Common weeds poisonous to grazing livestock
Identify the common weeds in Ontario that can poison livestock.
Introduction
Livestock can be poisoned or injured by certain plants while grazing or fed in stored feed. The OMAFRA fact sheet "Poisoning of Livestock by Plants", Agdex 130/643, reviews the types of poisoning which can occur and the effects on animal health and production.
Many common weeds in Ontario can poison livestock. This fact sheet identifies these weeds and describes the symptoms of poisoning. Because some poisons act very fast (as with the hemlocks) by the time the symptoms are evident, the chances of saving the animal are very slight. It is, therefore, important to learn to recognize these weeds beforehand and prevent poisoning from occurring. Most of these weeds can be controlled chemically or mechanically. In some cases, it may be more practical to simply fence off infested areas so that the animals do not have access to particularly hazardous weeds.
It should be noted that most of these weeds are unpalatable and animals will usually not graze them if given the choice. One of the most important steps in preventing animal suffering or loss is good pasture management. Keeping the desirable forage species producing throughout the grazing season, reduces the possibility of animals grazing poisonous weeds.
If symptoms of poisoning should occur, it is recommended that you call your veterinarian as soon as possible.
Common weeds poisonous to grazing livestock
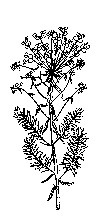
Poison Hemlockfootnote 1 (Conium maculatum)
- Where generally located
- waste areas
- road sides
- dry ditches
- Livestock affected
- cattle
- horses
- sheep
- goats
- Symptoms
- death may occur within 15 minutes
- frothing at the mouth
- uneasiness
- pain
- dilated pupils
- clamping of jaws
- grating of teeth
- vomiting
- weak, rapid pulse
- diarrhea
- bloating
- convulsions
- respiratory failure
- death
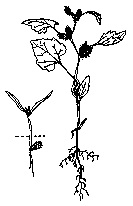
Water Hemlockfootnote 1 (Cicuta maculata)
- Where generally located
- wet pastures
- stream banks
- pond edges
- lake edges
- wet ditches
- edges of wet woods
- Livestock affected
- cattle
- horses
- sheep
- goats
- Symptoms
- death may occur within 15 minutes
- frothing at the mouth
- uneasiness
- pain
- dilated pupils
- clamping of jaws
- grating of teeth
- vomiting
- weak, rapid pulse
- diarrhea
- bloating
- convulsions
- respiratory failure
- death
Bracken Fern
footnote 1 (Pteridium aquilinum)- Where generally located
- open fields
- woodlands
- low ground
- dry, rocky soil
- Livestock affected
- horses
- cattle
- sheep
- Symptoms
- Horses:
- symptoms are slow to develop
- loss of flesh
- jaundice
- loss of appetite
- weakness
- staggering gait
- excitability
- paralysis
- Cattle and sheep:
- symptoms are slow to develop
- high fever
- labored breathing
- drooling
- hemorrhaging from nostrils
- blood in urine and feces
- convulsions
- Horses:
Marsh Arrow-Grass (Triglochin palustris)
- Where generally located
- marshes
- alkaline soils
- Livestock affected
- cattle
- sheep
- Symptoms
- symptoms appear rapidly
- rapid, difficult breathing
- almond odor to breath
- animals go down with head turned to one side
Horsetailfootnote 1 (Equisetum arvense)
- Where generally located
- poorly drained soils
- low, sandy, acid soils
- cultivated fields
- roadsides
- waste areas
- woods
- Livestock affected
- horses
- cattle
- sheep
- Symptoms
- symptoms are slow to develop
- jaundice
- loss of appetite
- weakness
- staggering gait
- excitability
- paralysis
Pokeweedfootnote 1 (Phytolacca americana)
- Where generally located
- (southern Ontario only)
- waste areas
- meadows
- edges of woods
- Livestock affected
- cattle
- Symptoms
- symptoms occur two or more hours after plants are eaten
- retching spasms
- vomiting
- purging
- convulsions
Marsh Marigoldfootnote 1 (Caltha palustris)
- Where generally located
- wet areas
- Livestock affected
- cattle
- Symptoms
- acute inflammation of the gastro-intestinal tract
- vomiting
- colic
- bloody urine
- diarrhea
- twitching of the eyelids
- weak pulse
- loud breathing
- reduce milk production
- tainted milk red in colour and bitter tasting
Tall Buttercupfootnote 1 (Ranunculus acris)
- Where generally located
- pastures
- meadows
- roadsides
- Livestock affected
- cattle
- horses
- sheep
- goats
- Symptoms
- inflammation and blisters where plant juice touched the animal
- mouth blisters cause drooling and loss of appetite
- other symptoms similar to those for marsh marigold
Wild Cherries Black (Prunus virginiana)
- Where generally located
- fence rows
- open woods
- Livestock affected
- cattle
- Symptoms
- same as with march arrow-grass poisoning
Lupine (Lupinus polyphyllus)
- Where generally located
- pastures
- meadows
- roadsides
- waste areas
- Livestock affected
- sheep
- cattle
- horses
- Symptoms
- nervousness
- labored breathing
- convulsions
- frothing at the mouth
- frenzy
- aimless running about
Saint-John's Wortfootnote 1 (Hypericum perforatum)
- Where generally located
- roadsides
- pastures
- Livestock affected
- horses
- cattle
- Symptoms
- photo-sensitivity
- inflammation of the unpigmented portion of the skin
- affected area becomes sore and reddened and may peel
- tongue and mouth may be affected
Nightshadefootnote 1 (Solanum sp.)
