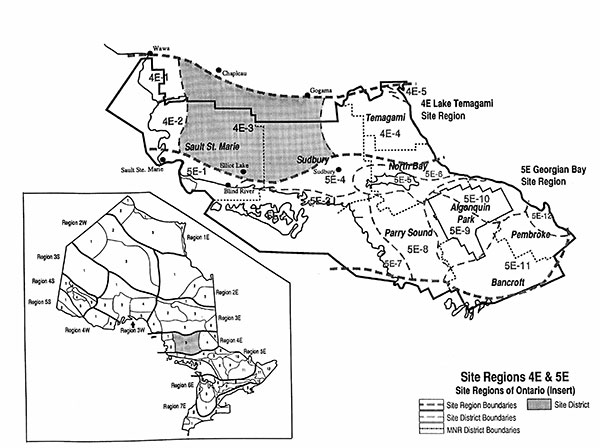
The Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve is located in Eco-District 4E-3, also known as the Mississagi Site District. This Eco-District is located in the center of Eco-Region 4E approximately between 81°30'W and 84°W Longitude, and 46°20'N and 47°50'N Latitude (Map 3) (Crins 1996).
4.1.2 Physical Site Description
The climate in Eco-District 4E-3 has been classified as a humid low boreal (LBh) eco-climatic region. Monthly precipitation ranges from 50-100 mm with maximums occurring in the summer period. The frost-free period extends from May to mid-September, while temperatures above 0°C last approximately seven months (Ecoregions Working Group 1989).
The vegetation of Eco-District 4E-3 is a transition between that associated with Boreal forest types and those characteristic of the Great Lakes—St. Lawrence forest region. The Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve is within the Temagami Forest Section of the Great Lakes-St. Lawrence Forest Region (Rowe 1972). The Temagami Forest Section is defined as a large upland area north of Lake Huron, stretching east and west from Lake Temagami, and occupying a generally southward-sloping surface. The typical association of this forest section consists of eastern white pine with scattered white birch and white spruce or a mixture of white birch, pine and spruce, with balsam fir, trembling and largetooth aspens (Rowe 1972).
Table 1 - Location reference table.
| Name | Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve |
|---|---|
| Eco-Region Eco-District (Hills 1959) | 4E Mississagi 4E-3 |
| Eco-Region Eco-District (Crins & Uhlig 2000) | 4E 4E-3 |
| MNR Administrative Region/District/ Area | Northeast Region Sudbury District Sudbury Area |
| Size | 82 ha |
| Nearest Town | Cartier |
| Township | Leinster |
| OBM Number | 470051900 |
| Topographical Map Name/Number | Venetian Lake 41 I/14 |
| Latitude/ Longitude | 46°53'N 81°20'W |
| Elevation | Minimum: 400 m Maximum: 440 m |
| Watershed | Lake Huron Basin 2CF |
| Wildlife Management Unit | WMU 39 |
| Forest Unit | Spanish Forest |
The 1990 Forest Resource Inventory (FRI) for the Spanish Forest was examined to determine the forest composition of the conservation reserve. The FRI interpretation reveals that the site is composed of four Working Groups white birch (Bw), white pine (Pw), black spruce (Sb), and jack pine (Pj) (Map 5). The majority of the site is occupied by two white birch stands having a composition of 50-60% white birch with mixtures of poplar (Po), black spruce, white spruce (Sw), white pine and jack pine. The other forest stands are smaller in size and are composed of stands dominated by either jack pine or black spruce. The black spruce stands are lowland stands with a small component of white birch. The jack pine stand is a young plantation established after recent harvesting along the southern edge of the conservation reserve. The forest in the conservation reserve is mature to over-mature. The ages for the forest stands range from 81 to 91 years for the black spruce and white birch, and 131 years of age for the white pine stand (Map 6).
Fire records indicate that no fires occurred in the area after 1920, no records are available prior to 1920. During a field visit though, some trees showed evidence of past fires indicating some disturbance from fire, mostly likely prior to 1920 (Figure 1).
Non-forest vegetation communities also exist in this site district such as wetlands of varied composition (bogs
Figure 1: Burnt tree, evidence of past fire.
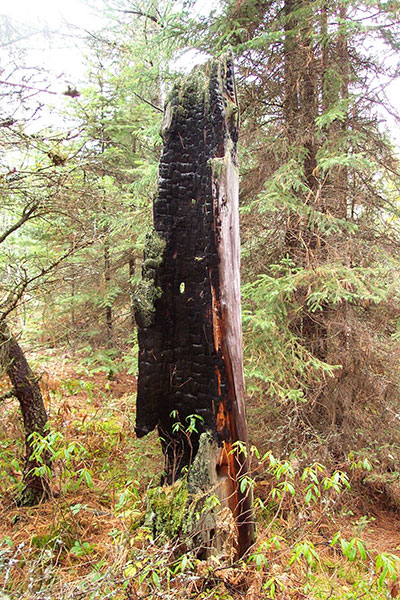

The Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve is located within the dome-like topography of the Canadian Shield, which is composed of Precambrian bedrock. The site is within the southern limits of the Abitibi Uplands subdivision. In Ontario, the Abitibi Uplands physiographic area is further divided into the Cobalt Plain in the east and the Penokean Hills that forms the north shore of Lake Huron. It is within the northeast corner of the Penokean Hills that the conservation reserve is located. This landscape is controlled by folded Proterozoic
Folds and faults are frequent throughout the Abitibi Subprovince subprovince and the granite
During the Pleistocene Epoch, all of Ontario was covered by a succession of ice sheets separated by interglacial periods. The last glacial advance, referred to as the Late or Classical Wisconsinan Stage, began approximately 23,000 years before present (Barnett 1992). During these periods a thin, discontinuous cover of till was deposited throughout the area by glacial ice. The till in along the northern rim of the Sudbury Basin, just south on the conservation reserve, has been generally described by Burwasser (1979) as sandy loam till with the actual range from sandy silt till through sand till.
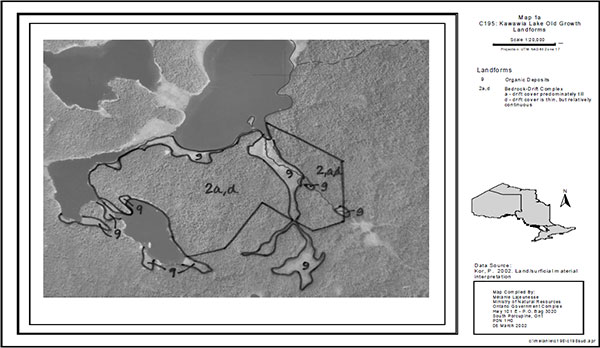
Erosional activity has been minimal since the disappearance of the ice sheet and the lowering of glacial lake water to present day levels. The site is dominated by bedrock drift complexes composed of till with small patches of organic deposits that have developed in depressions in the land surface. These organic deposits often overlie sand, silt and clay material (Map 4) (Kor 2002). Modern alluvium
Luvisols
Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve lies within the Spanish River Watershed. The northern boundary of the site is adjacent to Kawawia Lake and runoff from the site likely enters this lake. Kawawia Lake then drains into Bennet Lake, which subsequently joins the Onaping River system. The Onaping River system empties into the Vermillion River and subsequently into the Spanish River. The Spanish River then flows south and west into the North Channel of Lake Huron.
4.1.3 Administrative description
The legal description of the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve, regulated as Schedule 52 in Ontario Regulation 686/00 made under the Public Lands Act on December 20, 2000 and filed on December 21, 2000 amending Ontario Regulation 805/94, reads: In the geographic Township of Leinster, in the Territorial District of Sudbury, containing 82 hectares, more or less, being composed of that part of the said Township of Leinster designated as Part 1 on plan known as C195 Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve filed on October 19, 2000 in the Office of the Surveyor General.
The Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve is located within the Ministry of Natural Resources, Sudbury District administrative area, which covers an area of approximately 3,207,000 hectares.
The Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve is also located within the legal boundaries of the Spanish Forest Sustainable Forest License area, which encompasses approximately 1.2 million hectares and spans three MNR Districts – Chapleau, Timmins and Sudbury.
4.2 History of the site
The area where the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve is located would have been ice-free approximately 10,000 to 11,000 years ago and would have been inhabited by Ontario’s First Nations shortly after. There has been a European presence in the area since the mid-1700's when competition in the fur trade became intense. This lasted until the late 19th century when logging became the primary industry. The immediate area was logged for white and red pine and the Spanish River was used to transport the logs downstream. The arrival of the railway in 1883 changed the transportation of supplies and workers in the area (MNR 1985). Following the 1930s, the focus of logging changed from the red and white pine days to the harvest of spruce pulp, jack pine axe made ties, and mining timbers. During the late 1940s, a small sawmill was operated at Cartier station with mining timbers and lumber being shipped by rail to Sudbury (Thorpe 1950).
