Discover Indigenous culture and history along the TransCanada Trail
Dotted along Ontario’s TransCanada Trail are 25 educational trail markers honouring the culture and history of Indigenous peoples in Ontario. You can visit the markers in person or online through our interactive map below.
From Fort Erie to Midland to Pickering, you can read stories about Indigenous people and their lives, told in their own words.
The Aboriginal Leadership Partners Group and the Native Canadian Centre of Toronto worked with Indigenous communities and organizations, municipalities and land owners on the design and installation of the markers.
Highlights
Some of the markers tell stories that date back as far as the 1300s and recount Indigenous people’s agricultural, economic and cultural history. Some highlights:
- Mississaugas of the New Credit First Nation. The Mississaugas became known as the “good credit Indians” due to good business practices and the site took on their name: Credit Mission Village.
Read more from the marker. - Huron-Wendat Nation. Villages had to be moved every 10 to 15 years as soil became less fertile and firewood became scarce. The bones of ancestors who had died there were respectfully unearthed, then reburied together so ancestors could remain together, as in life, connected in a new community.
Read more from the marker. - Métis Nation of Ontario. The first Métis families – made up of French fur trader fathers, First Nations mothers and their mixed-ancestry children – developed in the second half of the 1600s. After the War of 1812, they began to settle in the Midland area to try their hand at farming.
Read more from the marker. - Six Nations of the Grand River. Since the 1850s, Haudenosaunee (pronounced “ho Dee no show nee,” meaning “people of the longhouse”) men have traveled far and wide to help build the tallest structures in North America including the CN Tower and the first World Trade Center. Today there are roughly 3,500 ironworkers in Ontario, 500 of which are Haudenosaunee.
Read more from the marker.
Interactive map
Click around the map to learn more. If you’d rather learn along the TransCanada Trail, pull up the map on your smartphone to guide your journey.
Full text of the markers
Huron-Wendat Markers
-
Dunsmore – Ancestral Huron-Wendat Settlement
Location: Arboretum Sunnindale Park, Barrie

This is a reconstructed ceramic vessel typical of the types found at the Dunsmore Site. The designs on the collar and neck portions of the vessel are used by archaeologists to date the site and to identify the ethnic affiliation of their makers. The Dunsmore site is a two-hectare, mid- to late fifteenth century unpalisaded ancestral Huron-Wendat settlement that had a complex history.
The site may have included both seasonal tenancies and year-round occupations. The settlement appears to have served as both a seasonal fishing camp and a semi-permanent agricultural village, perhaps involving members of several different communities. Sixteen houses of various sizes were recorded.
The growing of corn was the major economic activity and women planted, tended and harvested the crops. Corn could contribute as much as 60% of the diet of the Huron-Wendat people. It was eaten in soup or roasted over fire. It was used to make bread (or bannock) for local consumption or during long-distances travels. In such journeys, corn was also used in trading for other goods such as hides, fish, meat and tobacco.
-
Holly – Ancestral Huron-Wendat Village
Location: Huronia Park, Barrie
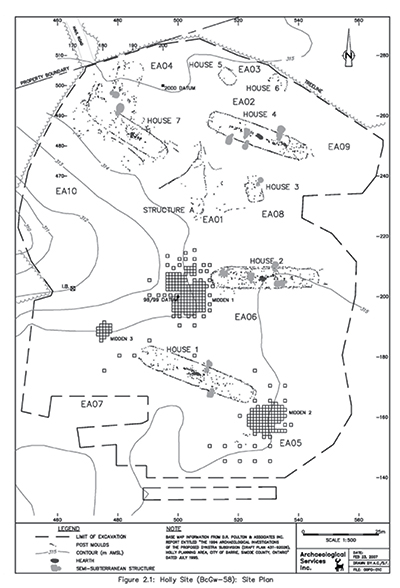
Photo: Courtesy of Archaeological Services Inc. The Holly site is one of a series of Huron-Wendat villages and special-purpose sites found within a 25 km2 area in southern Barrie.
The investigations of these sites have provided a significant opportunity for examining one or perhaps two communities moving through time. It also presented an occasion to investigate rarely observed components of ancestral Huron-Wendat settlement-subsistence systems as two other nearby sites (Wellington and Dykstra) are not base settlements or villages but serve some other function.
Holly includes at least four major longhouses showing substantial long-term domestic use and extensive re-building, possible special purpose structures, several large middens, and multiple exterior house rows of posts and associated features. As with some of the other major ancestral Huron-Wendat sites in southern Simcoe County, such as Wiacek, Hubbert and Dunsmore, no surrounding palisade was found, suggesting that these sites were occupied during a peaceful period in the fourteenth century.
-
Miller – Ancestral Huron-Wendat Village
Location: Pickering
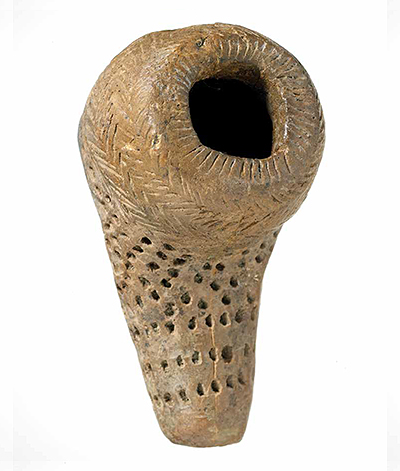