- Where generally located
- open dry woods
- cultivated fields
- pastures
- fence rows
- waste areas
- farm yards
- Livestock affected
- cattle
- horses
- sheep
- goats
- Symptoms
- abdominal pain
- stupidity
- dilation of pupils
- loss of appetite
- diarrhea
- loss of muscular coordination
- unconscious
- death
Jimsonweed (Datura stramonium)
- Where generally located
- cultivated fields
- farm yards
- Livestock affected
- cattle
- horses
- sheep
- goats
- Symptoms
- dilation of the pupils
- impaired vision
- fast, weak pulse
- nausea
- loss of muscular coordination
- violent, aggressive behaviours
- trembling
- milk is tainted
Milkweedfootnote 1 (Asclepias sp.)
- Where generally located
- dry, open areas
- pastures
- around woods
- roadsides
- waste areas
- cultivated fields
- Livestock affected
- cattle
- sheep
- horses
- Symptoms
- Cattle and sheep:
- loss of appetite
- constipation
- drooling
- excitable
- difficult breathing
- rapid, weak pulse
- convulsions
- death
- Horses:
- persistent colic
- Cattle and sheep:
Cocklefootnote 1 (Saponaria officinalis)
- Where generally located
- pastures
- cultivated fields
- roadsides
- waste areas
- Livestock affected
- horses
- cattle
- Symptoms
- restlessness
- grinding of teeth
- drooling
- colic
- diarrhea
- rapid breathing
- weak pulse
- coma
- death
Laurel (Kalmia sp.)
Sheep Pale or Bog
- Where generally located
- bogs
- wet evergreen woods
- Livestock affected
- cattle
- sheep
- goats
- Symptoms
- drooling
- watery eyes
- runny nose
- vomiting
- complete or partial blindness
- drowsiness
- convulsions
- paralysis
Tansy Ragwortfootnote 1 (Senecio sp.)
- Where generally located
- pastures
- hayfields
- waste areas
- roadsides
- Livestock affected
- horses
- cattle
- Symptoms
- nervousness
- chills
- pale mucous membranes
- loss of coat lustre
- strong, rapid pulse
- high temperature
- staggering gait
- weakness
- death
Spurgefootnote 1 (Euphorbia sp.)
Cypress Leafy
- Where generally located
- cultivated fields
- waste areas
- roadsides
- Livestock affected
- horses
- goats
- cattle
- sheep (leafy is non toxic to sheep)
- Symptoms
- Contact with sap:
- causes inflammation of skin
- Eating causes:
- diarrhea
- vomiting
- swelling around mouth and eyes
- abdominal pains
- muscle tremors
- sweating
- tainted milk has reddish colour, bitter taste
- Contact with sap:
White Snakeroot (Eupatorium rugosum)
- Where generally located
- wooded areas
- persists after woods are thinned out
- stream banks
- Livestock affected
- horses
- cattle
- goats
- sheep
- Symptoms
- Horses, cattle and goats:
- depression
- inactivity
- arched body
- hind feet place close together
- excessive salivation
- nasal discharge
- nausea
- rapid, labored breathing
- Sheep:
- above, except sheep stand with legs apart
- Horses, cattle and goats:
Cockleburfootnote 1 (Xanthium chinensis)
- Where generally located
- cultivated fields
- stream banks
- beaches
- farm yards
- Livestock affected
- horses
- cattle
- sheep
- Symptoms
- symptoms appear within a few hours
- weakness
- unsteady gait
- twisting of neck muscles
- depression
- nausea
- vomiting
- labored breathing
- rapid, weak pulse
- death
Sneezeweed (Helenium automnale)
- Where generally located
- wet areas
- roadside ditches
- stream banks
- Livestock affected
- cattle
- horses
- sheep
- Symptoms
- symptoms are slow to develop
- loss of vigor
- loss of flesh
- rapid pulse
- labored breathing
- loss of muscular control
- drooling
- high temperature
- dizziness
- spasms
- convulsions
Squirrel Corn/Dutchman's Breeches
(Dicentra sp.)
- Where generally located
- wooded areas (maple woods)
- Livestock affected
- cattle
- Symptoms
- symptoms develop 48 hours after plants are eaten
- trembling
- frothing at the mouth
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- labored breathing
- convulsions