4.3 Inventories
Table 2: Inventory and Survey Information for Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve.
Table 2 indicates the current status of natural heritage inventory that has occurred or that will be required in the near future.
| Reconnaissance | 2002 (Kor) – Photo Interp. | 1995 (Crins) | Required | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detailed | Not required | aerial reconnaissance survey | Not required | Not required |
| Further Requirements | aerial reconnaissance survey | aerial reconnaissance survey | Recreation Inventory |
5.0 State of the resource
The natural heritage of Ontario contributes to the economic, social and environmental well being of the province and its people. Protecting areas of natural heritage is therefore important for many reasons such as maintaining ecosystem health and providing habitat in order to maintain species diversity and genetic variability. Protected areas also provide scientific and educational benefits, they generate tourism, which bolsters local and regional economies, and they provide places where people can enjoy and appreciate Ontario’s natural diversity while enhancing their own health and well-being. In order to protect this vital natural heritage, Ontario has established a provincial parks and protected areas system to try and represent the entire suite of natural features and ecosystems within the province. This representation and criteria to determine the current quality of that representation are discussed below (MNR 1997c).
Representation
Completing the system of parks and protected areas is based on the concept of representation – capturing the full range of Ontario’s natural and cultural values. The goal of Ontario Parks is to place within the parks and protected areas system the best examples of our natural heritage including features, landscapes, and ecosystems at the Eco-District level
The Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve has been identified to contribute to the life science representation of the protected areas system in Ontario. Selection criteria for identification of the best representative life science features includes: diversity, integrity, associated earth science values, and special features. Due to the nature of very different types of life science values the application of the criteria may vary on a per-site basis. The Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve has provincial significance and is therefore an important representative feature of Ontario’s life science diversity.
Noble’s (1983) classification system defines the landform pattern of Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve as Va-1 or weakly broken deep outwash plain. The provincially significant old pine vegetation and intolerant hardwood complex that grows in association with this landform unit, is the only example of this interrelationship in the site district. Through further examination of the landforms existing within the site it was concluded that the area is dominated by sand outwash plain and till ground moraine. Under existing old growth policy at the time the white pine on site were considered old growth (i.e. greater than 121 years old). Current thinking concerning old growth suggests that these stands should be at least 150 years old before they are considered old growth. Therefore, the provincial significance is greatly reduced with the site’s key value being the mature white pine mixedwood on outwash and moraine veneer.
Quality of present representation
a) Diversity
Diversity is the measure of the relative number of different landforms or special features or numbers of different vegetation and wildlife communities found in an area. The greater the number and variability of these features the more diverse the area. The Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve’s diversity is considered to be low. This site supports old white pine in association with intolerant hardwoods such as poplar and white birch. The area also contains some stands of white birch, jack pine and black spruce. The black spruce and wetland communities will require further analysis in future aerial reconnaissance inventory.
Although comparatively the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve does not have a high degree of diversity in landform/vegetation units it still contributes to the overall diversity of the protected areas system in Ontario through its life science/landform contribution. The site itself is not very large, at only 82 hectares, but the life science value that it represents has both regional and provincial significance thus the landform/vegetation unit contribution is highly important.
b) Ecological factors
The basic components that help define ecological factors include the size, shape and the ability of the site to maintain itself over time (Thompson 1999). The ability of a site to buffer the core areas from adjacent land uses, its general location and location within the greater managed ecosystem will make the site more viable over time and help to contribute to the overall ecosystem health. Generally, larger sites with more diversity are better than small, non-diverse areas; sites with a more rounded or naturally delineated shape are better than long, linear sites; and sites that are linked to or near other protected areas are better than isolated protected areas.
The Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve is relatively small but its boundaries have been delineated by following natural or man-made features (such as creeks, and roads) and it includes complete forest stands that are important to the site. This type of boundary delineation is much better than artificially vectoring (straight lining) the boundaries, which could sever the core values being protected. However, portions of the southern and eastern boundaries are vectored making management for the site in the future more problematic. In addition, the key value (white pine community) is unevenly severed along its southern border; however, most of this value has been captured by the current configuration of the site. The southern boundary could have been improved if natural or cultural boundaries could have been used (i.e. road/trail). Since there has been recent forestry operations surrounding the site, supportive landscape management will be required in order to ensure protection of the core values during forestry rehabilitation measures or subsequent harvesting near the site. This site will thus require more direct protection to prevent disturbance and to ensure that the site can continue to contribute to the parks and protected areas system.
Another strong ecological factor that the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve has is its vicinity to several other protected areas. Within a distance of three townships from the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve, another protected area can be found. Recently, through Ontario’s Living Legacy, three other conservation reserves have been regulated. These areas are the Green Lake Old Pine Conservation Reserve and the Cartier Moraine Conservation Reserve, both in Cartier Township, and the Venetian Creek Old Pine Conservation Reserve in Tyrone Township. Also within the vicinity of the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve is the existing Halfway Lake Provincial Park located in Ulster and Antrim Townships. Three other proposed protected areas will also be placed into regulation that are in the vicinity of the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve – Onaping Lake Conservation Reserve starting in Munster Township, Friday and Scotia Lakes Conservation Reserve in Rhodes and Dunbar Townships, and Kitchener Township – Morton Lake Conservation Reserve in Roberts and Kitchener Townships. Also of importance is the newly created land use designation enhanced management area (EMA). EMAs have been established to provide more detailed land use direction in areas of special features or values. The Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve is located directly south of the Onaping/Friday/Scotia Lakes EMA. This EMA was created to manage recreational and resource sector uses to maintain the remote access character of the area, particularly the remote tourism lakes. This EMA also provides a linkage with other nearby protected areas, thus allowing for corridors and preventing protected area isolation.
c) Condition
The Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve is presently in good condition. The old pine stand is intact, however the jack pine forests and understory may have been disturbed in the past. FRI data indicates that this site still contains relatively old forest (Crins 1996). Further inventory work is required to get a full picture of the present condition of the life science values.
Natural disturbances may also occur on this site. The possibility of natural disturbances such as natural wind throw or past fire disturbances exists. The existence of past fire disturbance was confirmed through the existence of fire scars at the base of trees and "church doors". There is also the possibility of experiencing fire disturbances in the future, which could either be caused by natural mechanisms or human interference. Further ground work is required to positively identify any natural disturbances present.
d) Special features
The special feature that this site boasts is the provincially significant old white pine in association with intolerant hardwoods on the weakly broken deep outwash plain landform. No other special features are known however, the site contains a hill and a small wetland ravine that contribute to the hydrology of the Kawawia Lake basin.
e) Current land use activities
Current land use activities within or near the conservation reserve include snowmobiling, all terrain vehicle (ATV) use and hunting. Its location along the way to Kawawia Lake makes it a favoured travel corridor for recreationalists travelling to other destinations within the surrounding landscape or for hunting moose, bear or deer. The site falls within a small portion of one active trapline and one active bear management area as well as one baitfish harvest area.
Summary:
This conservation reserve was considered the best representation of old white pine mixedwood on weakly broken outwash plain within the Eco-District. As such, this landform/ vegetation combination is considered provincially significant. Through further investigation, it appears that the majority of the site contains mature pine on outwash and moraine veneer over bedrock. Regardless, the site is considered provincially significant and the key feature (pine stands) are well protected within its boundaries. This protected area will eventually support old growth white pine on outwash and moraine veneer, which will help the province meet some its old growth objectives in the future.
The site is generally undisturbed but has a low diversity and some inherent design limitations. The small size of the site and portions of the eastern and southern vectored boundaries ensured that some landform/vegetation features extend beyond the site’s boundaries. However the core white pine communities appear to be adequately protected within the site’s boundaries. Additional protection of core values will require consideration for the values within large landscape management plans or strategies. The natural heritage features are not significantly sensitive to current permitted uses; however, additional disturbance due to increased trail development or any forest or wetland community disturbance by humans would impact on the quality of the present representation within Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve.
5.1 Social/economic interest in the area
This section will address the contribution of the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve to the local economy and society through the opportunities it represents and the importance of these opportunities.
a) Linkage to local communities
The Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve is accessible from Highway 144 near Benny along forest access roads. This general area is popular for cottages and land use permits as well as for recreational opportunities such as hunting, fishing and Crown land campi Residents and visitors to Ontario seeking recreation at other nearby protected areas, lakes or outfitter camps may also seek complimentary recreation opportunities in the area of this conservation reserve. The site is located near the major access to the east side of Onaping Lake, though the trails that lead directly to the site have been permitted to naturally regenerate and passage is difficult with a vehicle.