This pipe was found at the Miller site and is the most ornate from the site. Extending about halfway down the bulbous bowl is a very fine herring-bone pattern; below this, and covering the stem is an irregular pattern of punctations. The Miller site was excavated in the 1950s by the Royal Ontario Museum and is a palisaded thirteenth century village consisting of six longhouses.
The structures ranged in size from 45.0 feet to 60.3 feet in length and from 20.6 feet to 27.0 feet in width. An irregular palisade was also recorded at the site, but no positive evidence of a gate or entrance to the village was found.
Life was not always easy for the Huron-Wendat. Such fortified villages were more common as violent conflict increased. By the early to mid-seventeenth century, the Iroquois, the historical enemies of the Huron-Wendat, were allied with the English, while the Huron-Wendat were allied with the French. Sporadic attacks by enemies led to the construction of palisades and earthwork complexes in easily defendable villages on top of slopes due to an ongoing concern for communal defense.
-
Turnbull – Ancestral Huron-Wendat Ossuary
Location: Simcoe County
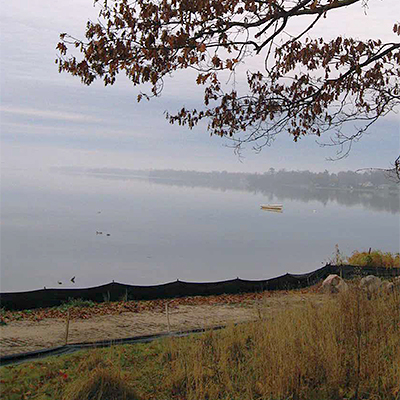

The ossuary was situated overlooking the shore of Lake Couchiching, which had been home to the ancestors in the ossuary. The site is protected under the Ontario Heritage Act. Turnbull is a fourteenth or fifteenth century Huron-Wendat ossuary encountered as a result of earthmoving activities relating to the construction of a residential subdivision.
Ossuaries of this size have been known to contain the secondary remains of 200 to 400 individuals. Ossuary burial is a practice characteristic of the Huron-Wendat culture and cosmology.
Generally, an ossuary was created when a village had to be moved every 10 to 15 years due to decreasing fertility of surrounding soils and increasing difficulty in finding firewood. Ancestors who had died during the occupation of the village were respectfully unearthed and then reburied all together and commingled within the ossuary. The purpose of this sacred form of burial practice was that ancestors would remain together, as they had in life, connected forever in a new community.
-
Wiacek – Fourteenth Century Ancestral Huron-Wendat Village
Location: Barrie
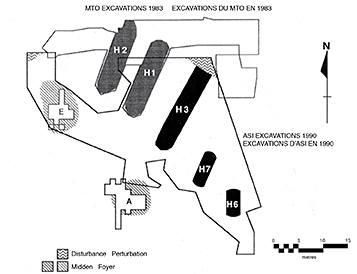
Limits of 1983 MTO and 1990 ASI excavations at the Wiacek site. The Wiacek site is an ancestral Huron-Wendat village located in the southern outskirts of the City of Barrie.
The site was partially excavated by the Ministry of Transportation in 1983. Additional excavations were undertaken at the site in 1990 in advance of the proposed construction of a subdivision. In total, seven longhouse structures were found at the site. Radiocarbon dates and the designs on ceramic vessels indicate an occupation in the mid- fourteenth century.
Huron was a name given by the French meaning “boar’s head” in reference to their hairstyle. Wendat is how they called themselves, meaning the “People of the Island.” The Huron-Wendat lived in bark-covered longhouses in villages sometimes surrounded by palisades. Matrilineal families and strong clans were guided by a great diplomatic tradition and their ability to achieve compromise.
-
Sebastian – Ancestral Huron-Wendat Site
Location: Pickering

This shell of a turtle was found on the surface of a pit that had been excavated during an educational archaeology program. It was probably discarded during its processing for food although turtle shells were used for adornment and to make rattles. Preliminary investigations of the ancestral Huron-Wendat Sebastien site yielded a total of 2,246 artifacts, which represent only a sample from the periphery of the site.
The site dates to the early thirteenth century. Artifacts recovered from archaeological sites are often key to understanding the vital trade and commerce of the Huron-Wendat people. Exotic artifacts help us to recognize their enduring connections with distant nations. Marine shell, for example, from the east coast, copper from the Lake Superior basin, iron from Basque whaling stations and walrus ivory from the Gulf of St. Lawrence all reveal fascinating long-distance contacts for the Huron-Wendat.
Other artifacts help us learn about their lifeways, for example, animal bones reflect hunting and fishing practices and their contribution to the economy. Other artifacts relate to their clothing and adornments. The Sebastian site has recently been home to Toronto and Region Conservation Authority educational and public archaeology programs.
-
Midland
Location: Huronia Park, Midland

Fort Mackinac, Michigan by Seth Eastman Midland and area were home to several First Nation communities prior to the appearance of French explorers early in the seventeenth century.
Jesuit priests subsequently founded a Roman Catholic mission in 1639, Sainte-Marie, which was the first European settlement to be established west of the pioneer communities in the St. Lawrence Valley. After increasing attacks from the Five Nations, the Jesuits and their followers burned the mission and abandoned it.
In the second half of the seventeenth century families were formed by French fur trader fathers, First Nations mothers, and their mixed-ancestry offspring. It was not until after the War of 1812, however, that these Métis families began to settle in the Midland area along with others who migrated from Drummond Island and Mackinac Island to try their hand at farming.
Mississaugas of the New Credit First Nation Markers
-
Don River – Former Don River Settlement
Location: Toronto

Watercolour painting of the Don River 1793 by Caroline Simcoe The Don River flows from headwaters on the Oak Ridges Moraine.
“Wonscotonach”, the Anishinaabe place name, likely translates to “burning bright point” and may refer to the practice of torchlight salmon spearing. The Mississauga had a seasonal settlement here, where they fished and hunted the marshlands for muskrat, duck and deer. This settlement fell into disuse as the Mississaugas moved westward to a newly established permanent village at the River Credit. Most archaeological evidence of the Mississaugas on this site has been destroyed. The river was essential to the Mississaugas as it connected with trail systems that are followed by present day Yonge Street, the gateway north.
-
Niagara Treaty
Location: Fort Mississauga, Niagara-on-the-Lake