The forest access roads in the area also double as snowmobile/ATV trails which provide a connection to the major trails under the jurisdiction of the Onaping Falls Snowmobile Club. Snowmobiling and ATV use are popular pastimes of many local people as well as tourists to the area. Winter snowmobiling activities bring tourism to the local area and the economic benefits are felt through spending at the local convenience stores, restaurants and gas stations.
Some of the other recreational/commercial activities that the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve represents may include hiking, bird watching, wildlife viewing, photography, canoeing/boating, fishing, small game hunting/trapping, and large game hunting (moose, bear). Hunting, trapping and fishing are long-standing traditional activities and they are also a vital part of the local economy. Economic benefits are seen at local establishments from bear and moose hunting parties as well as fishing enthusiasts; and trapping provides a source of income to local trapline holders.
b) Heritage estate contribution
The Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve contributes to the province’s parks and protected areas system through its regulation, representation and the long-term management of its natural heritage values.
The protected area system allows for permanent protection of our history and special features, and it will provide valuable areas as benchmarks to scientists and educators as more and more of Ontario’s land base is developed or altered from its natural state. Each protected area contributes to this heritage in its own unique way – whether it is a contribution to the preservation of an earth science value, a life science value, a recreational or economic opportunity, or through its cultural/historical significance. The designation of an area as a conservation reserve helps define its role in the system.
The Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve’s distinct contribution is a combination of life science/glacial history preservation, and educational and recreational opportunities. The site is also accessible, therefore scientists, educators and recreationalists alike will not have difficulty in accessing the site to learn about and enjoy its values.
c) First Nations
The Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve lies within the Robinson-Huron Treaty Area, Treaty #61. The in question has been identified as being within Sagamok Anishnawbek traditional area. The protection of this area as a conservation reserve and the Statement of Conservation Interest are not meant to infringe on the Treaty and Aboriginal Rights of any First Nation in any way. Traditional uses such as hunting, fishing, trapping and gathering will be respected. At the present time, there are no known land claims by First Nations for the area in question.
d) Mining interests
This conservation reserve has no mining tenure within it. Mining and surface rights have been withdrawn from staking within the conservation reserve boundaries under the Mining Act (RSO 1990 Chapter M.14). Mining will not occur in any regulated protected area.
e) Forest and fire management history
The conservation reserve is relatively undisturbed and has not been recently affected by forest harvest activities or recent fires.
f) Other Government Agencies, Departments or Crown Corporations
Other Government Agencies that may have an interest in the site include the Ministry of Citizenship (MCzP), the Ministry of Tourism, Culture and Recreation (MTCR), the Ministry of Transportation (MTO), and the Ministry of Municipal Affairs and Housing (MMAH). Although there are no known cultural heritage values present at this time if values were identified in the site the MNR would work with the MCzP to ensure proper protection of any cultural heritage resources. The MNR will also work in conjunction with the MTCR to identify/enhance any potential tourism opportunities, in particular where Resource-Based Tourism (RBT) potential is identified. RBT operations include hunting and fishing as well as ecotourism opportunities. Proper evaluation will be undertaken where opportunities are identified to ensure consistency with the management policies of this conservation reserve. At this time no highways are planned in or adjacent to this conservation reserve. However, in the future if a highway is planned in the vicinity of this conservation reserve the MNR and MTO would work together to ensure that construction would not occur within the boundaries of this protected area and that uses adjacent to the conservation reserve would have regard for the values being protected. The MNR would also work in conjunction with the MMAH should there be any proposed development in the area. Development of cottage lot subdivisions would not occur within the boundaries of the conservation reserve and proper protection of values would be given due regard should development occur in the immediate area.
g) Non Government Organizations and other Industry interests
Non Government organizations who may express an interest in the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve may include: the Partnership for Public Lands, the Federation of Ontario Naturalists, Northern Ontario Tourist Outfitters, the Sudbury and Area Trapper’s Council, the Ontario Federation of Anglers and Hunters, and the Sudbury Trail Plan Association.
The existence of this protected area will provide enhanced recreation potential and these associations may wish to approach the MNR as stewards of the protected area. The MNR will work in conjunction with any association who identifies an interest or compatible use potential within the site.
Other industries or companies that may have an interest in the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve may include the Prospector’s Association, the Sustainable Forest Licensee (Domtar Inc.), and the Aggregate Producer’s Association.
The interests of these companies or industries may be limited to recognizing the boundaries and values protected within the conservation reserve in order to uphold the MNR's management policies.
5.2 Fisheries and wildlife
There are three warmwater lakes that border this site to the north and west, Kawawia Lake and two of its extensions. This lake is home to northern pike, a popular game fishing species, cisco, and other species such as white sucker, and yellow perch. The lake survey also indicated the presence of crayfish and mussels. One of the extensions of Kawawia Lake is also a particularly good place to find aquatic vegetation.
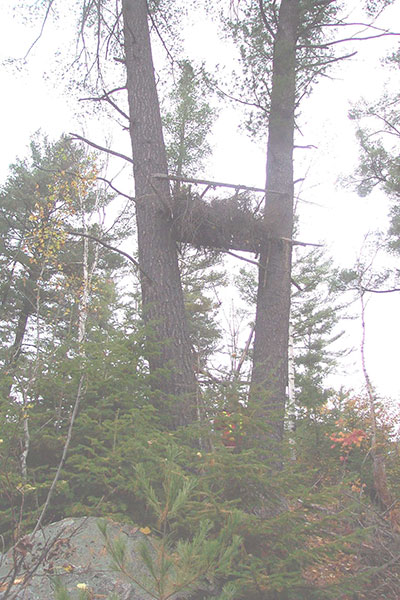
Wildlife on the site would be consistent with typical wildlife found in Eco-District 4E-3 including birds (loons and herons were noted during the lake survey), small furbearers and large ungulates. The site visit in November 2001 confirmed the presence of black bear and wolves by sightings of scat. The site is within one registered trapline and is adjacent to another trapline, it also falls into one Bear Management Area. Traplines have been present in the area since the 1950's and the local area has been successfully managed to maintain a healthy balance of wildlife populations. Local knowledge indicates that this area is a particularly good moose hunting area and there is a known moose feeding area nearby. A tree stand was also spotted near the very edge of the site (Figure 5). MNR's most recent moose surveys demonstrate however that this area contains a low moose population density. This area is within Wildlife Management Unit 39.
It is not known if any vulnerable, threatened or endangered species exist on or near the site. Further detailed habitat studies would address this.
5.3 Natural Heritage Stewardship
The Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve, a provincially significant old pine location, contributes to the natural heritage life science representation through its landform/ vegetation complexes. A site visit in November 2001 also confirmed the existence of numerous other vegetation species, such as twin flower, spaghnum moss, creeping snowberry, beaked hazel, bunchberry, and ground pine.
Figure 2 -Tree stand spotted near Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve.

A complete inventory of flora would identify other species that are present in the site. Earth science representation is also present in the weakly broken deep outwash plain, however this common landform alone has only local significance in this location. The conservation reserve also contributes to the variety of recreational opportunities that can be found in the parks and protected areas system. Currently there are no monitoring or research programs in place for this conservation reserve.
5.4 Cultural Heritage Stewardship
There are no known cultural heritage values within the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve and no detailed research has been conducted as of this date to document possible cultural heritage values. However, the area has been occupied for over a century and the possibility of heritage values being present does exist. If archaeological/ cultural resources are discovered within the conservation reserve proposals pertaining to the development/use of these cultural resources may be screened through direction provided in Conserving a Future For Our Past: Archaeology, Land Use Planning & Development In Ontario (MCzCR 1997).
5.5 Land use/current or past development
There is no mining tenure near the site and no mines have been developed on the site in the past. There are no patent lands nested within the site and there are no other forms of tenure such as land use permits or licenses of occupation.
5.6 Commercial use
Commercial use of the site includes black bear hunting, and commercial fur harvesting. The area is also included in a baitfish license.
5.7 Tourism/recreational use/opportunities
Current recreational uses and opportunities of the site include hiking, canoeing/boating, fishing, hunting, bird watching, etc. The nearby Onaping River system is a known canoe route and Kawawia Lake can be accessed from this route via a short portage. Winter activities such as ice fishing, skiing and snowshoeing are also potential recreational uses. Further detailed recreation inventory studies need to be undertaken to confirm the existence of recreational uses and potential.
Tomiko Lake Lodge, catering primarily to non-resident bear hunters, brings tourism to the area. Other tourism opportunities include snowmobiling and moose hunting.
The forest access road/trail network is the only form of existing infrastructure near the site.
5.8 Client services
Currently, client services are being provided at the Sudbury District MNR office in the form of knowledgeable staff and available fact sheets and site maps. Further client services will be developed as a result of this plan, please see section 6.2 State of the Resource Management Strategies.
6.0 Management guidelines
6.1 Management planning strategies
The land use intent outlined in the OLL Land Use Strategy (MNR 1999) provides context and direction to land use, resource management, and operational planning activities on Crown land. Commitments identified in the above strategy and current legislation (Policy 3.03.05 PLA) will form the basis for land use within Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve. Management strategies for these uses must consider the short and long-term objectives for the reserve. For up to date information on permitted uses refer to the Crown Land Use Atlas.
Protected areas will be managed to retain and/or restore natural features, processes and systems. They will also provide opportunities for compatible research, education and outdoor recreation activities (MNR 1997c). Proposed uses and development will be reviewed on a case-by-case basis. A Test of Compatibility, (Procedural Guidelines B – Land Uses PL 3.03.05) must be passed before they are deemed acceptable. The emphasis will be on ensuring that the natural values of the conservation reserve are not negatively affected by current and future activities. Therefore any application for new specific uses will be carefully studied and reviewed via the above environmental screening process.
Management strategies will also be consistent with the objectives of increasing public awareness, promoting responsible stewardship, providing marketing opportunities, and identifying Inventory Monitoring Assessment Reporting (IMAR) potential.
6.2 "State of the resource" management strategies
The development of this SCI and the long-term management and protection will be under the direction of the MNR's Sudbury Area Supervisor. The following section will deal with the management strategies that are specifically laid out to maintain, protect and enhance the existing natural heritage values and land use activities of the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve.
Natural Heritage Values
The management intent for the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve will be to allow for natural ecosystems, processes and features to operate undisturbed with minimal human interference while providing educational, research and recreational activities. Forest ecosystem renewal will only be entertained via a separate vegetative management plan.
Forest fire protection will be provided as per fire strategies used on surrounding public lands, under the direction of the provincial fire strategy. All wildfire occurrences will be considered a high priority and will actively be suppressed. Prescribed burning will be conducted only under the direction of the provincial fire strategy and authorized for the conservation reserve under a separate vegetative management plan. Prescribed burning may be utilized if deemed necessary to emulate natural disturbances and renew forest communities, prepare seed beds for research and/or education purposes or to meet additional objectives determined within a separate vegetative management plan. Consideration for the life science values will be the governing priority in any future vegetative management plan.
Defining compatible uses, enforcing regulations and monitoring and mitigating issues will protect all earth and life science features. Industrial activities such as commercial timber harvest and new hydro generation will not be permitted within the conservation reserve. Extraction of unconsolidated sand, gravel, soils or peat is not permitted. Energy transmission, communication and transportation corridors or construction of facilities are discouraged within the boundaries of the conservation reserve. Such structures negatively impact on the quality of representation features that require protection. Alternatives should be reviewed via larger landscape planning processes. New roads for resource extraction and/or private use will not be permitted. Other activities that do not pass a Test of Compatibility will be prohibited (MNR 1997a).
The introduction of exotic and/or invasive species will not be permitted. Programs may be developed to control forest insects and diseases where there is a concern that significant values may be compromised. Remedies must focus on the outbreak or infestation. Native biological or non-intrusive solutions should be applied whenever possible.
The collection/removal of vegetation and parts thereof may be permitted subject to a Test of Compatibility, the Area Supervisor may authorize such activities for purposes of wild rice harvesting, food harvesting, removing exotic species, rehabilitating degraded sites within the reserve, collecting seeds for maintaining genetic stock and/or for inventory or research. The cutting of trees for non-commercial purposes (e.g. fuel-wood) is not permitted.
MNR will provide leadership and direction for maintaining the integrity of this site as a heritage estate. To ensure MNR protection objectives are being fully met within the conservation reserve, activities on the surrounding landscape should consider the site’s objectives, heritage values and the design flaws currently present. MNR via input and plan review will ensure the conservation reserve’s values are considered in local and adjacent land use strategies and plans. Research, education and interpretation will be encouraged to provide a better understanding of the management and protection of the natural heritage values and will be fostered through local and regional natural heritage programs, initiatives and partnerships. Furthermore, adequate protection of core values will require cooperation with adjacent land users to help compensate for the conservation reserve’s small size and design flaws.
Cultural heritage values
It is not known if cultural heritage values exist in the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve, however, if values are confirmed management would be consistent with Conserving a Future For Our Past: Archaeology, Land Use Planning & Development In Ontario (MCzCR 1997). Research and studies should be conducted to determine the potential and/or existence of cultural or archeological resources. Since the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve has been accessible for many years there is a possibility that cultural or historical resources do exist.
Land use/past and existing development
The sale of lands within the conservation reserve is not permitted as per the OLL LUS (MNR 1999). No new recreational camps will be permitted. Road realignments, telecommunications and other resource networks will be discouraged from crossing the site and interrupting the conservation reserve’s natural state. New roads for resource extraction and/or private use will not be permitted.
Through the Ministry’s plan input and review program, applications for more intense use will be reviewed to ensure natural heritage values within the conservation reserve are considered and protected in planning decisions on adjacent private land.
Any new developments (e.g. tourism developments) proposed for the conservation reserve must go through a Test of Compatibility to ensure that the activity is permitted and to ensure the natural heritage values within the site are protected. If a proposal is considered, public consultation may be required. If accepted, an amendment of the SCI would be required.
Social/economic interest
The economic contribution of the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve to the local community could be harnessed through marketing strategies that will maintain existing tourism in the area allowing the nearby towns and tourist operators to benefit through money spent at the local businesses. Socially this area provides a recreational reserve for local people to enjoy for their own health and well being. The people of Ontario generally benefit either through direct enjoyment of the area or through the knowledge that a piece of our life science and glacial history has been preserved. Other interest groups such as colleges and universities can benefit from this reserve as a place to study several natural features and processes and the local parks, towns and tourist outfitters would benefit economically through the presence of researchers.
Fisheries and wildlife
Sport fishing and hunting will be permitted within this conservation reserve. Fishery and wildlife resources will continue to be managed in accordance with specific policies and regulations defined by the Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources under the Fish and Wildlife Conservation Act and the Sudbury Area Supervisor. Management of these resources will have consideration for the earth and life science features contained within the site.
Wildlife viewing activities may be enhanced via client services with the existing trail networks supporting this activity. New trail development may be entertained for this activity providing a Test of Compatibility is conducted and passed.
Commercial activities
Commercial, non-industrial activities such as fur harvesting, bait fish harvesting and Bear Management Areas will be managed according to prescriptions in the Land Use Strategy (MNR 1999). Fur harvesting traplines and bait fishing operations will be permitted to continue since there are no demonstrated conflicts between these activities and the values being protected. New operations would be subjected to a Test of Compatibility to ensure that the wildlife populations could sustain additional activity. Existing Bear Management Areas (BMAs) will be permitted to continue, however, new operations will not be permitted as per the Land Use Strategy (MNR 1999). MNR managers will work with operators to ensure that the natural heritage values within the conservation reserve are respected.
Tourism and recreation
The earth and life science features and their protection, shall be the overall theme for tourism and recreation within the conservation reserve. There are no existing tourism facilities located in or directly adjacent to this conservation reserve. Any proposed tourism infrastructure or facilities would be required to undergo at Test of Compatibility and if accepted, further planning would occur, requiring public consultation and an amendment to this document. The existing local tourist outfitters can continue accessing this reserve as they have in the past, however, MNR will work with the proponents to ensure the values of the conservation reserve are respected and maintained to the highest level possible (see previous Commercial Activities Strategies).
Most recreational activities that have traditionally been enjoyed in the area can continue provided they pose little or no threat to the natural ecosystems and features protected by the conservation reserve. Current activities include bird watching, hiking, skiing, ATV use and snowmobiling. Camping may also be a current use of the conservation reserve and will be permitted to continue.
Snowmobiles and All Terrain Vehicles (ATV's) are permitted on existing trails. Under the OLL LUS (MNR 1999), all mechanized travel is restricted to existing trails. Off trail vehicle use is permitted for the retrieval of game only. To protect the natural heritage features within the conservation reserve, MNR will seek direction from local communities on how to reduce off trail use, if such activities become problematic.
Client services
Clients indicating their interest in the management, planning and future use in the conservation reserve will be put on a mailing list and notified of any future planning initiatives for the site.
Client services will be provided at the Sudbury District office and at nearby provincial parks through interpretive pamphlets and knowledgeable staff. In the future, information may be delivered from different sources; however, MNR Sudbury District office will be the lead agency for responding to inquiries regarding access permitted and restricted activities, values and recreation opportunities. A management agreement may be pursued with an appropriate partner to share responsibilities for information services and the delivery of other aspects of this SCI. For example having the interpretive pamphlets available at local convenience stores and other appropriate businesses could provide additional client services venues.