Reproduction of 1764 Treaty of Niagara Covenant Chain Wampum Belt The Niagara Treaty of 1764, entered into by the British and a number of Indigenous Nations, extended the “Covenant Chain” alliance between the British Crown and the Iroquois in eastern North America to other First Nations in the north and west.
A series of treaty discussions took place in 1764 at Niagara, including a great congress in July 1764 that involved more than 2,000 British, Crown and Aboriginal participants. Members of the Iroquois Confederacy, the Mississauga/Algonquin, and the Huron Nations were among the participants. Today, the resulting arrangements between the Crown and First Nations are viewed by First Nations as involving an enduring promise of mutual support and respect.
The Niagara Treaty was entered into at Fort Niagara, which stood directly across the Niagara River from Fort Mississauga. The Treaty was consummated with the exchange of traditional “Wampum Belts”, woven with small beads, which conveyed the spirit and meaning of the agreement. The treaty proceedings at Niagara in 1764 were instrumental in establishing an enduring relationship of peace and friendship between the British Crown and Great Lakes First Nations that previously had been allied with the French.
-
Mouth of the Humber – Toronto Carrying-Place Trail
Location: Humber River, Toronto
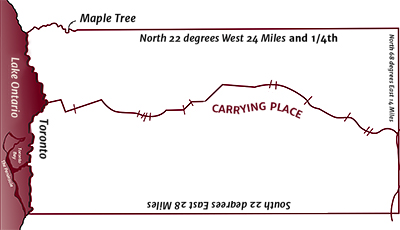
Toronto Carrying-Place Trail within boundaries of 1805 Toronto Purchase The Toronto Carrying-Place Trail was a major portage route, linking Lake Ontario with Lake Simcoe and the northern Great Lakes.
It was a convenient trail for hunters, traders, explorers, missionaries and native community members.
The Anishinaabe people in south and central Ontario won many battles against the Iroquois in the Beaver Wars. The victories forced the Iroquois to return to their traditional lands in what is now upstate New York. After a successful French-led expedition against a Seneca village on the Humber in 1687 or 1688, the Mississaugas built a seasonal village on the west bank of the river and used it for summer hunting, fishing and farming. In the winter, the Mississaugas would move north along the Carrying-Place Trail to hunt for food and furs.
By the mid-1800s, encroaching settlements disturbed this balanced, seasonal way of life and pressured the Mississaugas to relocate.
-
Credit River – Former Credit Mission Village
Location: JC Saddington Park, Mississauga

In 1826, the government built a village for the Mississaugas on their traditional lands on what is now the upper portion of the golf club property overlooking the Credit River Valley.
The village began as 20 dressed-log houses including a combined chapel and schoolhouse. The Mississaugas of the Credit Mission buried their dead at an unknown location under the present golf course.
The Credit Mission Village prospered and by the late 1830s there were nearly 50 houses with some 500 acres under cultivation. In addition, they owned and operated two sawmills and a schooner. They were known as the “good credit Indians” due to good business practices and the site took on their name.
Settlement pressures and an inability to secure title to the lands they occupied led to the Mississaugas moving from the Credit Mission Village in 1847 to their present day location in Brant/Haldimand County.
-
Dundurn Castle/Burlington Heights
Location: Dundurn Park, Hamilton
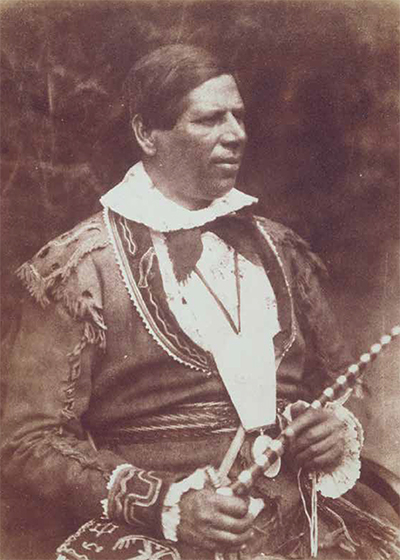