It is further recommended that visitors and conservation reserve users and the local population be informed of the significance and sensitivity of the site via fact sheets, community visits and other educational or interpretive programs.
Aboriginal interests
Traditional activities and aboriginal rights as defined in the Robinson-Huron Treaty #61 and other relevant Acts, will not be affected within the boundaries of this conservation reserve. The Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve is within the Sagamok First Nation’s area of interest and all Aboriginal and treaty rights will continue to be respected. The First Nation communities are encouraged to continue to use these areas as they have in the past.
6.3 Promote inventory monitoring and assessment reporting and research
Scientific research by qualified individuals or institutions, which contributes to the knowledge of natural and cultural history and to environmental and recreational management, will be encouraged. Requests or applications to conduct research will be filtered through the Sudbury District MNR office to ensure that the studies are non-invasive and that no values will be damaged in the process. Research programs will be subject to ministry policies and other legislation.
Approved research activities and facilities will be compatible with the protection objective. Any inventory, monitoring, assessment reporting (IMAR) or research developments or facilities will not be considered until a Test of Compatibility is conducted and proposal is approved by the Sudbury Area Supervisor. The Test of Compatibility or environmental screening process could include a review of the demand for structures or activities and may require more detailed life or earth science or cultural information and possibly more detailed planning. IMAR will be consistent with provincial/regional protocols and/or strategies. Permanent plots or observation stations may be established to which researchers can return over time. The Sudbury Area Supervisor may approve the removal of any natural or cultural specimen by qualified researchers. Any materials removed will remain the property of the Ministry of Natural Resources. Any site that is disturbed will be rehabilitated as closely as possible to its original state. The Sudbury Area Supervisor may apply additional conditions.
Particular research may focus on the interrelationship with other nearby protected areas – in particular to gauge the effectiveness of isolated protected areas and how these areas need to be connected through supportive landscape management in order to maintain ecosystem health and diversity. Also the effects of straight boundaries versus naturally delineated boundaries should be explored. Further research and monitoring requirements will be determined through forthcoming regional/provincial strategies.
Further inventories are required for life science evaluation, earth science evaluation and recreation use/potential. This research should be conducted at the earliest opportunity and this information should be incorporated into this report immediately following completion. The check-sheets that are completed as a requirement for this research should be appended to the updated Statement of Conservation Interest upon completion as well.
Additional research may focus on the interrelationship with other nearby protected areas – in particular to gauge the effectiveness of isolated protected areas and how these areas need to be connected through supportive landscape management in order to maintain ecosystem health and diversity. Also the effects of straight boundaries versus naturally delineated boundaries should be explored. Other specific research projects that could be undertaken may include: the effects of human disturbance on the site, determination of the existence of any rare, vulnerable or threatened species, and/or vegetation climax community. Further research and monitoring requirements will be determined through forthcoming regional/provincial strategies.
6.4 Implementation and plan review
The Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve Statement of Conservation Interest will be reviewed on an ongoing basis and as required. Implementation of the SCI and management of the reserve are the responsibility of the Sudbury Area Supervisor. Partnerships may be pursued to address management needs.
Adaptive management strategies will be used in the event of new information that has a significant effect on the current Statement of Conservation Interest. If changes in management direction are needed at any time, the significance of the changes will be evaluated. Minor changes that do not alter the overall protection objectives may be considered and approved by the District Manager without further public consultation and the plan will be amended accordingly. In assessing major changes, the need for a more detailed Resource Management Plan will first be considered. Where a RMP is not considered necessary or feasible, a major amendment may be considered with public consultation. The Regional Director will approve major amendments.
6.6 Marketing
The Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve will be marketed as a distinctive old growth white pine forest growing in association with intolerant hardwoods on a weakly broken deep outwash plain. Fact sheets will be prepared to inform the public about these values which will be available at the Sudbury District MNR office, local provincial parks as well as possibly at the tourist outfitters. Marketing efforts to increase use are not a priority and will be kept to a minimum.
7.0 References
Barnett, P.J. 1992. Quaternary geology of Ontario, in Geology of Ontario; Ontario Geological Survey, Special Volume 4, Part 2, p.1011-1088.
Boissonneau, A.N. 1965. Surficial geology of Algoma, Sudbury, Timiskaming and Nipissing; Ontario Department of Lands and Forests; Map S465, Scale 1:506 880.
Boissonneau, A.N. 1966. Glacial history of northeastern Ontario: I the Cochrane to Hearst area; Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, Vol.3, p.559-578.
Boissonneau, A.N. 1968. Glacial history of northeastern Ontario: II the Timiskaming-Algoma area; Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, Vol.5, p.97-109.
Bostock, H.S. 1970. Physiographic subdivisions of Canada; in Geology and Economic Minerals of Canada, Geological Survey of Canada, Economic Geology Report no. 1, p. 11-30.
Burwasser, G.J. 1979. Quaternary geology of the Sudbury area, District of Sudbury; Ontario Geological Survey, Report 181, 103 p.
Card, K. D., and Innes, D. G. 1981. Geology of the Benny Area, District of Sudbury. Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources. 117 p., ill., maps.
Cosec, M. 1998. Impact Statement. Lands for Life/Ontario’s Living Legacy – Site Archive C194. Internal Report.
Crins, W. J. 1996. Life Science Gap Analysis for Site District 4E-3. Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources Internal Report.
Davidson, R. J. 1997. Completing the Provincial Park System, A Priceless Legacy. Occasional Paper 3. Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources. 23 p.
Ecoregions Working Group, Canada Committee on Ecological Land Classification. 1989. Ecoclimatic Regions of Canada, Ecological Land Classification Series No. 23. Sustainable Development Branch, Canadian Wildlife Service, Conservation and Protection, Environment Canada, Ottawa, Ontario. 118 p., ill., maps.
Ferris, N., Ross, B., and Wong, W. 1997. Conserving A Future For Our Past: Archaeology, Land Use Planning and Development in Ontario; Ontario Archaeology Society, Inc.
Harris, A.G., McMurray, S.C., Unlig, P.W.C., Jeglum, J.K., Foster, R.F. and Racey, G.D. 1996. Field Guide to the Wetland Ecosystem Classification for Northwestern Ontari Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources, Northwest Science and Technology. Thunder Bay, ON. Field Guide FG-01. 74 pp. + Appendices.
Hills, G. A. 1959. A ready reference to the description of the land of Ontario and its productivity. Ontario Department of Lands and Forests.
Kor, P.S.G. 2002. Kawawia Lake Old Growth C195 Earth Science Inventory. MNR internal inventory record.
Ministry of Citizenship, Culture and Recreation. 1997. Conserving a Future for out Past: Archaeology, Land Use Planning and Development in Ontario. Revised 1998. Ontario Archaeological Society, Inc. 43 p.
Noble, T. W. 1983. Life Science Report, Site Region 4E, Northeastern Region. Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources. 150 p. (with additional pages in checksheets and appendix, 1:250 000 maps).
Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources. 1985. Chapleau District Background Information – Historic Use. Sudbury District Office Spanish River Files – 82.3 History and Culture.
Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources. 1997a. Conservation Reserves, Policy PL 3.03.05. 8 p.
Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources. 1997b. Conservation Reserves, Procedure PL 3.03.05. 22p.
Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources. 1997c. Nature’s Best. Ontario’s Parks and Protected Areas: The Framework and Action Plan. 37 p.
Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources. 1999. Ontario’s Living Legacy Land Use Strategy. Queen’s Printer for Ontario. 136 pp.
Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources. 2000. Beyond 2000. Queen’s Printer for Ontario. 20 p.
Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources and Ministry of Northern Development and Mines.2001. Implementing Ontario’s Living Legacy Land Use Strategy (July 1999), MNR_MNDM Answers to Frequently Asked Questions, Version 1.0. Unpublished. 14 p. Rowe, J. S. 1972. Forest Regions of Canada. Department of Fisheries and the Environment Canadian Forestry Service Publication No. 1300, Ottawa, Ontario. 172 p., maps.
Rowe, J. S. 1972. Forest Regions of Canada. Department of Fisheries and the Environment Canadian Forestry Service Publication No. 1300, Ottawa, Ontario. 172 p., maps.
Thompson, J. E. 1999. Building the System. Criteria to Consider when Allocating to Parks and Protected Areas. Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources, Internal Report. 7 p.
Thompson, J. E. 2001. Planning Process for Conservation Reserves Statement of Conservation Interest (SCI) and Resource Management Plans (RMP), Northeastern Region Guidelines, Version 2.1. Unpublished, 49 p.
Thorpe, T. 1950. Review of the Logging and Pulp Operations in the Sudbury District During the Years (1901-1950). Ontario Department of Lands and Forests Internal Report. 66 p.
8.0 Maps
Map 1 - Inset of Ontario showing location of Sudbury; larger map showing location of the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve in relation to Sudbury.
Enlarge Map 1 of Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve in relation to Sudbury
Map 2 - Site map of Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve.
Enlarge Site Map 2 of Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve.
Map 3 - Location of Site District 4E-3 (Crins, 1996).
Enlarge Map 3 of - Location of Site District 4E-3 (Crins, 1996).
Map 4 - Landforms.
Map 5 - Species Composition.
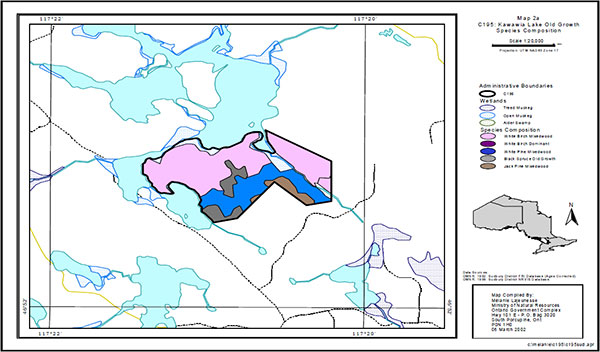
Enlarge Map 5 - Species Composition.
Map 6 - Age Distribution.
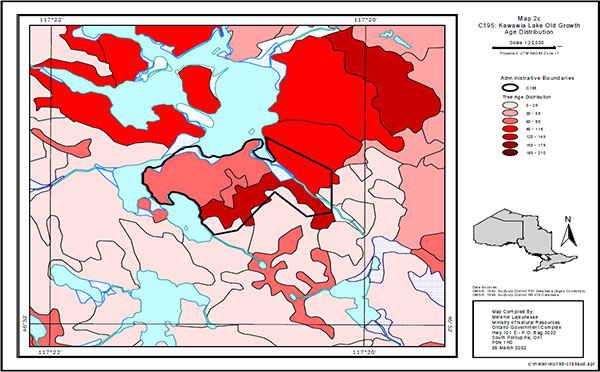
Enlarge Map 6 - Age Distribution.
9.0 Appendices
Appendix A: permitted uses table
Permitted uses table for conservation reserves as per policy
Recreation
| Activities | Conservation Reserve Policy - Permitted? Existing | Conservation Reserve Policy - Permitted? New | Policy Clarification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sport fishing | Yes | Yes | |
| Sport hunting | Yes | Yes | |
| Food gathering | Yes | Yes | |
| Facility infrastructure | Maybe | Maybe | Any new facilities are subject to a "test of compatibility" and approval by the Area Supervisor. |
| Rock Climbing/caving | Maybe | Maybe | Rock climbing and/or caving is permitted where it does not detrimentally affect the values to be protected. |
| Canoeing/kayaking | Yes | Yes | |
| Motorized boating | Yes | Yes | |
| Picnicking | Yes | Yes | |
| Camping | Maybe | Maybe | Camping is permitted where it does not detrimentally affect the values to be protected. |
Trails
| Activities | Conservation Reserve Policy - Permitted? Existing | Conservation Reserve Policy - Permitted? New | Policy Clarification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hiking trails | Yes | Maybe | Any new hiking trails will be subject to a "test of compatibility" and approval by the Area Supervisor. |
| Cross-country skiing trails | Yes | Maybe | Any new cross-country skiing trails are subject to a "test of compatibility" and approval by the Area Supervisor. |
| Cycling/ mountain biking trails | Yes | Maybe | Any new cycling trails are subject to a "test of compatibility" and Approval by the Area Supervisor. |
| Horse riding trails | Yes | Maybe | Any new horse riding trails are subject to a "test of compatibility" and approval by the Area Supervisor. |
| Snowmobiling trails | Yes | Maybe | Any new snowmobiling trails are subject to a "test of compatibility" and approval by the Area Supervisor. |
| Non-trail Snowmobiling | Maybe | Maybe | Non-trail snowmobiling is only permitted for the retrieval of game. |
| ATV trails | Yes | Maybe | Any new ATV trails are subject to a "test of compatibility" and approval by the Area Supervisor. |
| Non-trail ATV Use | Maybe | Maybe | Non-trail ATV use is only permitted for the retrieval of game. |
Science, education and heritage appreciation
| Activities | Conservation Reserve Policy - Permitted? Existing | Conservation Reserve Policy - Permitted? New | Policy Clarification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Research | Yes | Yes | |
| General walking | Yes | Yes | |
| Photography and painting | Yes | Yes | |
| Wildlife viewing | Yes | Yes | |
| Outdoor education/interpretation | Yes | Yes | |
| Collecting | No | No | Collecting may be permitted as part of an authorized research project. The issuance of permits will be considered on a per-site basis. |
Commercial activities
| Activities | Conservation Reserve Policy - Permitted? Existing | Conservation Reserve Policy - Permitted? New | Policy Clarification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food harvesting | Maybe | Maybe | Any new food harvesting is subject to a "test of compatibility" and approval by the Area Supervisor". |
| Fishing | Yes | Maybe | Any new commercial fishing is subject to a "test of compatibility" and approval by the Area Supervisor. |
| Baitfish harvesting | Yes | Maybe | Any new baitfish harvesting operations are subject to a "test of compatibility" and approval by the Area Supervisor. Transfer requests for existing baitfish operations will be considered on an on-going basis subject to a review of potential impacts. |
| Trapping | Yes | Maybe | Any new traplines are subject to a "test of compatibility" and approval by the Area Supervisor. Transfer requests for existing traplines will be considered on an on-going basis subject to a review of potential impacts. |
| Trap cabins | Yes | No | |
| Resort – outpost camps | Yes | Maybe | Any new outpost camps/resorts are subject to a "test of compatibility" and approval by the Area Supervisor. Transfer requests for existing outpost camps/resorts will be considered on an on-going basis subject to a review of potential impacts. |
| Outifitting – Bear Management | Yes | No | Transfer requests for existing Bear Management Areas will be considered on an on-going basis subject to a review of potential impacts. |
| Wild rice harvesting | Yes | Maybe | Any new wildrice operations will be subject to a "test of compatibility" and approval by the Area Supervisor. |
Resource management
| Activities | Conservation Reserve Policy - Permitted? Existing | Conservation Reserve Policy - Permitted? New | Policy Clarification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inventory/monitoring | Yes | Yes | |
| Featured species management | Maybe | Maybe | Any new featured species management is subject to a "test of compatibility" and approval by the Area Supervisor. |
| Natural systems management | Maybe | Maybe | Any new natural systems management will be subject to a "test of compatibility" and approval by the Area Supervisor. |
Industrial activities
| Activities | Conservation Reserve Policy - Permitted? Existing | Conservation Reserve Policy - Permitted? New | Policy Clarification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Timber harvesting | No | No | |
| Mineral exploration | No | No | |
| Mining | No | No | |
| Hydro power generation | No | No | |
| Energy transmission corridors/communication corridors | Yes | No | New communication lines and transmission corridors are discouraged from within conservation reserves but can be considered under unusual circumstances where there are no other viable alternatives and where the line/corridor does not significantly impact the values the site is trying to protect. Approval from the Area Supervisor is required. |
| Transport corridors | Yes | No | |
| Resource access roads | Yes | No | Existing roads can continue to be used. Continued use will include maintenance and may include future upgrading. New roads for resource extraction will not be permitted, with the exception of necessary access to existing forest reserves for mineral exploration and development. |
| Private access roads | Yes | No | |
| Fuelwood cutting | No | No | The cutting of trees for non-commercial purposes may be authorized by permit subject to a review of the impact of the values to be protected. This flexibility is only for leaseholders and property owners who do not have road access. |
| Extraction of peat, soil, aggregate | No | No |
Other activities
| Activities | Conservation Reserve Policy - Permitted? Existing | Conservation Reserve Policy - Permitted? New | Policy Clarification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Land disposition | Maybe | Maybe | Sale of Crown lands in a conservation reserve is not permitted, except for certain minor dispositions (e.g. sale of road allowance in front of existing cottage, sale of small parcels to provide adequate installation of a septic system) where it does not detrimentally affect the values the area is intended to protect. Renewals of existing leases or land use permits will be permitted. Tourism facilities can apply to upgrade tenure from LUP to lease. Requests for transfer of tenure will be considered on an on-going basis. New leases or land use permits will be allowed for approved activities. |
| Private recreation camps (hunt camps) | Yes | No | Transfer requests for existing private recreation camps will be considered on an on-going basis subject to a review of potential impacts. Existing private recreation camps may be eligible for enhanced tenure (i.e. lease) but not purchase of land. |
Appendix B: SCI Test of Compatibility
From the SCI Test of Compatibility NER Guideline in Planning process for Conservation Reserves Statement of Conservation Interest (SCI) and Resource Management Plans (RMP) Northeast Region Guidelines Version 2.1 September 17. 2001 Appendix 4, page 44.