Portrait of Kahkewaquonaby (Reverend Peter Jones) The Mississaugas (Anishinaabe Peoples) have lived in the Niagara and Great Lakes region since the late 17th century.
Known as Head-of-the-Lake on the North shore of Lake Ontario, this site was a strategic communication and trade junction. A trading post established by Colonel Richard Beasley became a key location of trade for the Mississaugas who established a permanent settlement nearby. Dundurn Castle now stands in this location.
In 1802, Mississauga Chief and Methodist Missionary the Reverend Peter Jones was born on the Heights. Jones worked tirelessly to promote Christianity among his people and helped them adapt to an increasingly dominant non-native world. The Heights had a military function during the War of 1812, in which the Mississaugas participated.
-
Toronto Islands
Location: Toronto
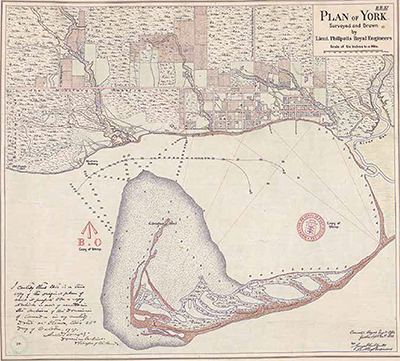
Plan of York surveyed and drawn by Lieut. Phillpotts Royal Engineers, 1818 The Mississaugas’ traditional lands are located in southern Ontario.
They spent their summers on these lands near the mouths of rivers and streams and on these Toronto Islands. The Toronto Islands were originally a long peninsula named “Menecing”, which translates “On the Island”.
The peninsula was a series of connected sand spits that held spiritual significance for the Mississaugas. The long beach was considered a place of healing and the Mississaugas brought their sick here to recuperate. Early references speak to the healthy atmosphere and the “peculiarly clear and fine” air of the peninsula. In addition to its restorative power, the peninsula was used for numerous ceremonial purposes including childbirth and burials.
In the 1850s, a series of storms disconnected the body of the peninsula from the mainland and led to the creation of the Toronto Islands as they exist today.
-
Brant’s Ford on the Grand River
Location: Brant’s Crossing, Brantford
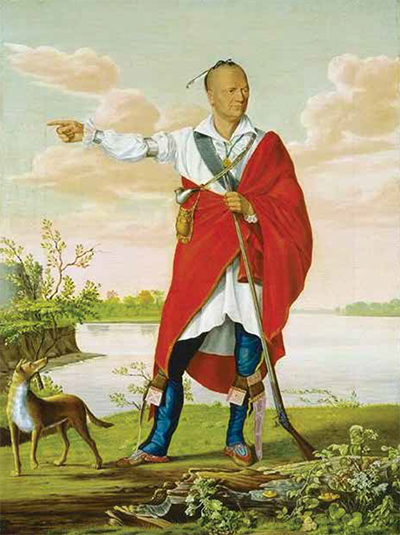

Thayendanegea (Joseph Brant), c. 1807 by William Berczy Following the American Revolution, some of the Haudenosaunee, (the people of the longhouse) commonly referred to as Six Nations or Iroquois, relocated to the Haldimand Tract along the Grand River from New York in 1784.
A Mohawk Village comprised of 400 inhabitants, log cabins, a long house and chapel was established near a shallow part of the Grand River which was used as a safe crossing point. It was named Brant’s Ford, later Brantford, after Joseph Brant, an important Mohawk military and political leader.
In 1813, Brant’s son, John, led a small contingent of warriors, aided by some British troops, and turned back an American advance that threatened to destroy the Mohawk Village. Today,
Her Majesty’s Royal Chapel of the Mohawks, now Ontario’s oldest Protestant church (built in 1785) is all that remains of the settlement that once stood here. The Mohawk Institute, a notorious residential school in operation from 1831 to 1970 also stands close to the site of the village.
-
Six Nations of the Grand River
Location: Brantford
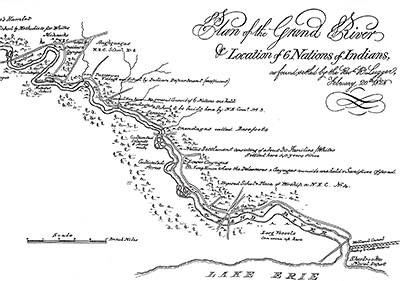
Grand River 1828 Members of the Haudenosaunee, (the people of the longhouse) commonly referred to as Six Nations and Iroquois, who allied themselves with the British during the American Revolution, faced persecution in the years that followed the establishment of the United States government.
In 1784, as a result of petitions to the Crown, Sir Frederick Haldimand, the Governor of Quebec (1778-1786), issued a proclamation that authorized the “Mohawk Nation and such others of the Six Nation Indians” to settle on a tract of land along the Grand River, “six miles deep from each side of the river” from Lake Erie to its head. About 2,400 Six Nations people relocated to the Grand River from their homeland in upstate New York.
Today, the Six Nations of the Grand River Territory has the largest First Nation population in Canada.
-
Indian Council House at Niagara
Location: Paradise Grove Park, Niagara-on-the-Lake

Council House becomes Fort George Hospital Near this place stood a Council House measuring 72’ by 26’ where Crown representatives met with Native leaders to bolster their treaty relationship.
Originally, the “King’s Fire” (the fire lit on behalf of the king at the meeting place between the British and their Native allies) was kindled near Albany, New York. The “King’s Fire” was moved to Fort Niagara during the American Revolution, and relocated here in 1797.
In 1812, leaders of the Haudenosaunee, (the people of the longhouse) commonly referred to as
Six Nations and Iroquois, held a Condolence Ceremony at Council House for Major General Isaac Brock and Lieutenant Colonel John Macdonell who were killed in action at Queenston Heights.
In 1813, the Council House was burnt by retreating American Forces and was rebuilt in 1815.
Following the relocation of the capital of Upper Canada to York in 1822, the Indian Department ended use of the Council House and it was repurposed as a hospital.
-
Native Trail Networks
Location: Hamilton
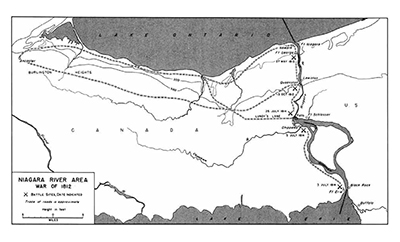
Niagara Trails 1812 According to Six Nations oral tradition, many major roads in southern Ontario are built upon ancient paths created by Native hunters, traders and diplomats.
These pathways connected the Native settlements to hunting grounds, trading posts, and forts. The most widely used was the Iroquois Trail, running along the base of the escarpment from Albany, New York, passing through Queenston and Ancaster and ending near Detroit, Michigan. The Mohawk Trail ran parallel, from St. Davids to Ancaster.
The Niagara River Trail started in Niagara-on-the-Lake and followed the Niagara River to the base of the escarpment at Queenston, connecting Lake Ontario to the Iroquois Trail. Another important pathway later became Plank Road, which is now Number 6 Highway. This pathway ran through the Six Nations reserve and connected favored fishing locations on Lake Ontario with Port Dover on Lake Erie. As you travel around the Golden Horseshoe, think of the ones who first walked these same routes.
-
High Steel Ironworkers
Location: Hto Park, Toronto
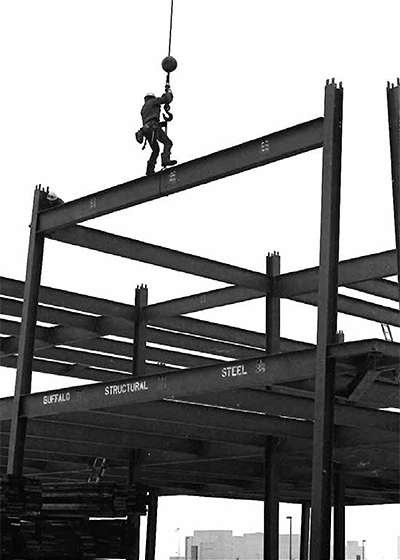

Russ Hill.
Photo by Rick HillConstructing steel skeletons for high-rise buildings or massive bridges became a specialty for many Haudenosaunee (people of the longhouse), commonly referred to as Six Nations and Iroquois, beginning in the 1850s with the Mohawks of Kahnawake and the construction of the Victoria Bridge in Montreal.
Following the collapse of the Quebec Bridge in 1907 and the deaths of 33 Haudenosaunee men, work was sought further afield. Since then, Haudenosaunee men have traveled far and wide to build the tallest structures in North America; many concentrating in New York City where up to 800 Mohawk ironworkers were employed. Haudenosaunee and Mi′kmaq ironworkers helped build both the first World Trade Center and the CN Tower. Today there are roughly 3,500 ironworkers in Ontario, 500 of which are Haudenosaunee. Next time you admire a tall skyscraper or the dramatic view from a big bridge, think of the Haudenosaunee ironworkers who made it possible.
Ontario Federation of Friendship Centres
-
Fort Erie Native Friendship Centre
Location: Mather Park, Fort Erie

In 1984, the Fort Erie Native Friendship Centre was recognized as the first Native Friendship Centre to acquire urban property without government capital assistance.
Since its beginnings, the Fort Erie Native Friendship Centre has served urban Aboriginal communities in and around Fort Erie, including Port Colborne, Welland, Wainfleet and Niagara Falls. More than 4,000 Aboriginal peoples reside in the region.
-
Hamilton Regional Indian Centre
Location: Gage Park, Hamilton