Test of Compatibility:
- Conformity to SCI – This is not applicable to evaluating current or new uses that come forward during the SCI planning proce However, the SCI should include a statement that speaks to the required screening of any future use or uses that are not covered in the current SCI
-
Screening Process – proposed uses for the area must be assessed before they are approve To establish a minimum standard, NER recommends that the Screening Process identified in Section 4.2 of A Class EA for Provincial Parks and Conservation Reserves Phase IIb: Draft Class EA (subject to approval by MOE) be used to screen projects and options.
The Screening Criteria from the draft Class EA (Table 4.1) is further detailed below within the context of SCI planning.
- Impact Assessment – the Test of Compatibility from the Conservation Reserve Policy PL 03.05 identifies the classes of values and main concepts that need to be considered in determining the impacts of uses on a specific Conservation Reserve. These include:
- Natural heritage
- Cultural
- Research activities
- Current uses
- Area administration
- Accommodating the use outside the CR
- Socio-economics
- Area accessibility
The class EA (Table 4.1) presents similar values and concepts under the following considerations:
- Natural environment
- Land use, resource management
- Social, cultural and economic
- Aboriginal
The above considerations and classes of values are meant to assist planning staff in answering the following questions for any potential use:
- Will the new use impact any values within the Conservation Reserve?
- If so how?
- To what degree?
- Is it tolerable?
The new screening process and associated criteria identified in Table 4.1 of the draft Class EA gives planning staff more direction than the Conservation Reserve Policy 3.03.05. However this section attempts to assist planning staff by providing some direction for further interpreting the criteria to complete a Test of Compatibility for uses within a Conservation Reserve.
The following information for each Conservation Reserve is available and can be used to assess the required criteria:
- Background information and current inventory data
- Current inventory evaluations (e.g. earth, life and recreational check-sheets)
- Future ongoing analysis on the site
Interpretation of background information & current inventory data:
Background information files, summaries and other data can be beneficial in determining additional criteria that could be added to or address criteria already mentioned in the EA screening process. Criteria that are linked to habitat needs or specific life or earth science features are often first record during a District’s initial review of a site. Databases such as NRVIS or documents such as Lake Survey files, Site District Reports or Forest Management Plans can identify the location of values and sometimes determine a value’s significance or sensitivities.
Current inventory evaluations:
The most current state of the resource for a specific OLL Conservation Reserve will be the earth, life and recreational check-sheet. These documents determine the current earth and life science values, their present state and their significance. The recreational check-sheets determine current recreational features and current and potential recreational activities and feature significance and sensitivity to present and future uses.
For earth and life science check-sheets, five (5) major sections are completed that include; representation and the quality of the representation (e.g. based on condition, diversity and ecological considerations) and special features. These five categories are reflected within the screening criteria presented in draft Class EA document or could be used to develop additional criteria. Some thoughts concerning the five categories are further discussed below.
Representation:
Representation within OLL inventoried sites contain the type, number, location and shape of the community based values within the Conservation Reserve. For example the number of different forest cover types, wetland and freshwater communities, earth science features or recreational features defined in recreational check-sheets. The survey determines if the values are totally within the site or if the value straddles the site’s boundary? This section and the significance section of the check-sheet can help you define significant earth or life science features, important wildlife habitat, or record the location and extent of old growth within a site or other features. Representation determines not only specific communities or special features but also establishes the core protected areas within the Conservation Reserve, which is a value that has to be protected as well. Finally, any list of screening criteria should mention the affect a potential permitted use may have on the quality of the representation present within the site. The quality of the site’s representation is mentioned in the following three categories below.
Condition:
Condition is the level of natural and human disturbance that the site has experienced to date. The major natural disturbances in Northeast Region include; burned, blown down, flooded or insect effected stands or areas. Human disturbances could include; clear-cut areas, mining related sites, drainage areas, ditches or pits, utility corridors, railways, roads, hiking or ATV trails, assess points, dams, cottages or other facilities on site. Such actions or structures can effect the site negatively by influencing specific special features (e.g. nest sites or wildlife travel corridors) or severing significant communities or the Conservation Reserve’s core protected areas. This section could help interpret the following screening criteria; affect on water quality, specific species or habitat needs or criteria that speak to undisturbed core protected areas. Such core protected areas criteria could include for example - affect a permitted use or potential use has on natural vegetation and habitat through fragmentation or how use could affect easily eroded or sensitive wind blown deposits?
Diversity:
This is a measure of the site’s life and earth science heterogeneity. For earth and life sciences the evaluation is based on the number and variety of natural landscape features and landforms for earth science values and the relative richness and evenness of a site’s life science components. For our life science check-sheet inventory we determine richness by counting the number of vegetative cover types present within a site and evenness as the proportion of each cover type represented within a site. So an OLL site that has many cover types of roughly the same size is more diverse than a site with few cover types or where a site has the same number of cover types but has reduced evenness (e.g. one cover type dominates with the other cover types present but with little area devoted to them). Criteria that speak to all aspects of diversity should be part of any screening process.
Ecological Considerations:
This is where we discuss the design of the site, its strengths and weaknesses and potential problems that may arise during planning. Ecological considerations include; size, shape, buffering capacity from adjacent land use activities, watershed location and linkage to the larger landscape. Generally speaking the following are some rules of thumb;
- larger sites are preferred over smaller sites because of their greater potential for ecological diversity and stability
- rounder sites are better than elongated sites for they have more intact core and can buffer adjacent land use activities better than elongated site
- sites that contain headwaters have more control over environmental inputs than sites located down stream
- biological boundaries that are linked to larger undisturbed lands are better than cultural boundaries such as roads or railway lines that sever the site from its larger landscape for long periods of time. Cultural boundaries are preferred over vector boundaries that can divide or fragment core protected areas
So by looking at the size, shape and location of a site with respect to its larger environment, planners may be able to address specific screening criteria. Such screening criteria could include; affect water quality or quantity, affect on fish and wildlife habitat and linkages, affect of drainage, sedimentation and erosion, potential long term planning problems because a site is very small in size or linear in shape, etc.
Special features:
Of all the data that is collected within a site, the special features section may be the most easily understood values. Generally landscape and habitat values are mentioned under the representation section of the check-sheet with specific values such as; Old Growth, Species at Risk (SAR), colonial birds, moose aquatic feeding areas, raptor nests, etc. are presented within this section. Data are available from FMP's or NRVIS databases as well as fish and wildlife files and reports and know recreation values available from District staff. The Class EA screening criteria contains a number of these values.
Note: Within the check-sheets be sure to review the significance level, recommendations and associated documentation listed with any particular check-sheet. For more information on check-sheet development see J.E. Thompson, 2001. Life science check-sheets information template. OMNR internal report. 6pp.
Future ongoing analysis on the site:
If during planning specific information is not available to complete impact assessment analysis, then SCI's should not the information gap and document the need to collect the required information in the future. In addition, future inventory, monitoring, assessment and research within the Conservation Reserve may also help planners and managers deal with future uses and impact assessments.
Appendix C: Public and Aboriginal Consultation Summary
1. Site name and proposed size (ha):
Kawawia Lake Old Growth (82 ha.)
2. Land Use Strategy Area #:
Conservation Reserve C195
3. MNR District:
Sudbury District
4.0 Public and Aboriginal consultation
4.1 Public consultation
Details of public consultation:
- District Manager letter was sent in October 2001 letting stakeholders know that planning was commencing for the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserve and to notify us know by mail or phone if they were interested in being contacted when the draft SCI was ready for public review. Adjacent landowners, municipalities and other groups or individuals who may have had an interest in the site were contacted, including the following breakdown:
- Ministry of Municipal Affairs and Housing
- Nickel District Conservation Authority
- Domtar Incorporated
- Ministry of Northern Development and Mines
- Ministry of Transportation
- Local Service Board of Cartier
- Bell Canada
- City of Greater Sudbury
- Spanish Forest Local Citizen’s Committee
- Inco Limited
- Partnership for Public Lands
- 61 interested individuals and/or adjacent landowners
- Newspaper advertisement in October 2001 asking the public to notify us if they are interested in being on the mailing list for review of the draft S The ad appeared in the following papers:
- Sudbury Star
- Le Voyageur
- The following summarizes the number of responses received:
- 29 individuals and/or organizations would like to be notified when the draft SCI is for public review
- District Manager letter sent in September 2002 letting stakeholders know the draft SCI is ready for public review. Letters were only sent to the 29 individuals and/or organizations that asked to be notifie
- The following summarizes the number of responses received:
- 6 individuals and/or organizations requested copies of the draft SCI for review
Summary of significant issues:
No issues were raised.
Analysis of issues:
No issues were raised.
4.2 Aboriginal consultation
Details of Aboriginal consultation:
- District Manager letter sent in October 2001 to initiate consultation with First Nations on the planning on the Kawawia Lake Old Growth Conservation Reserv The letter was sent to the following:
- Ojibways of Sucker Creek
- United Chiefs and Council of Manitoulin
- Wikwemikong Unceded Nation
- Sheguiandah
- Zhiibaahaasing
- M'Chigeeng
- Whitefish Lake
- Sagamok Anishnawbek
- Sheshegwaning
- Wahnapitae
- Wauwauskinga
- The following summarizes the number of responses received:
- 1 band member from Whitefish Lake First Nation notified MNR that she would be interested in reviewing the draft SCI
- District Manager letter and a copy of the draft SCI was sent in July 2002 to the following First Nations for comments:
- Ojibways of Sucker Creek
- United Chiefs and Council of Manitoulin
- Wikwemikong Unceded Nation
- Sheguiandah
- Zhiibaahaasing
- Union of Ontario Indians
- M'Chigeeng
- Whitefish Lake
- Sagamok Anishnawbek
- Sheshegwaning
- Wahnapitae
- Wauwauskinga
- The following summarizes the number of responses received:
- 12 Verbal (phone conversations initiated by MNR)
- District staff met with:
- Chief of the Ojibways of Sucker Creek (S 12/02)
- Lands technician from Sagamok Anishnawbek (S 30/02)
- Robinson-Huron Chiefs (Oct. 16/02)
- Director of Sustainable Development for Wahnapitae First Nation (Nov. 1/02)
- Chief of Wikwemikong (Nov. 14/02)
- Chief of Sheshegwaning (Dec. 3/02)
- Lands technician from Whitefish Lake First Nation (Jan. 10/03)
- Lands technician from Wikwemikong First Nation (Feb. 11/03)
- The Chief of Ojibways of Sucker Creek met with MNR staff on September 12, 2002 to discuss OLL. He expressed no concern with the sites being planned for this year for his community but knew there would be an impact at the treaty level. He mentioned that he would speak to the Union of Ontario Indians (UOI) to see if they could provide us with support on OLL. We never heard anything from UOI
- The Chief of McChigeeng First Nation was contacted by telephone on October 15, 2002 he discussed with Suzanne Arsenault the planning of this year’s OLL sites. He was not concerned with any of them
- Zhiibaahaasing was contacted by telephone on September 23, 2002 and October 10, 2002 to discuss OLL. The lands technician mentioned he had reviewed the packages sent to the community by MNR and would contact us if the Chief wanted to meet. Despite our attempts no meeting has been scheduled to date
- Wikwemikong Unceded Nation was contacted by telephone on November 4, 2002 to discuss OLL. At that time we were informed that the Chief would be meeting with our DM the next week. Cindy Blancher-Smith and Bruce Richard met with the chief November 14, 2002 and discussed broadly the projects MNR Sudbury is involved in and how they could participate. The lands specialist met with MNR staff on February 11, 2003 to discuss OLL. A brief overview of OLL was given. He requested that a package be sent to him with a map of all OLL sites in the district, a status list of the sites and a summary of past consultation with his community
- Wauwauskinga was contacted by telephone on October 10, 2002 and December 9, 2002 to discuss OLL. The lands tech will be speaking to Chief and Council about OLL and will let us know if they want to meet us. Despite our attempts no meeting has been scheduled to date
- Sagamok Anishnawbek met with MNR staff on September 30, 2002 to discuss OLL. The lands technician mentioned the community would not be interested in the planning of this year’s sites but it is part of the area where they traditionally hunt, fish and collect herbs
- Sheguiandah First Nation was contacted by telephone on October 1, 20 The Chief said he would look at the packages sent to him and contact us if he would like to meet. Despite our attempts no meeting has been scheduled to date
- Sheshegwaning First Nation was contacted by telephone on September 10, 2002 about OLL. A meeting was scheduled. December 3, 2002 a meeting was held between MNR representatives and the Chief. He did not want to discuss OLL, he was upset with the consultation process to date with respect to the project. He felt OLL was infringing on aboriginal treaty rights
- Wahnapitei First Nation was contacted by telephone on September 12, 2002 to discuss OLL, a meeting was arranged. MNR staff met with the Director of Sustainable Development on November 1, 2002 to discuss OLL. He had an interest in reviewing 2 of this year’s SCIs for C213 and C166
- Whitefish Lake First Nation was contacted by telephone on Nov. 1, 2002 to discuss OLL. The lands technician met with MNR staff January 10, 2003 to discuss OLL. He had no interest in the planning of this year’s sites
- The Robinson-Huron Chiefs (15 of 19 attended) held a meeting on October 16, 2002 and MNR Sudbury was invited to present all projects in treaty area within the next year. OLL was one of the projects mentioned and there was discussion on the project
Summary of significant issues:
- First Nations do not consider any contact with MNR consultation
- First Nations feel the OLL process is fl They believe that decisions are already made before consultation begins
- First Nations feel the OLL process does not respect native culture and their rights
Analysis of issues:
None of the above issues can be dealt with through the planning exercise.
It is our understanding that the policies which have been developed (and which are fundamentally disagreed with) are not up for further negotiation.
5.0 Recommendations:
Recommend that the statement of conservation interest be approved as the management direction for the conservation reserve.
6.0 Approval of consultation documentation
MNR District Contact Person:
Natalie Avoledo
OLL Planner
Phone: (705) 564-7612
Fax: (705) 564-7879
Ontario Parks Contact Person:
N/A
Cindy Blancher-Smith
District Manager
Sudbury District
Date March 2003
Ontario Parks Contact Person:
N/A
Appendix D: Statement of Conservation Interest Amendments
Footnotes
- footnote[1] Back to paragraph Bog: Peatland with water table at or near the surface with surface often rising above surrounding terrain. Sites are strongly acid and nutrient poor. Bogs contain peat accumulations of more than 40 centimetres deep. Species include Sphagnum spp. or Peat Mosses and ericaceous shrubs including Bog Rosemary (Andromeda glaucophylla), Leatherleaf (Chamaedaphne clayculata), Creeping Snowberry (Gaultheria hispidula), Bog Laurel (Kalmia polifolia), and Labrador Tea (Ledum groenlandicum) (Harris et. al. 1996).
- footnote[2] Back to paragraph Fen: Peatland with water table at or above the surface with very slow water movement through communities via seepage that results in a more mineral, nutrient and oxygen-rich environment than bogs. Generally fens contain peat accumulations greater than 40 cm deep. Sometimes floating mat with sedges, mosses, shrubs, and sparse tree layer present. Indicator plants include: Larch (Larix laricinea) and Eastern White Cedar (Thuja occidentalis) or Black Spruce (Picea mariana), Speckled Alder (Alnus incana), Dwarf Birch (Betula pumila), Bluejoint Grass (Calamagrostis canadensis), assorted sedges, Sweet Gale (Myrica gale) with ericaceous shrubs present – especially in more nutrient poor fens (Harris et. al.1996).
- footnote[3] Back to paragraph Proterozoic relates to the later part of the Precambrian Era, characterized by the oldest forms of life.
- footnote[4] Back to paragraph Granite is a course-grained igneous or fire-formed rock composed mostly of minerals including: quartz, mica, feldspar, etc.
- footnote[5] Back to paragraph Greenstone is an igneous rock containing feldspar and hornblende.
- footnote[6] Back to paragraph Gneiss is a course grained metamorphic rock.
- footnote[7] Back to paragraph Alluvium is defined as a deposit of fertile soils left during a time of flooding and is generally associated with river valleys or delta areas.
- footnote[8] Back to paragraph Luvisols are well to imperfectly drained mineral soils that have developed under the influence and growth and decomposition of forest vegetation in mild to cold climates. Their main characteristics are a light colored eluvial or leached Ae horizon and an illuvial or zone of accumulation textural B horizon (Clayton et. al.1977).
- footnote[9] Back to paragraph Terrestrial diversity is defined on the basis of the 14 Eco-Regions and 67 Eco-Districts of the province which were classified by Hills (1959) and further modified by Crins and Uhlig (2000). An Eco-District is a distinctive physiographic area found within the Eco-Region. Each of the Eco-Districts contains landform patterns and biological productivity traits that distinguish it from the other Eco-Districts. In each Eco-District, smaller landscape units are defined, based on recurring landform patterns. These patterns, and the vegetative communities and species that they support, constitute the biological systems and values to be represented (MNR 1997c).