In 1972, a group of Aboriginal people established a temporary cultural centre, housed on Park St. South.
The people felt there was a great need for a “Gathering Place” in the Hamilton community. The area is home to over 15,000 people who identify as having Aboriginal ancestry.
The Hamilton Regional Indian Centre offers programs to all at all stages of the Life Cycle, delivered in a holistic manner and in ways that maintain and celebrate Aboriginal traditions and cultures.
-
Niagara Regional Native Centre
Location: Niagara-on-the-Lake
Since 1972, the Niagara Regional Native Centre has provided key supports in the development of the Aboriginal Community by working in unity to identify and address community needs.
This is done through leadership, advocacy within the larger community, and promoting a better understanding between Native and non-native people.
The Niagara Regional Native Centre serves the areas of St. Catharines, Niagara Falls,
Thorold, Grimsby, Lincoln, Niagara-on-The-Lake, Pelham, Wainfleet and West Lincoln, and has an Aboriginal population of over 7,000 members.
-
Peel Aboriginal Network
Location: Jc Saddington Park, Mississauga

Peel Aboriginal Network (“PAN”) started in 2006 as a gathering place for Indigenous people in the Peel region.
They opened their own cultural centre three years later and began providing programs and services to the Aboriginal community in the region.
-
Georgian Bay Native Friendship Centre & Barrie Native Friendship Centre
Location: Vas Kuchar Memorial Park, Midland

The Georgian Bay Native Friendship Centre and the Barrie Native Friendship Centre are members of the Ontario Federation of Indigenous Friendship Centres, a network of 28 urban Aboriginal service organizations.
Georgian Bay Native Friendship Centre is an award-winning organization, established in 1986, that serves urban Anishnabek peoples in surrounding towns and areas including Midland and Penetanguishene; Tiny Township; Tay Township; Coldwater; and Southern Georgian Bay including Honey Harbour and Port Severn. The region is home to more than 5,000 Aboriginal residents.
Since 1988, the Barrie Native Friendship Centre community has created a place for Aboriginal people to share culturally relevant stories, histories, language and food. The Barrie Native Friendship Centre serves a growing Aboriginal population that has grown eight-fold over the past 30 years.
-
Toronto Council Fire Native Culture Centre & Native Canadian Centre of Toronto
Location: The Toronto Inukshuk Park, Toronto

Toronto Council Fire and Native Canadian Centre of Toronto are prominent Aboriginal organizations mandated to serve the needs of Toronto’s Aboriginal community.
Located at 439 Dundas Street East, Toronto Council Fire Native Cultural Centre continues to maintain an important presence in Regent Park and has grown to become an integral link between Aboriginal and non-Aboriginal agencies throughout the Greater Toronto area through the delivery of relevant cultural, social and educational programming and services. Toronto Council Fire is a member of the Ontario Federation of Indigenous Friendship Centres.
Located at 16 Spadina Road, Native Canadian Centre of Toronto provides programs and services based on Aboriginal cultures and traditions. The Centre has a long-standing history of delivering relevant social, recreational and cultural programming. Native Canadian Centre of Toronto is the product of years of work by dedicated individuals who have truly succeeded in creating a meeting place for Aboriginal people in Toronto.
-
Treaty Council at Burlington Heights
Location: Harvey Park, Hamilton
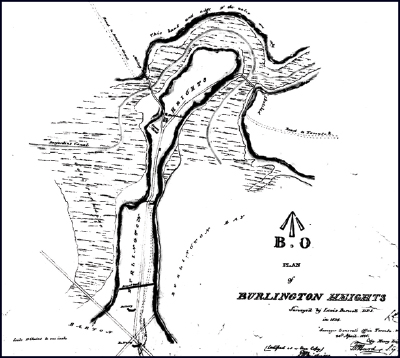
1834 Burlington Heights British Col. William Claus, Deputy Superintendent General of Indian Affairs, presented a wampum belt to Native allies for their assistance during the War of 1812.
As Deputy Superintendent General of Indian Affairs for the British government in Upper Canada during the War of 1812, Claus presented a wampum belt to the Haudenosaunee (Six Nations/Iroquois) and other Native allies, thanking them for their assistance in the war against American aggression. Several important treaty councils were held at Burlington Heights, a narrow strip of land with steep slopes making it a natural defensive location for the British.
The wampum belt is significant because it was the last of hundreds of belts to be exchanged between Great Britain and the Haudenosaunee. The War of 1812 was one of the last times Native Nations were recognized as allies of the Crown, although Indigenous people across North America continue to serve in times of conflict.
“This Belt which I now hand to you I ask in compliance with your Customs be sent by you with these my words in his behalf to all the Nations in friendship with your Great Father the King of England.” Col. William Claus, April 1815